Abstract
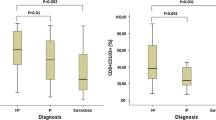
Pulmonary histiocytosis X is characterized by an accumulation of CD-1-positive histiocytosis X cells in the lung, which also can be found in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). However, it has recently been demonstrated that CD-1-positive cells can also be detected in BALF of patients with other interstitial lung diseases and in healthy smokers. We therefore examined the frequency of CD-1-positive cells in a pool of patients with different pulmonary disorders, according to their smoking habits and diagnoses. We have studied the bronchoalveolar lavage in patients with pulmonary histiocytosis X (n=6), sarcoidosis (n=88), and in 97 patients with other miscellaneous lung disorders by using the immunoperoxidase method to detect CD-1-positive cells on glass slides.
All patients with histologically proven histiocytosis X displayed more than 5% CD-1-positive cells, whereas patients with other pulmonary disorders showed no more than 3.6% CD-1-positive BAL cells. The dividing line of 5% CD-1-positive cells was not influenced by patients’ smoking habits. The identification of CD-1-positive cells in BALF appears to be useful in diagnosing pulmonary histiocytosis X.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonnet D, Kermarec J, Marotel C, L’Her P, Levaguerresse R, Heyraud JD, Natali F, de Muizon H, Allard P (1987) Données du lavage broncho-alvéolaire et histiocytose X pulmonaire. Rev Pneumol Clin 43:121–130
Bross KJ, Pangalis GA, Staatz CG, Blume KG (1978) Demonstration of cell surface antigens and their antibodies by the peroxidase antiperoxidase method. Transplantation 25:331–334
Casolaro MA, Bernaudin JF, Saltini C, Ferrans VJ, Crystal RG (1988) Accumulation of Langerhans’s cells on the epithelial surface of the lower respiratory tract in normal subjects in association with cigarette smoking. Am Rev Respir Dis 137:406–411
Chollet S, Soler P, Dournovo P, Richard MS, Ferrans VJ, Basset F (1984) Diagnosis of pulmonary hystiocytosis X by immunodetection of Langerhans’ cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Am J Pathol 115:225–232
Chollet S, Dournovo P, Richard MS, Soler P, Basset F (1982) Reactivity of hystiocytosis X cells with monoclonal anti T6 antibody. N Engl J Med 307:685 (letter)
Colby TV, Lombard C (1983) Histiocytosis in the lung. Hum Pathol 14:847–856
Crystal RG, Bitterman PB, Rennard SI, Hance AJ, Keogh BA (1984) Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract. N Engl J Med 310:235–244
Danel C, Israel-Biet D, Costabel U, Rossi GA, Wallaert B (1990) The clinical role of BAL in pulmonary histiocytosis X. In: Klech H, Hutter C (eds) Clinical guidelines and indications for bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL): Report of the European Society of Pneumology Task Group on BAL. Eur Respir J 3:949–950
Friedman PJ, Liebow AA, Sokoloff J (1981) Eosinophilic granuloma of lung. Clinical aspects of primary histiocytosis in the adult. Medicine 60:385–396
Gaensler EA, Carrington CB (1980) Open biopsy for chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease: clinical, roentgenographic, and physiologic correlations in 502 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 30:411–426
Hance AJ, Basset F, Saumon G, Danel C, Valeyre D, Battesti JP, Chrétien J, Georges R (1986) Smoking and interstitial lung disease. The effect of cigarette smoking on the incidence of pulmonary histiocytosis X and sarcoidosis. Ann NY Acad Sci 465:643–656
Hance AJ, Cadranel J, Soler P, Basset P (1988) Pulmonary and extrapulmonary Langhans cell granulomatosis (histiocytosis X). Semin Respir Med 9 (4):349–368
Marcy TW, Reynolds HY (1985) Pulmonary histiocytosis X. Lung 163:129–150
Murphy GF, Bhan AK, Sato S, Mihm MC, Harriet TJ (1981) A new immunologic marker for the human Langhans cells. N Engl J Med 304:791–792 (letter)
National Institutes of Health (1985) Summary and recommendations of a workshop on the investigative use of fiberoptic bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage in individuals with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 132:180–182
Nezelof C, Basset F, Rousseau MF (1973) Histiocytosis X: histogenetic arguments for a Langerhans’ cell origin. Biomedicine 18:365–371
Rousseau-Merck MF, Barbey S, Jaubert F, Bach MA, Chatenoud L, Nezelhof C (1983) Reactivity of histiocytosis X cells with monoclonal antibodies. Pathol Rest Pract 177:8–12
Soler P, Chollet S, Jacque C, Fukuda Y, Ferrans VJ, Basset F (1985) Immunocytochemical characterization of pulmonary histiocytosis X cells in lung biopsies. Am J Pathol 118:439–451
Vetter N, Krisch K (1989) Immunzytochemische Untersuchungen in der Diagnostik der pulmonalen Histiozytosis X. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 114 (3):91–95
Wall CP, Gaensler EA, Carrington CB, Hayes JA (1981) Comparison of transbronchial and open lung biopsies in chronic infiltrative lung diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis 123:280–282
Xaubet A, Agusti C, Picado C, Guerequiz S, Martos JA, Carrion M, Agusti-Vidal A (1989) Bronchoalveolar lavage analysis with anti-T6 monoclonal antibody in the evaluation of diffuse lung diseases. Respiration 56:161–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auerswald, U., Barth, J. & Magnussen, H. Value of CD-1-positive cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of pulmonary histiocytosis X. Lung 169, 305–309 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02714167
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02714167