Abstract
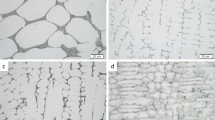
The possible microstructures resulting from both fusion and solid-state processing of Ti-26Al-11Nb at. pct (Ti-15Al-21Nb wt pct) have been determined. The particular microstructure produced was primarily a function of the cooling rate from theβ solvus. The most rapid cooling rate, associated with pulsed Nd:YAG (yttrium-aluminum-garnet) laser welding, resulted in a microstructure in which the high-temperatureβ underwent an ordering reaction on cooling to the CsCl (B2) crystal structure. Intermediate cooling rate (≈60 °C/s) specimens [characteristic of the fusion zone and heat-affected zone (HAZ) in arc welds] were found to undergo a complete transformation (no retainedβ observed) to an acicularα 2 microstructure. Electron microprobe and analytical electron microscopy (AEM) analyses revealed no statistically significant compositional dψerences spatially within this structure. These two observations suggest that the transformation reaction in this cooling rate regime involves, at least in part, a compositionally invariant shear component. Controlled slow cooling rate (0.1 °C/s) experiments produced Widmanstätten microstructures which were two-phase (α 2 +β). The retainedβ phase was observed to be highly enriched (≈35 wt pct) in Nb. The transformedα 2 exhibited a very low dislocation density. Solidification cracking of fusion welds was not observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.A. Lipsitt:High Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys, MRS, Symp. Proc., C.C. Koch, C.T. Liu, and N.S. Stoloff, eds., 1984, pp. 351–64.
F. LeMaitre:Mém. Sci. Rev. Metall., 1970, pp. 563–74.
K.C. Wu:Weld. J., 1981, pp. 219s–226s.
F.D. Mullins and D.W. Becker:Weld. J., 1980, pp. 177s–182s.
W.A. Baeslack III and C.M. Banas:Weld. J., 1981, pp. 121s–130s.
W.A. Baeslack III and F.D. Mullins:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, pp. 1948–52.
T.J. Mascorella: M.S. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 1987.
W.A. Baeslack in, M.J. Cieslak, and T.J. Headley:Scripta Metall., 1988, pp. 1155–60.
R. Strychor, J.C. Williams, and W.A. Soffa:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, pp. 225–34.
R. Strychor and J.C. Williams:Solid ⇒ Solid Phase Transformations, Hubert I. Aaronson, David E. Laughlin, Robert F. Sekerka, and C. Marvin Wayman, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1982, pp. 249–53.
Gleeble 1500, Duffers Scientific, Inc., Troy, NY.
W.F. Chambers: Sandia Report SAND85-2037, Albuquerque, NM, 1985.
T.T. Nartova and G.G. Sopochkin:Russ. Metall. (Metally), 1970, p. 138.
O.N. Andreyev:Russ. Metall. (Metally), 1970, p. 127.
Metals Handbook, 8th ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1973, vol. 8, p. 284.
Metals Handbook, 8th ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1973, vol. 8, p. 264.
Smithells Metals Reference Book, 6th ed., E.A. Brandes, ed., Butterworth’s, London, 1983, pp. 13–56 and 13–71.
D.L. Moffat and U.R. Kattner:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, pp. 2389–97.
M.C. Flemings:Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1974, p. 148.
M.J. Cieslak and P.W. Fuerschbach:Metall. Trans. B, 1988, pp. 319–29.
C.R. Heiple and J.R. Roper:Trends in Welding Research in the United States, S.A. David, ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1982, pp. 489–515.
J.C. Williams:Titanium and Titanium Alloys, J.C. Williams and A.F. Belov, eds., Plenum Press, Oxford, 1982, pp. 1477–98.
S.M.L. Sastry and H.A. Lipsitt:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, pp. 1543–52.
K.S. Jepson, A.R.G. Brown, and J.A. Gray:The Science, Technology and Application of Titanium, R.I. Jaffee and N.E. Promisel, eds., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1966, pp. 677–90.
M. Morinaga, N. Yukawa, and H. Actachi:Tetsu-to-Haganè, 1986, no. 6, pp. 21–28.
D. Rosenthal:Trans. AIME, 1946, pp. 849–66.
G.A. Knorovsky and P.W. Fuerschbach:Proc. Int. Conf. on Advances in Welding Science and Technology, S.A. David, ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1986, pp. 393–400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cieslak, M.J., Headley, T.J. & Baeslack, W.A. Effect of thermal processing on the microstructure of Ti-26Al-11Nb: Applications to fusion welding. Metall Trans A 21, 1273–1286 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698255
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698255