Abstract
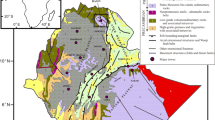
The Gondwana basins of peninsular India are traditionally considered as extensional-rift basins due to the overwhelming evidence of fault-controlled synsedimentary subsidence. These basins indeed originated under a bulk extensional tectonic regime, due to failure of the attenuated crust along pre-existing zones of weakness inherited from Precambrian structural fabrics. However, disposition of the basins and their structural architecture indicate that the kinematics of all the basins cannot be extensional. To maintain kinematic compatibility with other basins as well as the bulk lateral extension, some basins ought to be of strike-slip origin. The disposition, shape and structural architecture of the Satpura basin, central India suggest that the basin could be a pull-apart basin that developed above a releasing jog of a left-stepping strike-slip fault system defined by the Son-Narmada south fault and Tapti north fault in consequence to sinistral displacement along WSW-ENE. Development of a sedimentary basin under the above-mentioned kinematic condition was simulated in model experiments with sandpack. The shape, relative size, stratigraphic and structural architecture of the experimental basin tally with that of the Satpura basin. The experimental results also provide insights into the tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Satpura basin in particular and pull-apart basins in general.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydin A A and Nur A 1985 The types and roles of stepovers in strike slip tectonics, In: Strike-slip deformation, basin formation, and sedimentation (eds) K T Biddle and N Christie-Blick,SEPM Spec. Publ. 37 35–45.
Barnes P M, Sutherland R, Davy B and Delteil J 2001 Rapid creation and destruction of sedimentary basins on mature strike-slip faults: an example from the offshore Alpine Fault, New Zealand;J. Struct. Geol. 23 1727–1739.
Basile C and Brun J P 1999 Transtensional faulting patterns ranging from pull-apart basins to transform continental margins: an experimental investigation;J. Struct. Geol. 21 23–37.
Basu T N and Shrivastava B B P 1980 Structure and tectonics of Gondwana basins of peninsular India;Fifth International Gondwana Symposium, Wellington, New Zealand Pp. 177-182.
Biswas S K 1999 A review on the evolution of rift basins in India during Gondwana with special reference to western Indian basins and their hydrocarbon prospects. In:Proc. Indian National Sci. Acad. Special issue on Gondwana assembly: new issues and perspectives (eds) A Sahni and R S Loyal, Pp. 261-283.
Biswas S K 2003 Regional Tectonic framework of the Pranhita-Godavari basin, India;Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 21 543–551.
Casshyap S M and Qidwai H A 1974 Glacial sedimentation of late Palaeozoic Talchir diamictite, Pench valley coalfield, central India;Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 85 749–760.
Casshyap S M and Khan A 2000 Tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Gondwanan Satpura basin of central India: evidence of pre-Trap doming, rifting and palaeoslope reversal;Journal of South African Earth Sciences 31 59–66.
Casshyap S M, Tewari R C and Khan A 1993 Alluvial fan origin of Bagra Formation (Mesozoic Gondwana) and tectonostratigraphic implications;J. Geol. Soc. India 56 489–504.
Chakraborty C, Mandal N and Ghosh S 2003a Kinematics of the Gondwana basins of the peninsular India;Tectonophysics 377 299–324.
Chakraborty C, Ghosh S K and Chakraborty T 2003b Depositional Record of Tidal-Flat Sedimentation in the Permian Coal Measures of Central India: Barakar Formation, Mohpani Coalfield, Satpura Gondwana Basin;Gondwana Research 6 817–827.
Christie-Blick N and Biddle K T 1985 Deformation and basin formation along strike slip faults In: Strike-slip deformation, basin formation, and sedimentation (eds) K T Biddle and N Christie-Blick,SEPM Spec. Publ. 37 1–35.
Crawford A R 1978 Narmada-Son lineament of India traced into Madagascar;J. Geol. Soc. India 19 144–153.
Crookshank H 1936 Geology of the two northern slopes of the Satpuras between the Morand and Sher rivers;Mem. Geol. Surv. India 66 173–381.
Crowell J C 1974 Origin of late Cenozoic basins in southern California, In: Tectonics and Sedimentation (ed.) W R Dickinson,SEPM Spec. Publ. 22 190-204.
Das B and Patel N P 1984 Nature of the Narmada-Son lineament;J. Geol. Soc. India 25 267–276.
Dooley T and Mcclay K R 1997 Analog modelling of pullapart basins;American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin 81 1804–1826.
Ghosh S K, Chakraborty C and Chakraborty T 2004 Combined tide and wave influence on sedimentation of Lower Gondwana coal measures of central India: Barakar Formation (Permian), Satpura Basin;J. Geol. Soc. London 161 117–131.
Harris L B and Beeson J 1993 Gondwanaland significance of lower Palaeozoic deformation in central India and SW Western Australia;J. Geol. Soc. London 150 811–814.
Hobday D K 1987 Gondwana coal basins of Australia and South Africa; tectonic setting, depositional systems and resources, In:Coal and coal-bearing strata: recent advances (ed.) A C Scott,Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ. 32 219-233.
Horsefield W T 1977 An experimental approach to basement-controlled faulting;Geologie en Mijnbouw 56 363–370.
Ingersoll R V and Busby C J 1995 Tectonics of sedimentary basins. In:Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins (eds) C J Busby and R V Ingersoll, Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, Pp. 1–52.
Kaila K L 1986 Tectonic framework of Narmada-Son Lineament; a continental rift system in central India from deep seismic soundings, Reflection seismology: a global perspective; American Geophysical Union,Geodynamics Series 13 133–150.
Maulik P K, Chakraborty C, Ghosh P and Rudra D 2000 Mesoand macro-scale architecture of a Triassic fluvial succession: Denwa Formation, Satpura Gondwana basin, Madhya Pradesh;J. Geol. Soc. India 56 489–504.
Mishra D C, Gupta S B, Rao MBS, Venkatarayudu and Laxman G 1987 Godavari basin-a geophysical study;J. Geol. Soc. India 30 469–476.
Mishra D C, Chandra Sekhar D V, Venkata Raju D Ch and Vijay Kumar V 1999 Crustal structure based on gravity-magnetic modelling constrained from seismic studies under Lambert Rift, Antarctica and Godavari and Mahanadi rifts, India and their interrelationship;Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 172 287–300.
Naqvi S M, Rao D and Narain H 1974 The protocontinental growth of the Indian Shield and the antiquity of its rift valleys;Precambrian Research 1 345–398.
Narula P L, Acharyya S K and Banerjee J 2000 Seismotectonic atlas of India and its environs;Geological Survey of India 87 1–87.
Peters J and Singh S K 2001 Satpura basin-an example of pre-rift, syn-rift and post-rift Gondwana sedimentation in India;J. Geol. Soc. India 57 309–320.
Raja Rao C S 1982Coalfields of India Vol-II, Coal resources of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Orissa and Maharashtra.Bulletin Geological Survey of India, Series A 45 103.
Raja Rao C S 1983Coalfields of India Vol-III, Coal resources of Madhya Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir.Bulletin Geological Survey of India Series A 45 204.
Raja Rao C S 1987Coalfields of India Vol-IV Part I Coal resources of Bihar,Bulletin Geological Survey of India Series A 45.
Ray S and Chakraborty T 2002 Lower Gondwana fluvial succession of the Pench-Kanhan valley, India: stratigraphic architecture and depositional controls;Sedim. Geol. 151 243–271.
Robinson P L 1967 The Indian Gondwana Formations A review;First Symposium on Gondwana Stratigraphy, Ar Del Plata, Argentina 201-268.
Sims D, Ferrill D A and Stamatakos J A 1999 Role of ductile decollement in the development of pull-apart basins: experimental and natural examples;J. Struct. Geol. 21 533–554.
Veevers J J and Tewari R C 1995 Gondwana master basin of Peninsular India between Tethys and the interior of the Gondwanaland Province of Pangea;Memoir Geological Society of America 187 1–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, C., Ghosh, S.K. Pull-apart origin of the Satpura Gondwana basin, central India. J Earth Syst Sci 114, 259–273 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702949
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702949