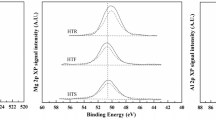
Abstract
Palladium-hydrogen interaction on supported Pd catalysts of different metal dispersions has been studied by hydrogen chemisorption and back-sorption, and by temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) of either deuterium or hydrogen from the Pd surface after different initial gas dosages. Pd interacts with three hydrogen species whose amounts vary with the metal dispersion and with the dosage pressure. The amount of hydrogen strongly adsorbed on the Pd surface increases with the metal dispersion but is unaffected by the hydrogen pressure. The amount of hydrogen absorbed in the bulk of Pd is significant with a poorly dispersed catalyst, particularly when the hydrogen pressure is higher than about 10 Torr, but decreases with the metal dispersion. Hydrogen weakly bound with Pd shows two characteristic TPD peaks, whose intensity depends on the metal dispersion and the initial gas dosage. The peak at 270-330 K, assigned to the recombination of absorbed hydrogen with surface hydrogen, is large with a poorly dispersed catalyst and grows with the initial hydrogen dosage. The intensity of the peak at 215-226 K is not affected by the metal dispersion or by the hydrogen dosage. It has been concluded that an analysis of the intrinsic properties of Pd catalysts should be based on an understanding of the hydrogen species associated with the catalysts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aben, P. C., “Palladium Areas in Supported Catalysts-Determination of Palladium Surface Areas in Supported Catalysts by Means of Hydrogen Chemisorption,”J. Catal.,10, 224 (1968).
Aldag, A.W. and Schmidt, L. D., “Interaction of Hydrogen with Palladium,”J. Catal.,22, 260 (1971).
Aoki, K., Yokoyama, S., Kuskabe, K. and Morooka, S., “Preparation of Supported Palladium Membrane and Separation of Hydrogen,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,13, 530 (1996).
Behm, R. J., Penka, V., Cattania, M.-G., Christmann, K. and Ertl, G., “Evidence for “Subsurface” Hydrogen on Pd(110); An Intermediate between Chemisorbed and Dissolved Species,”J. Chem. Phys.,78(12), 7486 (1983).
Benson, J. E., Hwang, H. S. and Boudart, M., “Hydrogen-Oxygen Titration Method for the Measurement of Supported Palladium Surface Areas,”J. Catal.,30, 146 (1973).
Borodzinski, A., Dus, R., Frak, R., Janko, A. and Palczewska, W., “A Study of the Role of the Palladium Hydride Phase in the Activity and Selectivity of Palladium Catalysts in Acetylene Hydrogenation,” in Proceedings of the 6 International Congress on Catalysis,1, 151 (1976).
Bourdart, M. and Hwang, H. S., “Solubility of Hydrogen in Small Particles of Palladium,”J. Catal.,39, 44 (1975).
Buchner, H., “The Hydrogen/Hydride Energy Concept,” in Hydrides for Energy Storage; The Proceedings of an International Symposium held in Geilo, Andresen, A. E. and Maeland, A. J. Eds., 569 (1977).
Conrad, H., Ertl, G. and Latta, E. E., “Adsorption of Hydrogen on Palladium Single Crystal Surfaces,”Surface Science,41, 435 (1974).
Chou, P. and Vannice, M. A., “Calorimetric Heat of Adsorption Measurements on Palladium,”J. Catal.,104, 1 (1987).
Konvalinka, J. A. and Scholten, J. J. F., “Sorption and Temperature-Programmed Desorption of Hydrogen from Palladium and from Palladium on Activated Carbon,”J. Catal.,48, 374 (1977).
Lee, D. K., “Green-oil Formation and Selectivity Change in Selective Hydrogenation on Titania-Supported and Unsupported Palladium Catalysts for Acetylene Removal from Ethylene-rich Stream,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,7, 233 (1990).
Ragaini, V., Giannantonio, R., Magni, P., Lucarelli, L. and Leofanti, G., “Dispersion Measurement by the Single Introduction Method Coupled with the Back-Sorption Proceduere; A Chemisorption and TPD Study of the Different Chemisorbed Hydrogen Species,”J. Catal.,146, 116 (1994).
Shin, E.W., Choi, C. H., Chang, K. S., Na, Y. H. and Moon, S. H., “Properties of Si-modified Pd Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Acetylene,”Catalysis Today,44, 137 (1998).
Shu, J., Grandjean, B. P. A., Van Neste, A. and Kaliaguine, S., “Catalytic Palladium-based Membrane Reactors: A Review,”Can. J. Chem. Eng.,69, 1036 (1991).
Thomas, Ch. L., “Catalytic Processes and Proven Catalysts,” Chap 12 and Chap 13, Academic Press, New York (1970).
Wang, S. Y., Moon, S. H. and Vannice, M. A., “The Effect of SMSI (Strong Metal-Support Interaction) Behavior on CO Adsorption and Hydrogenation on Pd Catalysts,”J. Catal.,71, 167 (1981).
Zakumbaeva, G. D., Zakarina, N. A., Naidin, V. A., Dostiyarov, A.M., Toktabaeya, N. F. and Litvyakova, E. N., “Properties of Monodisperse Pd/MgO Catalysts,”Kinet. Catal.,24, 379 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, E.W., Cho, SI., Kang, J.H. et al. Palladium-hydrogen interaction on supported palladium catalysts of different metal dispersions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 17, 468–472 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706862
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706862