Abstract
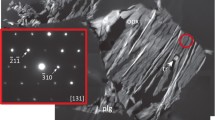
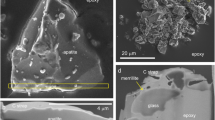
Back scattered electron and transmission electron imaging of lunar soil grains reveal an abundance of submicrometer-sized pure Fe0 globules that occur in the rinds of many soil grains and in the submillimeter sized vesicular glass-cemented grains called agglutinates. Grain rinds are amorphous silicates that were deposited on grains exposed at the lunar surface from transient vapors produced by hypervelocity micrometeorite impacts. Fe0 may have dissociated from Fe-compounds in a high temperature (>3000°C) vapor phase and then condensed as globules on grain surfaces. The agglutinitic glass is a quenched product of silicate melts, also produced by micrometeorite impacts on lunar soils. Reduction by solar wind hydrogen in agglutinitic melts may have produced immiscible droplets that solidified as globules. The exact mechanism of formation of such Fe0 globules in lunar soils remains unresolved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen C C, Morris R V and Mckay D S 1994 Experimental reduction of lunar mare soil and volcanic glass;JGR-Planets 99 23,173–23,185.
Allen C C, Morris R V and McKay D S 1996 Oxygen extraction from lunar soils and pyroclastic glass;JGR-Planets 101 26,085–26,095.
Arnold J R 1975 A Monte Carlo model for the gardening of the lunar regolith;The Moon 13 159–172.
Basu A 1977 Steady state, exposure age and growth of agglutinates in lunar soils;Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 8th, Pp. 3617-3632.
Basu A and Meinschein W G 1976 Agglutinates and carbon accumulation in Apollo 17 lunar soils;Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 7th, Pp. 337-369.
Bhandari N and Shah V G 1979 Potassium-rich globules in the Luna-20 soil;Proceedings Indian National Acad. Sci. (Part A),45(3) 5–6.
Bean A L, Conrad C C Jr. and Gordon R F 1970 Crew observations; Apollo 12 Preliminary Science Report, NASA SP-235, Pp. 29–38.
Chanda S K 1963 Cementation and diagenesis of the Lameta beds, Lametaghat MP, India;J. Sed. Pet. 33 728–738.
Christofferson R, Keller L P and McKay D S 1996 Microstructure, chemistry, and origin of grain rims on ilmenite from the lunar soil finest fraction;Meteoritics Planet. Sci. 31 835–848.
Cintala M J 1992 Impact-induced thermal effects in the lunar and Mercurian regoliths;JGR-Planets 97 947–973.
Clanton U S, McKay D S, Laughon R B and Ladle G H 1973 Iron crystals in lunar breccias;Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 4th, Pp. 925-931.
Cloud P, Margolis S V, Moorman M, Barker J M, Licari G R, Krinsley D and Barnes V E 1970, Micromorphology and surface characteristics of lunar dust and breccia;Science 167 776–778.
Crawford D A and Schultz P H 1999 Electromagnetic properties of impact-generated plasma, vapor and debris;Int. J. Impact Eng. 23 160–180.
Hapke B 1975 Effects of vapor-phase deposition processes of the optical, chemical, and magnetic properties of the lunar regolith;The Moon 13 339–353.
Hapke B 2001 Space weathering from Mercury to the asteroid belt;JGR-Planets 106 10,039–10,073.
Heiken G, Vaniman D and French B M (eds) 1991, Lunar Sourcebook, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, p. 736.
Housley R M, Cirlin E H, Paton N E and Goldberg I B 1974 Solar wind and micrometeorite alteration of the lunar regolith;Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 5th, Pp. 2623-2642.
Housley R M, Grant R W and Abdel-Gawad M 1972 Study of excess Fe metal in the lunar fines by magnetic separation, Mossbauer spectroscopy, and microscopic examination.Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 3rd, Pp. 1065-1076.
James C, Basu A, Wentworth S J and McKay D S 2001 Grain size distribution of Fe0 globules in lunar agglutinitic glass: first results from Apollo 17 soil 78421;Geol. Soc. Am., Abstr. Prog. 33 A311.
James C, Letsinger S, Basu A, Wentworth S J and McKay D S 2002 Size distribution of Fe0 globules in lunar agglutinitic glass; Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. XXXIII, Abstract # 1827 (CD-ROM).
Keller L P and Clemmet S J 2001 Formation of nanophase iron in the lunar regolith: Lunar Planet. Sci. XXXII, Abstract # 2097 (CD-ROM).
Keller L P and McKay D S 1993 Discovery of vapor deposits in the lunar regolith;Science 261 1305–1307.
Keller L P and McKay D S 1992 Micrometer-sized glass spheres in Apollo 16 soil 61181; implications for impact volatilization and condensation:Proc. of the Lunar and Planetary Sci. Conf. 22nd,22 137–141.
Keller L P and McKay D S 1997 The nature and origin of rims on lunar soil grains;Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 61 1–11.
Khan A and Mosegaard K 2001 New information on the deep lunar interior from an inversion of lunar free oscillation periods;Geophys. Res. Lett. 28 1791–1794.
Khan A, Mosegaard K and Rasmussen K L 2000 A new seismic velocity model for the Moon from a Monte Carlo inversion of the Apollo lunar seismic data;Geophys. Res. Lett. 27 1591–1594.
Margolis S V, Barnes V, Cloud P and Fisher R V 1971 Surface micrography of lunar fines compared with tektites and terrestrial volcanic analogs;Proc. of the Lunar Sci. Conf. 2nd, Pp. 909-921.
McKay D S and Basu A 1983 The production curve for agglutinates in planetary regoliths;Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 14th, Pp. B193–B199.
McKay D S, Fruland R M and Heiken G H 1974 Grain size and evolution of lunar soils;Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 5th, Pp. 887–906.
McKay D S, Heiken G H, Basu A, Blanford G, Simon S, Reedy R, French B M and Papike J J 1991 The lunar regolith; In: Lunar Sourcebook, Heiken G H, Vaniman D and French B (eds), Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, Pp. 285–356.
Morris R V 1977 Origin and evolution of the grain-size dependence of the concentration of fine-grained metal in lunar soils: the maturation of lunar soils to a steady-state stage:Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 8th, Pp. 3719-3748.
Morris R V 1980 Origins and size distribution of metallic iron particles in the lunar regolith;Proc. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 11th, Pp. 1697–1712.
Schaal R B and Horz F 1977 Shock metamorphism of lunar and terrestrial basalts;Proc. Lunar Planet Sci. Conf. 8th,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., Pp. 1697-1729.
Schultz P H 1996 Effect of impact angle on vaporization;JGR-Planets 101 21,117–21,136.
Spudis P D 1996 The Once and Future Moon, Washington, Smithsonian, p. 308.
Sugita S and Schultz P H 1999 Spectroscopic characterization of hypervelocity jetting: comparison with a standard theory;JGR-Planets 104 30,825–30,845.
Stöffler D, Gault D E, Wedekind J and Polkowski G 1975 Experimental hypervelocity impact into quartz sand: Distribution and shock metamorphism of ejecta;JGR 80 4062–4077.
Taylor S R 1982 Planetary Science: A Lunar Perspective. LPI, Houston, U.S.A., p. 481.
Taylor L A and Cirlin E-H 1985 A review of ESR studies on lunar samples; In: ESR Dating and Dosimetry, Ikeya M and Miki T (eds) Tokyo, IONICS, Pp. 19–29.
Yakovlev O I, Dikov Yu P, Gerasimov M V, Wlotzka F and Huth J 2002 The behavior of Pt in silicate melts during impact-simulated high temperature heating; Lunar Planet. Sci. XXXIII Abstract # 1271 (CD-ROM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basu, A. Nanophase Fe0 in lunar soils. J Earth Syst Sci 114, 375–380 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702956
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702956