Abstract
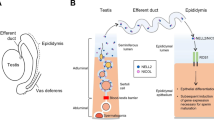
Inhibin/activin subunit (α, βA, and βB) immunoreactive protein localization patterns and cell type specific inhibit α-subunit mRNA expression have been examined in early-to midgestational age human fetal testes. The scarcity of available third trimester human fetal tissue has, however, prevented a complete examination throughout the gestational period and the cell specific expression of follistatin and βA- and βB-subunit mRNAs are currently unknown at any gestational age. In the present study, this gap is filled and report mRNA expression patterns of inhibin/activin subunits in mid- and late-gestational age (21–33 wk) human fetal testes and testicular duct system. We also report the first examination of follistatin mRNA signals in the human fetal gonad is also reported. Inhibin/activin α-subunit mRNA signal is present in both tubular and interstitial cells, and βB-subunit mRNA is expressed in seminiferous tubules, in mid- and late-gestational age human fetal testes. Inhibin/activin βA-subunit mRNA was detected in the interstitial cells of remarkably well preserved mid (21 and 22 wk) and late (29 wk) gestational age testis, and is the only activin-system factor mRNA also expressed in tissue of the duct system of the testis (smooth muscle cells of the epididymis). Follistatin mRNA signal was equal to background levels in testicular and duct tissues at all ages examined. These cell specific expression patterns suggest prominent and possibly differential roles for the inhibins and activins, unopposed by gonadal follistatin, in the human fetal male reproductive system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vale, W., Hsueh, A., Rivier, C., and Yu, J. (1990). In:The inhibin/activin family of hormones and growth factors, eds. (Sporn, M. M. and Roberts, A. B., eds.) Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg) Vol. 95, pp. 211–248.
Albers, N., Hart, C. F., Kaplan, S. L., and Grumbach, M. M. (1989).Endocrinology 125, 675–678.
Albers, N., Bettendorf, M., Hart, C. F., Kaplan, S. L., and Grumbach, M. M. (1989).Endocrinology 124, 3089–3094.
Rabinovici, J., Goldsmith, P. C., Roberts, V. J., Vaughan, J., Vale, W., and Jaffe, R. B. (1991).J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 73, 1141–1149.
Massa, G., De Zegher, F., and Vanderschueren-Lodeweyckx, M. (1992).Biol. Neonate 61, 150–155.
Rombauts, L., Vanmontfort, D., Verhoeven, G., and Decuypere, E. (1992).Biol. Reprod. 46, 1211–1216.
Torney, A. H., Robertson, D. M., Hodgson, Y. M., and de Kretser, D. M. (1990).Endocrinology 127, 2938–2946.
Voutilainen, R. (1992).Horm. Res. 38, 66–71.
Wongprasartsuk, S., Jenkin, G., McFarlane, J. R., Goodman, M., and De Kretser, D. M. (1994).J. Endocrinol. 141, 219–229.
Roberts, V. J., Meunier, H., Sawchenko, P. E., and Vale, W. (1989).Endocrinology 125, 2350–2359.
Roberts, V. J., Sawchenko, P. E., and Vale, W. (1991).Endocrinology 128, 3122–3129.
Roberts, V. J., and Barth, S. L. (1994).Endocrinology 134, 914–923.
Erämaa, M., Heikinheimo, K., and Voutilainen, R. (1992).J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75, 806–811.
Arnold, A. P. (1981).J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 207–211.
Kaipia, A., Toppari, J., Huhtaniemi, I., and Paranko, J. (1994).Endocrinology 134, 2165–2170.
Thomas, G. B., Davidson, E. J., Engelhardt, H., Baird, D. T., McNeilly, A. S., and Brooks, A. N. (1995).J. Endocrinol. 145, 35–42.
Vliegen, M. K., Schlatt, S., Weinbauer, G. F., Bergmann, M., Groome, N. P., and Nieschlag, E. (1993).Cell Tissue Res. 273, 261–268.
Vannelli, G. B., Barni, T., Forti, G., Negro-Vilar, A., Vale, W., Serio, M., and Balboni, G. C. (1992).Cell Tissue Res. 269, 221–227.
Plant, T. M., Winters, S. J., Attardi, B. J., and Majumdar, S. S. (1993).Hum. Reprod. 8, 41–44.
Majumdar, S. S., Mikuma, N., Ishwad, P. C., Winters, S. J., Attardi, B. J., Perera, A. D., and Plant, T. M. (1995).Endocrinology 136, 1969–1977.
Illingworth, P. J., Groome, N. P., Byrd, W., Rainey, W. E., McNeilly, A. S., Mather, J. P., and Bremner, W. J. (1996).J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81, 1321–1325.
Anawalt, B. D., Bebb, R. A., Matsumoto, A. M., Groome, N. P., Illingworth, P. J., McNeilly, A. S. and Bremner, W. J. (1996).J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81, 3341–3345.
Mather, J. P., Attie, K. M., Woodruff, T. K., Rice, G. C., and Phillips, D. M. (1990).Endocrinology 127, 3206–3214.
Hakovirta, H., Kaipia, A., Söder, O., and Parvinen, M. (1993).Endocrinology 133, 1664–1668.
Boitani, C., Stefanini, M., Fragale, A., and Morena, A. R. (1995).Endocrinology 136, 5438–5444.
Matzuk, M. M., Kumar, T. R., and Bradley, A. (1995).Nature 374, 356–360.
Kojima, I., Mogami, H., Kawamura, N., Yasuda, H., and Shibata, H. (1993).Exp. Cell Res. 206, 152–156.
Kanzaki, M., Nobusawa, R., Mogami, H., Yasuda, H., Kawamura, N., and Kojima, I. (1995).Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 108, 11–16.
Kogawa, K., Nakamura, T., Sugino, K., Takio, K., Titani, K., and Sugino, H. (1991).Endocrinology 128, 1434–1440.
Nakamura, T., Takio, K., Eto, Y., Shibai, H., Titani, K., and Sugino, H. (1990).Science 247, 836–838.
Shimonaka, M., Inouye, S., Shimasaki, S., and Ling, N. (1991).Endocrinology 128, 3313–3315.
Shimasaki, S., Koga, M., Buscaglia, M. L., Simmons, D. M., Bicsak, T. A., and Ling, N. (1989).Mol. Endocrinol. 3, 651–659.
Michel, U., Albiston, A., and Findlay, J. K. (1990).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 173, 401–407.
Roberts, V. J., Barth, S., el-Roeiy, A., and Yen, S. S. (1993).J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 77, 1402–10.
Shimasaki, S., Koga, M., Esch, F., Cooksey, K., Mercado, M., Koba, A., Ueno, N., Ying, S.-Y., and Ling, N. (1988).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 4218–4222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, V.J. Tissue-specific expression of inhibin/activin subunit and follistatin mRNAs in mid- to late-gestational age human fetal testis and epididymis. Endocr 6, 85–90 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02738807
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02738807