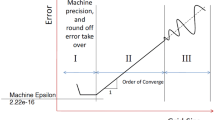
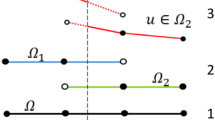
Abstract
The finite element method entails several approximations. Hence it is essential to subject all new finite elements to an adequate set of pathological tests in order to assess their performance. Many such tests have been proposed by researchers from time to time. We present an adequate set of tests, which every new finite element should pass. A thorough account of the patch test is also included in view of its significance in the validation of new elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allman D J 1984 A compatible triangular element including vertex rotation for plane elasticity analysis.Comput. Struct. 19: 1–8
ANSYS 1996 Introduction to ANSYS. Release 5.3, Swanson Analysis Systems Inc., Houston, PA
Babuska I 1971 Error bounds for finite element methods.Number Math. 16: 322–333
Babuska I 1973 The finite element method with Lagrange multipliers.Number Math. 20: 179–192
Babuska I, Scapolla T 1989 Bench mark computation and performance evaluation for a rhombic plate bending problem.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 28: 155–179
Bachrach W E 1987 An efficient formulation of hexahedral elements with high accuracy for bending and incompressibility.Comput. Struct. 26: 453–467
BÄcklund J 1978 On isoparametric elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 12: 731–732
Bassayya K, Shrinivasa U 2000 A 14-node brick element, PN5X1, exactly representing linear stress fields.Comput. Struct. 74: 147–165
Bassayya K, Bhattacharya K, Shrinivasa U 2000 Au eight-node brick element, PN 340, to represent every constant stress field exactly.Comput. Struct. 14: 441–460
Belytschko T, Lasry D 1988 A fractal patch test.IntJ. Numer. Meth. Engng. 26: 2199–2210
Belytschko T, Stolarski H, Liu W K, Carpenter N, Ong J S J 1985 Stress projection for membrane and shear locking in shell finite elements.Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engng. 51: 221–258
Belytschko T, Wong B L, Stolarski H 1989 Assumed strain stabilization procedure for the 9-node Lagrange shell element.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 28: 385–414
Bergan P G, Felippa C A 1985 A triangular membrane element with rotational degrees of freedom.Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engng. 50: 25–69
Bhattacharya K, Bassayya K, Shrinivasa U 1996 Development of an eight-node isoparametric brick element using Papcovitch-Neuber functions.Comput. Struct. (under review)
Bigdeli B, Kelly D W 1997C*- convergence in the finite element method.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 40: 4405–4425
Bretl J L, Cook R D 1979 A new eight-node solid element.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 14: 593–615
Brezzi F 1974 On the existence, uniqueness and approximation of saddle point problems arising from Lagrange multipliers.Rev. Francaise Autom. Inf. Rech. Oper., Aual. Numer. 8: 129–151
Chandra S, Prathap G 1989 A field-consistent formulation for the eight-noded solid finite element.Comput. Struct. 33: 345–355
Chandra S, Kumar P, Chattopadhya L, James D 2001 Report No. PD-ST-XXX, National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore
Chapelle D, Bathe KJ 1993 The inf-sup test.Comput. Struct. 47: 537–545
Cheung Y K, Chen W 1988 Isoparametric hybrid hexahedral elements for three dimensional stress analysis.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 26: 677–693
Cheung Y K, Chen W 1992 Refined hybrid method for plane isoparametric elements using an orthogonal approach.Comput. Struct. 42: 683–694
Choi J K, Lim J K 1995 General curved beam elements based on the assumed strain fields.Comput. Struct. 55: 379–386
Claudio F, Maria M 1998 Some finite elements for the static analysis of beams with varying crosssection.Comput. Struct. 69: 191–196
Felippa C A, Haugen B J 1995 From the individual element test to finite element templates: evolution of the patch test.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 38: 199–229
Gifford L N 1979 More on distorted isoparametric elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 14: 290–291
Graf W, Chang T Y, Saleeb A F 1986 On the numerical performance of three dimensional thick shell elements using a hybrid/mixed formulation.Finite Elements Anal. Design. 2: 357–375
Hauptmann R, Schweizerhof K 1998 A systematic development of solid shell element formulations for linear and nonlinear analyses employing only displacement degrees of freedom.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 42: 49–69
Hayes L J 1981 Practical stability test for finite elements with reduced integration.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 17: 1689–1695
Irons B M 1966 Engineering applications of numerical integration in stiffness methods.AIAA J. 4: 2035–2037
Irons B M, Barlow J 1964 Comments on ‘Matrices for the direct stiffness method by R J Melosh’.AIAA J. 2: 403–404
Irons B M, Loikkanen M 1983 An engineer’s defence of the patch test.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 19: 1391–1401
Irons B M, Razzaque A 1972Experience with the patch test for convergence of finite elements in mathematical foundation of the finite element method (ed.) A K Aziz(New York: Academic Press) pp 557–587
Iosilevich A, Bathe K J, Brezzi F 1997 On evaluating the inf-sup condition for plate bending elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engg. 40: 3639–3663
John S Y, Wayne K E, Norman F A 1999 Finite elements for materials with strain gradient effects.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 44: 373–391
Lee N S, Bathe K J 1993 Effect of element distortions on the performance of isoparametric elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 36: 3553–3576
Levy S 1953 Structural analysis and influence coefficients for delta wings.J. Aeronaut. Sci. 20: 449–454
MacNeal R H 1951 The solutions of elastic plate problems by electrical analogies.Trans. ASME, J. Appl. Mech. 18: 59–67
MacNeal R H 1987 A theorem regarding the locking of tapered four-noded membrane elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 24: 1793–1799
MacNeal R H, Harder R L 1985 A proposed set of problems to test finite element accuracy.Finite Elements Anal. Design 1: 3–20
Mallikarjuna Rao K, Shrinivasa U 2001 A 20-node hexahedral element, PN6X1, exactly representing linear stress fields.Comput. Struct, (submitted)
Melosh R J 1963 Structural analysis of solids.Proc. Am. Soc. Civil Eng. ST4-89: 205–223
Muskhelishvili N I 1953Some basic problems of the mathematical theory of elasticity (Groningen: Noordhoff)
Murakami Y 1987Stress intensity factors handbook (Oxford: Pergamon) pp 909–911
NAFEMS 1988 Proposed NAFEMS linear bench marks. National Agency for Finite Element Method and Standards, U K
Noor A K, Babuska I 1987 Quality assessment and control of finite element solutions.Finite Elements Anal. Design 3: 1–26
Oliveira A E R 1977 The patch test and the serial convergence criteria of the finite element method.Int. J. Solids Struct. 13: 159–78
Pian T H H, Sumihara K 1984 Rational approach for assumed stress finite elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 20: 1685–1695
Punch E F, Atluri S N 1984 Development and testing of stable, invariant, isoparametric curvilinear 2- and 3-dimensional hybrid stress elements.Comput. Meth. Appl. Eng. 47: 331–356
Razzaque A 1986 The patch test for elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 22: 63–71
Robinson J 1986 New FEM user project — single element test for aspect ratio sensitivity of solids (Part I).Finite Element News 1: 26–32
Sander G, Beckus P 1977 The influence of the choice of connectors in the finite element method.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 11: 1491–1505
Smith M 1990 Bench mark tests for geometrically non-linear two dimensional beams.Finite Elements Anal. Design 3: 40–43
Sorin M D, Bordan E I 1999 Study of warping torsion of thin walled beams with open cross-section using macro-elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 44: 853–868
Strang G, Fix G J 1973An analysis of the finite element method (Englewood cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall).
Stricklin J A, Ho W S, Richardson E Q, Haisler W E 1977 On isoparametric vs linear strain triangular elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 11: 1041–1043
Stummel F 1980 The limitations of the patch test.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 15: 177–188
Sze K Y 1992 Efficient formulations of robust hybrid elements using orthogonal stress or strain interpolants and admissible matrix formulation.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 35: 1–20
Sze K Y 1996 Admissible matrix formulation from orthogonal approach to explicit hybrid stabilization.Finite Elements Anal. Design 24: 1–30
Sze K Y, Ghali A 1993 Hybrid hexahedral element for solids, plates, shells and beams by selective scaling.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 36: 1519–1540
Sze K Y, Chen W, Cheung Y K 1992 An efficient quadrilateral plane element with drilling degrees of freedom using orthogonal stress modes.Comput. Struct. 42: 695–705
Tada H, Paris P C, Irwin G R 1973The stress analysis of cracks handbook (Hellerstown: Del Res. Corp.) p. 4
Taylor R L, Beresford P J, Wilson E L 1976 A non conforming element for stress analysis.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 10: 1211–1219
Taylor R L, Zienkiewicz O C, Simo J C, Chan A H C 1986 The patch test — a condition for asserting term convergence.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 22: 39–62
Timoshenko S P, Krieger S W 1959Theory of plates and shells 2nd edn. (New York: McGraw-Hill) pp 51–143
Venkatesh D N, Shrinivasa U 1995 Generation of eight-node brick element using Papcovitch-Neuber function.Comput. Struct. 54: 1077–1084
Venkatesh D N, Shrinivasa U 1996a Hexahedral elements using PN functions — Applications to beams.Comput. Struct. 60: 305–313
Venkatesh D N, Shrinivasa U 1996b Plate bending with hexahedral PN elements.Comput. Struct. 60: 635–641
Verhegghe B, Powell G H 1986 Control of zero-energy modes in 9-node plane element.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 23: 863–869
Verma A, Melosh R J 1987 Numerical tests for assessing finite element model convergence.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engg. 24: 843–857
Veubeke B F D 1974 Variational principles and the patch test. 1974,Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 8: 783–801
Watson J O 1995 Singular boundary elements for the analysis of cracks in plane strain.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 38: 2389–2411
Weissman S L 1996 High accuracy, low-order three-dimensional brick elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 39: 2337–2361
White D W, Abel J F 1989 Testing of shell finite element accuracy and robustness.Finite Elements Anal. Design 6: 129–151
Wilson E L, Ibrahimbegovic A 1990 Use of incompatible displacement modes for the calculation of element stiffnesses or stress.Finite Elements Anal. Design 7: 229–241
Yunus S M, Saigal S, Cook R D 1989 On improved hybrid finite elements with rotational degrees of freedom.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 28: 785–800
Zhang W U, Chen D P 1997 The patch test conditions and some multivariable finite element formulations.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 40: 3015–3032
Zienkiewicz O C, Taylor R L 1991The finite element method (New York: McGraw-Hill)
Zienkiewicz O C, Taylor R L 1997 The finite element patch test revisited. A computer test for convergence, validation and error estimates.Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engg. 149: 223–254
Zienkiwicz O C, Taylor R L, Nakazawa S 1986 The patch test for mixed formulations.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engg. 23: 1873–1883
Zienkiewicz O C, Xu Z, Zeng L F, Samuelsson F, Wiberg N 1993 Linked interpolation for Reissner-Mindlin plate elements: Part I — A simple quadrilateral.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 36: 3043–3056
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, K.M., Shrinivasa, U. A set of pathological tests to validate new finite elements. Sadhana 26, 549–590 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703459
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703459