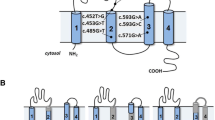
Abstract
Genetic polymorphisms associated with structural changes of their gene product are important in terms of their potential relation with diseases. Therefore, in this study, splice-site variants of the transmembrane serine protease geneTMPRSS4, nephronophthisis geneNPHP4, and organic-cation transporter geneORCTL4, were selected from the dbSNP single nucleotide polymorphism database as candidates to identify genetic polymorphisms associated with a structural change in their mRNA transcripts. The allele frequencies of theTMPRSS4 c.4-7A>G,NPHP4 c.2818-2A>T, andORCTL4 c.517-2A>C polymorphisms in a Japanese population were determined to be 0.42, 0.10, and 0.27, respectively, by PCR-SSCP analysis. Next, the effect of these polymorphisms on the mode of pre-mRNA splicing was investigated by RT-PCR analysis followed by sequencing analysis. TheTMPRSS4, NPHP4, andORCTL4 polymorphisms were associated with the production of the r.4-6_4-1ins transcript, the r.2818_2823del and r.2818_2859del transcripts, and the r.517-94_517-1ins; r.517-2a>c and r.517_620del transcripts, respectively. Since the proteins encoded by all these transcripts are associated with relatively significant structural changes in the form amino acid insertion/deletion and premature termination, their functional ability may be greatly reduced. Our demonstration of structural changes in mRNA transcripts as a result of splice-site polymorphisms implies that they may be of biological significance in certain pathological conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams M. D., Rudner D. Z. and Rio D. C. 1996 Biochemistry and regulation of pre-mRNA splicing.Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8, 331–339.
Benzing T., Gerke P., Hopker K., Hildebrandt F., Kim E. and Walz G. 2001 Nephrocystin interacts with Pyk2, p130(Cas), and tensin and triggers phosphorylation of Pyk2.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9784–9789.
den Dunnen J. T. and Antonarakis S. E. 2000 Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion.Hum. Mutat. 15, 7–12.
den Dunnen J. T. and Paalman M. H. 2003 Standardizing mutation nomenclature: why bother?Hum. Mutat. 22, 181–182.
Humar B., Toro T., Graziano F., Muller H., Dobbie Z., Kwang-Yang H., Eng C., Hampel H., Gilbert D., Winship I., Parry S., Ward R., Findlay M., Christian A., Tucker M., Tucker K., Merriman T. and Guilford P. 2002 Novel germlineCDH1 mutations in hereditary diffuse gastric cancer families.Hum. Mutat. 19, 518–525.
Mollet G., Salomon R., Gribouval O., Silbermann F., Bacq D., Landthaler G., Milford D., Nayir A., Rizzoni G., Antignac C. and Saunier S. 2002 The gene mutated in juvenile nephronophthisis type 4 encodes a novel protein that interacts with nephrocystin.Nat. Genet. 32, 300–305.
Nishiwaki T., Daigo Y., Tamari M., Fujii Y. and Nakamura Y. 1998 Molecular cloning, mapping, and characterization of two novel human genes, ORCTL3 and ORCTL4, bearing homology to organic-cation transporters.Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 83, 251–255.
Otto E., Hoefele J., Ruf R., Mueller A. M., Hiller K. S., Wolf M. T., Schuermann M. J., Becker A., Birkenhager R., Sudbrak R., Hennies H. C., Nurnberg P. and Hildebrandt F. 2002 A gene mutated in nephronophthisis and retinitis pigmentosa encodes a novel protein, nephroretinin, conserved in evolution.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 1161–1167.
Shinmura K., Tao H., Yamada H., Kataoka H., Sanjar R., Wang J., Yoshimura K. and Sugimura H. 2004 Splice-site genetic polymorphism of the human kallikrein 12 (KLK12) gene correlates with no substantial expression of KLK12 protein having serine protease activity.Hum. Mutat. in press.
Varshavsky A. 2003 The N-end rule and regulation of apoptosis.Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 373–376.
Wallrapp C., Hahnel S., Muller-Pillasch F., Burghardt B., Iwamura T., Ruthenburger M., Lerch M. M., Adler G. and Gress T. M. 2000 A novel transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS3) overexpressed in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Res. 60, 2602–2606.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, H., Shinmura, K., Tsuneyoshi, T. et al. Effect of splice-site polymorphisms of theTMPRSS4, NPHP4 andORCTL4 genes on their mRNA expression. J Genet 84, 131–136 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02715838
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02715838