Summary
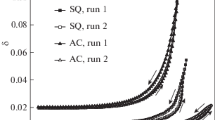
The effect of the addition of 25 at. % tantalum as substitutional solute on the internal-friction spectrum of niobium containing oxygen and nitrogen as interstitial solutes has been studied at a frequency of 1 Hz. Tantalum has been chosen because it hasa) the same atomic size,b) higher shear modulus,c) about the same chemical affinity towards nitrogen andd) higher chemical affinity towards oxygen than niobium. The relaxation spectrum of the alloy contains two main peaks, which correspond to the oxygen and nitrogen Snoek peaks in unalloyed niobium, and consist of four and two constituent peaks respectively. The additional peaks arise from relaxation processes caused by stress-induced reorientation of oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the neighbourhood of tantalum atoms. Since there is no difference in the atomic diameters of niobium and tantalum atoms, the associated activation energies for the relaxation processes causing the additional peaks are affected by the differences in their shear moduli and their chemical affinities towards oxygen and nitrogen.
Riassunto
Si è studiato alla frequenza di 1 Hz l'effetto dell'aggiunta di 25 at. % di tantalio in soluzione sostituzionale sullo spettro di attrito interno del niobio contenente ossigeno e azoto come soluti interstiziali. Si è scelto il tantalio perché haa) la stessa grandezza atomica,b) un modulo di taglio più alto,c) circa la stessa affinità chimica con l'azoto ed) maggiore affinità chimica con l'ossigeno del niobio. Lo spettro di rilassamento della lega contiene due picchi principali, che corrispondono ai picchi di Snoek dell'ossigeno e dell'azoto nel niobio, ciascuno dei quali consiste di quattro e due picchi costituenti, rispettivamente. I picchi aggiuntivi sorgono dai processi di rilassamento indotti da sforzo dovuti alla riorientazione degli atomi di ossigeno e azoto nella vicinanza degli atomi di tantalio. Poiché non c'è differenza nei diametri atomici degli atomi di niobio e tantalio, le energie di attivazione associate per i processi di rilassamento che provocano i picchi addizionali sono influenzate dalla differenze nei loro moduli di taglio e nelle loro affinità chimiche con l'ossigeno e l'azoto.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. C. Szkopiak andJ. T. Smith:J. Phys. D.,8, 1273 (1975).
R. S. Kê:Phys. Rev.,71, 533 (1947).
M. S. Ahmad, D. E. Barrow, E. A. Little andZ. C. Szkopiak:J. Phys. D,4, 1460 (1971).
C. Wert andJ. Marx:Acta Met,1, 113 (1953).
L. D. Dijkstra andR. J. Sladek:Trans. AIME,197, 69 (1953).
A. S. Nowick andB. S. Berry:I.B.M. Journ. Res. Dev.,5, 297, 312 (1961).
T. Gladman andF. B. Pickering:Journ. Iron Steel Inst.,203, 1216 (1965).
M. S. Ahmad andZ. C. Szkopiak:Journ. Phys. Chem. Sol.,31, 1799 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Traduzione a cura della Redazione.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szkopiak, Z.C. The Snoek peaks in niobium-25 at. % tantalum alloy. Nuov Cim B 33, 293–301 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02722496
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02722496