Abstract
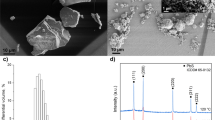
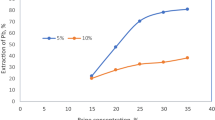
This work aims at recovering lead from frit glass waste of electronic plants by using the electrochemical method comprising two successive steps of lead leaching and electrodeposition. In the leaching step, it was found that nitric acid and acetic acid are better solutions for the dissolution of lead oxide compared with sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, and sulfuric acid. More than 95% of the lead was leached by 0.1 M nitric acid or 0.5 M acetic acid at 0.5% weight by solid volume. In the electrodeposition step, more than 95% of lead can be removed with high current efficiency from the leaching solution at an optimum current density. The values of the optimum current density of 0.5 and 1 M acetic electrolytes were between 8.8–10 mA/cm2, whereas those for 0.1 M and 0.5 M of nitric acid were 15 and 27.5 mA/cm2, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, I. C., Rochon, A. M., Gesser, H. D. and Sparling, A. B., “Electrodeposition of Six Heavy Metals on Reticulated Vitreous Carbon Electrode,”Water Res.,18(2), 227 (1984).
Allen, P. D. and Bhaumik, V. H., “Washing of Various Lead Compounds from a Contaminated Soil Column,”J. Environ. Eng.-ASCE,124(11), 1066 (1998).
Carreno, G., Sosa, E., Gonzalez, I., Ponce-De-Leon, C., Batina, N. and Oropeza, M. T., “Anion Influence in Lead Removal from Aqueous Solution by Deposition onto a Vitreous Carbon Electrode,”ElectrochemicaActa,44(15), 2633 (1999).
Kim, H. T. and Lee, K., “Application of Insoluble Cellulose Xanthate for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16, 298 (1999).
Kim, S. J., Jeung, S. Y. and Moon, H., “Removal and Recovery of Heavy Metal Ions in Fixed and Semi-fluidized Beds,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,15, 637 (1998).
Kim, S. J., Lim, K. H., Joo, K. H., Lee, M. J., Kil, S. G. and Cho, S. Y., “Removal of Heavy Metal-cyanide Complexes by Ion Exchange,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 1078 (2002).
Musson, S. E., Jang, Y.C., Townsend, T. G. and Chung, I. H., “Characterization of Lead Leachability from Cathode Ray Tube using the Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure,”Environ. Sci. Technol.,34(20), 4376 (2000).
Park, J. K. and Choi, S. B., “Metal Recovery Using Immobilized Cell Suspension from a Brewery,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 68 (2002).
Park, J. S. and Moon, S. H., “Use of Cascade Reduction Potential for Selective Precipitation of Au, Cu, and Pb in Hydrochloric Acid Solution,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 797 (2002).
Pourbaix,Atlas d’équilibres électrochimiques à 25 °C, Paris, Ed. Gauthier-Villars, 256 (1963).
Rastogi, R P., Das, I., Pushkarna, A. and Chand, S., “Oscillations and Pattern Formation During Electrodeposition of Lead Metal in Batch and Flow Reactors,”J. Phys. Chem.,97(18), 4871 (1993).
Ried, M.,Heavy Metal Removal from Sewage Sludge: Practical Experiences with Acid Treatment, Pretreatment in Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 327 (1988).
Weast, R. C., 1969,Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Ohio, USA, 5th edition, The Chemical Rubber Co., Cleveland.
Widner, R.C., Sousa, M. F. B. and Bertazzoli, R., “Electrolytic Removal of Lead using a Flow-through Cell with a Reticulated Vitreous Carbon Cathode,”J. Appl. Electrochem.,28(2), 201 (1998).
Wong, L. and Henry, J. G.,Biological Removal and Chemical Recovery of Metals from Sludges, Proc. Ind. Waste. Conf. 39th, 515 (1985).
Wozniak, D. J. and Huang, J. Y. C., “Variables Affecting Metal Removal from Sludge,”J. Water Poll. Control Fed.,54(12), 1574 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pruksathorn, K., Damronglerd, S. Lead recovery from waste frit glass residue of electronic plant by chemical-electrochemical methods. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 22, 873–876 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705667
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705667