Abstract
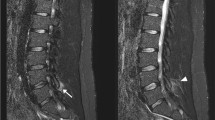
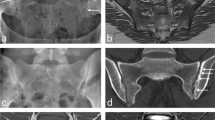
Tophaceous gout causing cord compression with a normal serum urate level and with no current symptoms of polyradiculopathy is a rare occurrence. We describe the computed tomographic (CT) findings of large, well-defined marginal and juxtamarginal erosions containing urate deposits which resulted in extradural cord compression in the cervical spine of a patient with chronic polyarticular tophaceous gout.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Resnick D, Reinke RT. Early onset of gout arthritis. Radiology 1975;114:67–73.
Fenton P, Young S, Pritis K. Gout in the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77:767–71.
Jajic I. Gout in the spine and sacroiliac joints: radiologic manifestations. Skeletal Radiol 1982;8:209–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giuliano, V., Keough, J.E. & Dadparvar, S. Tophaceous gout of the cervical spine causing cord compression: Computed tomographic diagnosis. Emergency Radiology 5, 162–163 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02749102
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02749102