Abstract
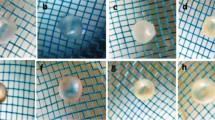
Vanadium compounds are potent in controlling elevated blood glucose levels in experimentally induced diabetes. However the toxicity associated with vanadium limits its role as therapeutic agent for diabetic treatment. A vanadium compound sodium orthovanadate (SOV) was given to alloxan-induced diabetic Wistar rats in lower doses in combination withTrigonella foenum graecum, a well-known hypoglycemic agent used in traditional Indian medicines. The effect of this combination was studied on lens morphology and glucose metabolism in diabetic rats. Lens, an insulin-independent tissue, was found severely affected in diabetes showing visual signs of cataract. Alterations in the activities of glucose metabolizing enzymes (hexokinase, aldose reductase, sorbitol dehydrogenase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) and antioxidant enzymes (glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase) besides the levels of related metabolites, [sorbitol, fructose, glucose, thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) and reduced glutathione (GSH)]were observed in the lenses from diabetic rats and diabetic rats treated with insulin (2 IU/day), SOV (0.6 mg/ml),T. f. graecum seed powder (TSP, 5%) and TSP (5%) in combination with lowered dose of vanadium SOV (0.2 mg/ml), for a period of 3 weeks. The activity of the enzymes, hexokinase, aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase was significantly increased whereas the activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase decreased significantly in lenses from 3 week diabetic rats. Significant increase in accumulation of metabolites, sorbitol, fructose, glucose was found in diabetic lenses. TBARS measure of peroxidation increased whereas the levels of antioxidant GSH decreased significantly in diabetic condition. Insulin restored the levels of altered enzyme activities and metabolites almost to control levels. Sodium orthovanadate (0.6 mg/ml) andTrigonella administered separately to diabetic animals could partially reverse the diabetic changes, metabolic and morphological, while vanadate in lowered dose in combination withTrigonella was found to be the most effective in restoring the altered lens metabolism and morphological appearance in diabetes. It may be concluded that vanadate at lowered doses administered in combination withTrigonella was the most effective in controlling the altered glucose metabolism and antioxidant status in diabetic lenses, these being significant factors involved in the development of diabetic complications, that reflects in the reduced lens opacity
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Aldose reductase
- G6PDH:
-
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GR:
-
glutathione reductase
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
glutathione
- SDH:
-
sorbitol dehydrogenase
- TBARS:
-
thiobarbituric acid reactive species
- SOV:
-
sodium orthovanadate
- TSP:
-
Trigonella foenum graecum seed powder
References
Adachi K 1995 Effects of vanadate on glucose metabolism in the lens of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes-ketohexokinase and aldolase activity;Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 99 34–39
Altomare E, Vendemiale G, Grattagliano I, Angelini P, Micelli-Ferrari T and Cardia L 1995 Human diabetic cataract: role of lipid peroxidation;Diabetes Metabolism 21 173–179
Anuradha C V and Ravikumar P 2001 Restoration on tissue antioxidants by fenugreek seeds(Trigonella foenum graecum) inalloxan-diabetic rats;Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 45 408–420
Baquer N Z, Gupta D and Raju J 1998 Regulation of metabolic pathways in liver and kidney during experimental diabetes: Effects of antidiabetic compounds;Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 13 63–80
Baquer N Z, McLean P and Greenbaum A L 1973 Enzymic differentiation in pathways of carbohydrate metabolism in developing brain;Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 53 1282–1288
Bergmeyer H U, Bernt E, Schmidt F and Stork F 1974Assay for hexoses (New York: Academic Press)
Brichard S M, Okitolonda W and Henquin J C 1988 Long term improvement of glucose homeostasis by vanadate treatment in diabetic rats;Endocrinology 123 2048–2053
Chung S S M, Ho E C M, Lam K S L and Chung S K 2003 Contribution of Polyol Pathway to Diabetes-Induced Oxidative Stress;J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14 S233-S236
Chylack L K and Cheng H M 1978 Sugar metabolism in the crystalline lens;Surv. Ophthalmol. 23 26–34
Domingo J L 2002 Vanadium and tungsten derivatives as antidiabetic agents: a review of their toxic effects;Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 88 97–112
Domingo J L, Gomez M, Llobet J M, Corbella J and Keen C L 1991 Improvement of glucose homeostasis by oral vanadyl or vanadate treatment in diabetic rats is accompanied by negative side effects;Pharmacol. Toxicol. 68 249–253
Domingo J L, Gomez M, Sanchez D J, Liobet J M and Keen C L 1995 Toxicology of vanadium compounds in diabetic rats: The action of chelating agents on vanadium accumulation;Mol. Cell Biochem. 153 233–240
Efimov A S, Obrosova I G and Velikii N N 1984 Sorbitol pathway of glucose metabolism in streptozotocin diabetes of varying duration and severity (abstract);Probl. Endokrinol. (Mosk). 30 71–76
Erden M and Bor N M 1984 Changes in reduced glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione peroxidase after radiation in guinea pigs;Biochem. Med. 31 217–227
Farkas T F and Patterson J W 1957 Insulin and the lens;Am. J. Ophthalmol. 44 341–346
Freeman B A and Crapo J D 1982 Biology of diseases: free radicals and tissue injury;Lab. Invest. 47 412–426
Genet S, Kale R and Baquer N Z 2002 Alterations in antioxidant enzymes and oxidative damage in experimental diabetic rat tissues: Effect of Vanadate and fenugreek(Trigonella foenum graecum);Mol. Cell Biochem. 236 7–12
Gerlach U and Hiby W 1974 Assay of sorbitol; inMethods in enzymatic analysis (ed.) H U Bermeyer (New York: Academic Press) vol. 3, pp 1323–1330
Gonzalez A M, Sochor M, Hothersall J S and McLean P 1978 Effect of experimental diabetes on the activity of hexokinase in rat lens: an example of glucose overutilization in diabetes;Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 84 858–864
Gonzalez A M, Sochor M and McLean P 1983 The effect of an aldose reductase inhibitor (Sorbinil) on the level of metabolites in lenses of diabetic rats;Diabetes 32 482–485
Gonzalez A M, Sochor M and McLean P 1987 The effect of an aldose reductase inhibitor (sorbinil) on the levels of metabolites in lenses of diabetic rats;Diabetes 32 482–485
Griffith O W 1980 Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinyl-pyridine;Anal. Biochem. 107 207–212
Grover J K, Yadav S and Vats 2002 Medicinal plants of India with anti-diabetic potential;V. J. Ethnopharmacol. 81 81–100
Gumaa K and McLean P 1972 The kinetic quantitation of ATP.D-glucose-6-phosphotransferase;FEBS Lett 27 293–297
Gupta A, Gupta R and Lal B 2001 Effect ofTrigonella foenumgraecum (fenugreek) seeds on glycemic control and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double blind placebo controlled study;J. Assoc. Physicians India 49 1057–1061
Heylinger C E, Tahiliani A G and McNeill J H 1985 Effect of Vanadate on elevated blood glucose and depressed cardiac performance of diabetic rats;Science 227 1474–1477
Kinoshita J H, Futterman S, Satoh K and Marola L O 1963 Factors affecting the formation of sugar alcohols in ocular lens;Biochim. Biophys. Acta 74 340–350
Kuck J F 1962 Glucose metabolism and fructose synthesis in the diabetic rat lens;Invest. Ophthalmol. 1 390–395
Lawrence R A and Burk R F 1976 Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium deficient rat liver;Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 71 952–958
Lee A Y and Chung S S 1999 Contributions of polyol pathway to oxidative stress in diabetic cataract;FASEB J. 13 23–30
Levari R, Kirnblueth W and Wertheimer E 1961 The effect of insulin on the uptake of monosaccharides by the rat lens;J. Endocrinol. 22 361–369
Lou M F 2003 Redox regulation in the lens;Prog. Retin Eye Res. 22 657–682
Lou M F, Dickerson J E, Garadi R and York B M 1988 Glutathione depletion in the lens of galactosemic and diabetic rats;Exp. Eye Res. 46 517–530
Lowry O H, Rosebrough N J, Farr A L and Randall R J 1951 Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent;J. Biol. Chem. 193 265–275
Malone J I, Knox G, Benford S and Tedesco T A 1980 Red cell sorbitol: an indicator of diabetic control;Diabetes 29 861–864
Meyerovitch J, Farfel Z, Sack J and Shechter Y 1987 Oral administration of Vanadate normalizes blood glucose levels in Streptozotocin-treated rats;J. Biol. Chem. 262 6658–6662
Mitton K P, Linklater H A, Dzialoszynski T, Sanford S E, Starkey K and Trevithick J R 1999 Modelling cortical cataractogenesis 21: in diabetic rat lenses taurine supplementation partially reduces damage resulting from osmotic compensation leading to osmolyte loss and antioxidant depletion;Exp. Eye Res. 69 279–289
Moorthy R, Prabhu K, Murthy P S and Bull 1989 Studies on the isolation of hypoglycemic principle from the seeds of fenugreek(Trigonella foenum graecum) seeds;Diabetes 9 69–72
Pirie A 1957 The biochemistry of the eye;Bibl. Ophthalmol. 49 287–377
Pugazhenthi S and Khandelwal R L 1990 Insulin like effects of Vanadate on hepatic glycogen metabolism in non-diabetic and Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats;Diabetes 39 821–827
Puri D, Prabhu K and Murthy P S 1994 Hypocholesterolemic effect of hypoglycemic principle of fenugreek(Trigonella foenum graecum) seeds;Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 9 13–16
Raheja B S, Iyer P D, Bhargava D and Krishnaswamy P R 1981 Glycosylated haemoglobin: its value in the management of diabetes mellitus;J. Assoc. Physicians India 29 609–613
Raju J, Gupta D, Rao A R, Yadava P K and Baquer N Z 2001Trigonella foenum graecum (fenugreek) seed powder improves glucose homeostasis in alloxan diabetic rat tissues by reversing the altered glycolytic, gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzymes;Mol. Cell Biochem. 224 45–51
Ramasamy R, Oates P J and Schaefer S 1997 Aldose reductase inhibition protects diabetic and non-diabetic rat hearts from ischemic injury;Diabetes 46 292–300
Roshchin I V, Ordzhonikidze E K and Shalganova I V 1980 Vanadium — toxicity, metabolism, carrier state;J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 24 377–383
Sauvaire Y, Baissac Y O, Petit P and Ribes G 1996 Steroid saponins from fenugreek and some of their biological properties;Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 405 37–46
Saxena A K, Saxena P, Kale R K and Baquer N Z 1992 Effect of Vanadate administration on polyol pathway in diabetic rat kidney;Biochem. Int. 26 59–68
Saxena A K, Saxena P, Kale R K and Baquer N Z 1993 Impaired antioxidant status in diabetic rat liver: Effect of vanadate;Biochem. Pharmacol. 45 539–542
Shechter Y 1990 Insulin-mimetic effects of vanadate. Possible implications for future treatment of diabetes;Diabetes 39 1–5
Siddiqui M A and Rahman M A 1980 Effect of hyperglycemia on the enzyme activities of lenticular tissues of the rats;Exp. Eye Res. 31 463–469
Slaughter M R, Thakkar H and O’Brien P J 2003 Differential expression of the lenticular antioxidant system in laboratory animals: A determinant of species predilection to oxidative stress-induced ocular toxicity;Curr. Eye Res. 26 15–23
Sochor M, Baquer N Z and McLean P 1988 Effect of aldose reductase inhibiter sorbinil on metabolites in diabetic lens;Biochem. Pharmacol. 37 3349–3356
Takamarg Y, Kubo E, Tsuzuki S and Akagi Y 2003 Apoptotic cell death in the lens of rat sugar cataract;Exp. Eye Res. 77 51–57
The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus 2003 Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus;Diabetes Care 26 S5-S20
Varma S D, Scocket S S and Richards R D 1979 Implications of aldose reductase in cataracts in human diabetes;Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 18 237–241
Williamson J R, Chang K, Frangos M, Hasan K S, Ido Y, Kawamura T, Nyengaard J R, Van den Enden M, Kilo C and Tilton R G 1993 Hyperglycemic pseudohypoxia and diabetic complications;Diabetes 42 801–813
Willsky G R, Willsky A B G, Kostyniak P J, Yang L Q, Khan H R and Crans D C 2001 Effect of vanadium (iv) compounds in the treatment of diabetes: In vivo and in vitro studies with vanadyl sulfate and bis(maltolato)oxovanadium (iv);J. Inorg. Biochem. 85 33–42
Wohaieb S A and Godin D V 1987 Alterations in free radicals tissue-defense mechanisms in Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rat: effects of insulin treatment;Diabetes Care 36 1014–1018
Wolff S P 1993 Diabetes mellitus and free radicals. Free radicals, transition metals and oxidative stress in the aetiology of diabetes mellitus and complications;Br. Med. Bull. 49 642–652
Yagi K 1984Assay for blood plasma or serum (New York: Academic press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preet, A., Gupta, B.L., Yadava, P.K. et al. Efficacy of lower doses of vanadium in restoring altered glucose metabolism and antioxidant status in diabetic rat lenses. J. Biosci. 30, 221–230 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703702
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703702