Abstract
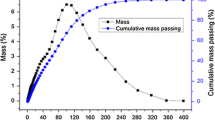
Tribomechanics is a part of physics that is concerned with the study of phenomena that appear during milling under dynamic conditions. Tribomechanical micronization and activation (TMA) of whey protein concentrates (WPC) and zeolites (type clinoptilolite) were carried out. Samples of powdered WPC and zeolite were treated with the laboratory TMA equipment. The treatment was carried out at two various rotor speeds: 16,000 and 22,000 r.p.m. at ambient temperature. Analyses of the particle size and distribution as well as the specific area and scanning electron microscopy were carried out on the powdered WPC and zeolite, before and after the TMA treatment. Suspensions of the WPC and zeolite were treated with ultrasound, just before determining the particle size distribution, at 50 kHz. The results showed that tribomechanical treatment causes significant decrease in particle size, change in particle size distribution and increase in specific area of WPC and zeolite. These changes of the treated materials depend on the type of the material, the level of inserting particles, the planned angle of the impact, internal rubbing and the planned number of impacts. The effects found became stronger as the rotor speed of the TMA equipment increased (16,000 to 22,000 rpm). Ultrasonic treatment of suspension of tribomechanically treated WPC resulted infurther breakdown of partly damaged protein globules as proved with the statistic analyses. No further changes in their granulometric composition were caused by ultrasonic treatment of a suspension of tribomechanically treated zeolite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apenten R K O, Buttner B, Mignot B, Pascal D, Povey M J W 2000 Determination of the adiabatic compressibility of bovine serum albumen in concentrated solution by a new ultrasonic method.Food Hydrocolloids 14: 83–91
Bhushan B 2000 Nanoscale tribophysics and tribomechanics.Proc. 12th Int. Conf. on Wear of Materials (Atlanta, GA: Soc. Tribol. Lubric. Eng.) pp 25–29
Bohren C F, Huffman D R 1983Absorption and sccatering of light by small particles (New York: Wiley) pp 89–91
Boranić M 2000 What a physician should know about zeolites.Liječnički Vjesnik 122: 292–298
Bryant C M, McClements D J 1999 Ultrasonic spectroscopy study of relaxation and scattering in whey protein solutions.J. Sci. Food Agric. 79: 1754–1760
Cefali E A, Nolan J C, McConnell W R, Walters D L 1995 Pharmacokinetic study of zeolite A, sodium aluminosilicate, magnesium silicate and aluminum hydroxide in dogs.Pharmaceut. Res. 12: 270–274
Colic M, Pavelic K 2000 Molecular mechanisms of aticancer activity of natural dietetic products.J. Mol. Med. 78: 333–336
Dumay E M, Kalichevsky M T, Cheftel J C 1998 Pressure and heat-induced gelation of mixed Β-lactoglobulin/polysaccharide solutions: scanning electron microscopy of gels.Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 31: 10–19
Galazka V B, Dickinson E, Ledward D A 1996 Effect of high pressure on the emulsyfing behavior of beta-lactoglobulin.Food Hydrocolloids 10: 213–219
Galazka V B, Dickinson E, Ledward D A 2000 Influence of high pressure processing on protein solutions and emulsion.Curr. Opinion Colloid Interface Sci. 5: 182–187
Herceg Z 2000Influence of tribomechanical micronization of physical properties of whey proteins. Ph D thesis, Faculty of Food Technology and Biotechnology, Zagreb, pp 134–146
Herceg Z, Hegedušić V, Rimac S 2000 Influence of hydrocolloid addition on the rheological properties of whey proteins model solutions.Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Food Rheology and Structure. Zurich, pp 378–379
Herceg Z, Lelas V, škreblin M 2002 Influence of tribomechanical micronization on the rheological properties of whey proteins.Food Technol. Biotechnol. 40: 145–156
Joyner R, Stockenhuber M 1999 Preparation, characterization and performance of Fe-ZSM-5 catalysts.J. Phys. Chem. 103: 5963–5976
Lelas T 1998 Vorrichtung zum Mikronisieren von Materialien und neuartige Verwendungsmoglichkeiten derartig mikronisierter Materialien. Patent: PCT/1B 99/00757, Geneva
Lelas V, Herceg Z 2002 Influence of tribomechanical treatment on the phase transition temperatures of whey proteins model systems.Proc. Int. Conf. on Innovation in Food Processing Technology and Engineering, Bangkok, pp 24–34
Lelas V, Herceg Z, Rimac-Brnčič S 2003 Physical properties of tribomechanicaly micronized whey proteins.Proc. New Functional Ingredients and Foods, Copenhagen, pp 58–59
Messens W, Dewttinck K, Van Camp J, Huyghebeart A 1999 High pressure treatment of dairy products.Agric. Biol. Environ. Sci. 31: 115–121
Pavelic Ket al 2000 Natural zeolite clinoptilolite: New adjuvant in anticancer therapy.J. Mol. Med. 78: 656–661
Tratnik L 1998Milk technology, biochemistry and microbiology (Zagreb: Croatian Milk Soc.) pp 345–380
Van Camp J, Feys G, Huyghebaert A 1996Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 29: 49–57
Washington C 1992 Particle size analysis in pharmaceutics and other industries. Department of Pharmaceutical Science, University of Nottingham, pp 107–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herceg, Z., Lelas, V., Brnčić, M. et al. Tribomechanical micronization and activation of whey protein concentrate and zeolite. Sadhana 29, 13–26 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706998
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706998