Abstract
Evaluation of a child with cerebral palsy (CP) requires a multidisciplinary approach with a team of professionals comprising of a pediatrician or pediatric neurologist, occupational therapist, a physiotherapist, child psychologist, and a social worker. The assessment is necessary to confirm the diagnosis, determine the cause, assess the motor function and associated problems. The diagnosis of CP is clinical but selected investigations may be required for ascertaining the cause. Evaluation includes assessment for common medical problems of childhood particularly nutritional disorders and assessment of family functioning. Additional disabilities are common. Routine assessment of vision and hearing is required in children with CP. Since CP is a changing disorder, some limitations may not be evident early in life but manifest in the school age or later. The evaluation of a child with CP is an ongoing process and should be a part of continuing care as the child grows from infancy to adolescence
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosen MG, Dickinson JC. The incidence of cerebral palsy.Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992; 167:417–423.
Lacey JL, Henderson-Smart DJ. Assessment of preterm infants in intensivecare unit to predict cerebral palsy and motor outcome at 6 years.Dev Med Child Neurol 1998; 40:310–318.
Van den Hout BM, Eken Pet al. Visual, cognitive and neurodevelopmental outcome at 5 1/2 yr in children with perinatal haemorrhagic-ischemic brain lesions.Dev Med Child Neurol 1998; 40:820–828.
Ellenberg J, Nelson K. Early recognition of infants at high risk for cerebral palsy and examination at age four months.Dev Med Child Neurol 1981; 23: 705.
Mutch LW, Alberman E, Hagberg B, Kodama K, Velickovic MV. Cerebral palsy epidemiology:where are we now and where are we going?Dev Med Child Neurol 1992; 34: 547–555.
MacLennan A. International cerebral palsy task force: A template for defining a causal relation between acute intrapartum events and cerebral palsy: international consensus statementBMJ 1999; 319:1054–1059.
Sankar R, Pulger T, Rai B, Gomathi S, Gyatso TR, Pandav GS. Epidemiology of endemic cretinism in Sikkim, India.Indian J Pediatr 1998; 65:303–309.
Hauser SE, Peters H. Glutaric aciduria type I: An underdiagnosed cause of encephalopathy and dystonia dyskinesia syndrome in children.J Pediatr Child Health 1998; 34:302–304.
Liptak GS. The child who has severe neurologic impairment.Ped Clin North Amer 1998; 45:123–144.
Sanger TD, Mauricio RD, Gaebler-spira D, Hallet M, Mink, JW. Classification and definition of disorders causing hypertonia in childhood.pediatric 2003; 111: e89–97.
Fosang AL, Galea MP, McCoy AT, Reddihough DS, Story I. Measures of muscle and joint performance in the lower limb of children with cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 2003; 45: 664–670.
Davids JR, Foti T, Dabelstein J, Blackhurst DW, Bagley A. Objective assessment of dyskinesia in children with cerebral palsy.J Pediatr Orthop 1999; 19: 211–214.
Singhi PD, Ray M, Suri G. Clinical spectrum of cerebral palsy in north India an analysis of 1,000 cases.J Trop Pediatr 2002; 48:162–166.
Teplin SW, Howard JA, O’Connor MJ. Self-concept of young children with cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 1981; 23: 730–738.
Goodman R, Graham P. Psychiatric problems in children with hemiplegia: cross sectional epidemiological survey.BMJ 1996; 312:1065–1069.
Surveillance of cerebral palsy in Europe. Prevalence and characteristics of children with cerebral palsy in Europe.Dev Med Child Neurol 2002; 44:633–642.
Guzzetta A, Fazzi B, Mercuri E, Bertucceli Bet al. Visual function in children with hemiplegia in the first years of life.Dev Med Child Neurol 2001; 43:321–329.
Srivastava VK, Laisram N, Srivastava RK. Cerebral palsy.Indian Pediatr 1992; 29:993–996.
Brizzolara D, Pecini C, Brovedani P, Ferretti G, Cipriani P, Cioni G. Timing and type of congenital brain lesion determine different patterns of language lateralization in hemiplegic children.Neuropsychologia 2002; 40(6): 620–632.
Reilly S, Skuse D, Poblete X. Prevalence of feeding problms and oral motor dysfunction in children with cerebal palsy: a community survey.J Pediatr 1996; 129: 877–882.
Fishman LN, Bousvaros A. Gastrointestinal issues in the child with cerebral palsy.International Seminars in pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1999; 8:1–9.
Gangil A, Patwari AK, Aneja S, Ahuja B, Anand VK. Feeding problems in children with Cerebral palsy.Indian Pediatr 2001; 38:839–846.
Henderson RC, Lark RK, Gurka MJ, Worley Get al. Bone density and metabolism in children and adolescents with moderate to severe cerebral palsy.Pediatrics 2002; 110 (5).
Morrel DS, Pearson MJ, Sauser DD. Progressive bone and joint deformities of the spine and lower extremities in Cerebral palsy.Radio Graphics 2002; 22:257–268.
Corrnel MS. The hip in cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 1995; 37:3–18.
Lonstein JE, Beck K. Hip dislocation and subluxation in cerebral palsy.J Pediatr Orthop 1986; 6:521–526.
Saito N, Ebara S, Ohotsuka K, Kumeta H, Takaoka K. Natural history of scoliosis in spastic cerebral palsy.Lancet 1998; 351(9117): 1687–1692.
Carlsson M, Hagberg G, Olsson I. Clinical and aetiological aspects of epilepsy in children with cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 2003; 45(6): 371–376.
Hadjipanayis A, Hadjichristodoulou C, Youroukos S. Epilepsy in patients with cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 1997; 39:659–663.
Aneja S, Ahuja B, Taluja V, Bhatia VK. Epilepsy in children with cerebral palsy.Indian J Pediatr 2001; 68:111–115.
Ashwal S, Russman BS, Blascoe PA, Miller G, Sandier Aet al. Practice parameter: diagnostic assessment of the child with cerebral palsy: report of the quality standards subcommittee of American Academy of Neurology and practice committee of the child neurology society.Neurology 2004; 23 : 851–863.
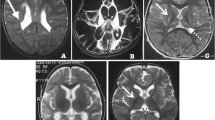
Candy EJ, Hoon AH, Capute AJ, Bryan RN. MRI in motor delay: important adjunct to classification of cerebral palsy.Pediatr Neurol 1993; 9:421–429.
Okumura A, Kato T, Kuno K, Hayakawa F, Watanbe K. MRI findings in patients with spastic cerebral palsy II: correlation with type of cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 1997; 39:369–372.
Hoon AH, Reinhardt EM, Kelley RI, Breiter SN, Morton DH, Naidu SBet al. Brain magnetic resonance imaging in suspected extrapyramidal cerebral palsy: observations in distinguishing genetic-metabolic from acquired causes.J Pediatr 1997; 131: 240–245.
Palisano RJ, Rosenbaum PL, Walter Set al. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in child with cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 1997; 39:214–223.
Singhi P. The child with cerebral palsy-clinical consideration and management.Indian J Pediatr 2001; 68:531–536.
Liptak GS, O’Donnel M, Conaway M, Chumlea WC, Worley G, Henderson RC, Fung Eet al. Health status of children with moderate to severe cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 2001; 43:364–370.
Singhi P. Counselling the parents of a child with cerebral palsy.Indian Pediatr 1988; 25:368–370.
Manuel J, Naughton MJ, Balkrishnan R, Paterson Smith B, Koman LA. Stress and adaptation in mothers of children with cerebral palsy.J Pediatr Psychol 2003; 28:197–201.
Mobarak R, Khan NZ, Munir S, Zaman SS, McConachie H. Predictors of stress in mothers of children with cerebral palsy in Bangladesh.J Pediatr Psychol 2000; 25:427–433.
McConachie H, Huq S, Munir S, Kamrunnahar, Akhter N, Ferdous Set al. Difficulties for mothers in using an early intervention service for children with cerebral palsy in Bangladesh.Child Care Health Dev 2001; 27(1): 1–12.
Sala DA, Grant AD. Prognosis for ambulation in cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 1995; 37:1020–1026.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aneja, S. Evaluation of a Child with Cerebral Palsy. Indian J Pediatr 71, 627–634 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724123
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724123