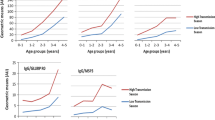
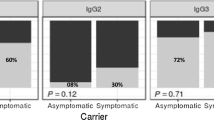
Abstract
Blood samples collected from individuals belonging to an endemic area in Uttar Pradesh, were tested for plasmodial antigen specific immunoglobulin A (IgA) by enzyme immuno assay using soluble extract ofPlasmodium falciparum from culture. Among 773 (20.18%,P < 0.0001) samples 156 sera demonstrated a detectable seropositivity for antigen specific IgA. IgA levels were higher among individuals who experienced repeated attacks of malaria compared to acute infected patients. Among seropositive individuals the IgA titers were found increased with the age. Immunoglobulin isolated from sera having high level of IgA showed growth inhibitory effect inPlasmodium falciparum in vitro. A group of sera with high IgA antibody againstPlasmodium falciparum crude antigen showed seronegativity with specific peptides. Statistically, no positive or negative correlations were observed between antigen specific IgG and IgA. However, there was a tendency towards negative correlation between IgA and IgM. Mechanisms for the parasite specific IgA production remain to be established.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avrameas S and Ternynck T 1969 The crosslinking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunosorbents;Immunochemistry 6 53–66
Biswas S, Saxena Q B and Roy A 1990 The natural occurrence of circulating antibodies in populations of endemic malarious areas;Indian J. Malariol. 27 139–148
Biswas S and Sharma Y D 1991 Lack of correlation between red cell invasion by merozoites and anti-heat shock protein-70 antibody levels in malaria patients sera;Int. J. Parasitol. 21 213–217
Collins W E, Contacos P G, Skinner J C, Harrison A J and Gell L S 1971 Patterns of antibody and serum protein in experimentally induced human malaria;Trans. R. Soc. Trap. Med. Hyg. 65 43–58
Deloron P, Duverseau Y T, Zevallos-Ipenza A, Magloire R, Stanfill P S and Phuc Nguyen-Dinh 1987 Antibodies to Pf 155, a major antigen ofPlasmodium falciparum: seroepidemiological studies in Haiti;Bull. WHO 65 339–344
Früh K, Doumbo O, Muller H M, Koita O, McBride J, Crisanti A, Toura S and Bujard H 1991 Human antibody responses to the major merozoite surface antigen ofPlasmodiun falciparum is strain specific and short lived;Infect. Immun. 59 1319–1324
McGregor I A 1981Immune phenomena in naturally acquired human malaria (WHO/MAL/81)966, 1–12
Perlmann H, Perlmann P, Berzins K, Wahlin B, Troye-Blomberg M, Hagstadt M, Anderson I, Hong B, Peterson E and Bjorkmann A 1989 Dissection of the human antibody responses to the malaria antigen Pf 155/RESA into epitope specific components;Immunol. Rev. 112 115–132
Trager W and Jensen J B 1976 Human malaria parasites in continuous culture;Science 193 673–675
Zavala F, Tarn T P and Masuda A 1986 Synthetic peptides as antigens for the detection of humoral immunity toPlasmodium falciparum sporozoites;J. Immunol. Methods 93 55–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, S., Saxena, Q.B., Roy, A. et al. Naturally occurring plasmodium-specific IgA antibody in humans from a malaria endemic area. J Biosci 20, 453–460 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703849
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703849