Abstract
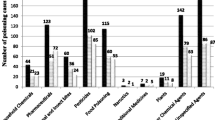
Poisoning in children is a common accident and poison information services should be aware of the toxic agents responsible for poisoning in the community. A retrospective hospital based study was performed, before-the establishment of the National Poisons Information Centre in Sri Lanka. There were 4,556 admissions of poisoning to the selected hospitals in the Western Province in 1986 and of this, 540 (11.4%) were below 15 years. Males accounted for 66%. Kerosene oil was responsible for 47% of the poisoning cases in less than 5 years age group, while kerosene oil, pesticides and plants/mushrooms were the commonest toxic agents in the 5 to 14 years age group. The case fatality rate was 3.2%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatton F, Tiret L, Nicand V. Measurement of accident morbidity.World Health Stat 1986; 39: 268–280
Henry J, Volans G. ABC of poisoning. Part 1: Drugs, London :British Medical Association 1984; 10–13.
Wiseman HM, Guest K, Murray VSG, Volans, GN. Accidental poisoning in childhood: A multicentre study 1. General epidemiology.Hum Toxicol 1987; 6 : 293–301.
Craft AW, Sibert JR. Accidental poisoning in children.Br Hosp Med 1977; 16: 469–478.
Seneviratne B, Thambipillai S. Pattern of poisoning in a developing agricultural country.Br J Preventive Social Med 1974; 28: 32–36.
Lucas GN, Poisoning in childhood-an analysis of 136 consecutive cases.Ceylon J Child Health 1988; 17: 3–6.
Jackson RH. Childhood poisoning: Perspectives and problems.Hum Toxicol 1983; 2 : 285–293.
Lucas GN. Childhood poisoning deaths-a case study.Ceylon J Child Health 1994; 23: 11–13.
Sibert JR, Newcombe RG. Accidental ingestion of poisons and child personality.Postgrad Med J 1977; 53: 254–256.
Basavaraj DS, Forster DP. Accidental poisoning in young children.J Epidemiol Community Health 1982; 36: 31–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernando, R., Fernando, D.N. Childhood poisoning in Sri Lanka. Indian J Pediatr 64, 457–460 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02737748
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02737748