Abstract
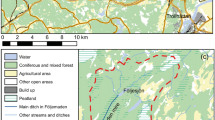
Cores were collected from the length of Pakuranga estuary, a small urban estuary in Auckland, New Zealand, to determine sedimentation and contaminant history, and in particular the impact of urbanization. Catchment sediment loads for the most recent history (1953–1995), including urbanization since 1960, were reconstructed using the landcover history and soil erosion modeling. Pollen and14C dating and pre-urban landcover history were used to reconstruct early estuary sedimentation (i.e., post-3000 yr BP to 1960). Heavy metal concentrations, particle size,137Cs, pollen, and catchment sediment loads were all needed to disentangle the complex estuarine response to urbanization.137Cs profiles did not reflect the historical fallout pattern, but deposition of137Cs-labelled eroded catchment soil, coinciding with peaks in urban construction. Temporal variations in stormwater137Cs concentrations are likely due to varying contributions from137Cs-rich topsoil and137Cs-poor subsoils. A similar pattern was observed in heavy-metal concentrations and attributed to street runoff rather than topsoil being diluted by metal-poor subsoils. Dating of the sediment profiles showed that during urbanization sedimentation rates in the tidal creek and estuary were higher than sedimentation rates associated with past agricultural landuse and the original forest landcover. Urbanization has brought about substantial environmental changes in the upper estuary through continued infilling of shallow, intertidal areas, contamination by heavy metals to levels of ecological concern, sediment textural changes, and rapid mangrove colonization of formerly bare intertidal sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Alexander, C. R., R. G. Smith, F. D. Calder, S. J. Schropp, andH. L. Windom. 1993. The historical record of metal enrichment in two Florida estuaries.Estuaries 16:627–637.
Auckland Regional Council, 1995. The environmental effects of urban storm-water runoff. ARC Environment and Planning Division Technical Publication No. 53. Auckland Regional Council. Aukland, New Zealand.
Benoit, G., T. F. Rozan, P. C. Patton, andC. L. Arnold. 1999. Trace metals and radionuclides reveal sediment sources and accumulation rates in Jordan Cove, Connecticut.Estuaries 22: 65–80.
Bradley, W. H. 1929. The varves and climate of the Green River Epoch:United States Geological Survey.Professional Paper 158E: 87–110.
Cooper, A. B. andA. D. Bottcher. 1993. Basin-scale modelling as a tool for water-resource planning.Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 119:306–323.
Department of Scienctific and Industrial Research. 1968. Soils of New Zealand, Part 3. Soil Bureau Bulletin 26(3), Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Wellington, New Zealand.
Douglas, I. 1985. Urban sedimentology.Progress in Physical Geography 9:255–280.
Hattaway, R. 1982. Early farming activities in the Howick District.Auckland-Waikato Historical Journal 1:24–27.
Herald, J. R. 1989. Hydrological impacts of urban development in the Albany Basin, Auckland. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Geography, University of Auckland, New Zealand.
Hicks, D. M. 1994. Storm sediment yields from basins with various land-uses in the Auckland area. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Misc. Report No. 183, Christchurch, New Zealand.
Hogg, A. G., D. J. Lowe, andC. Hendy. 1987. University of Waikato radiocarbon dates I.Radiocarbon 29:263–301.
Hume, T. M. andM. S. McGlone. 1986. Sedimentation patterns and catchment use change recorded in the sediments of a shallow tidal creek, Lucas Creek, Upper Waitemata Harbour, New Zealand.New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 20:677–687.
Jantschik, R., F. Nyffeler, andO. F. X. Donard. 1992. Marine particle size measurement with a stream-scanning laser system.Marine Geology 106:239–250.
Knisel, W. G. 1980. CREAMS, a field scale model for chemicals, runoff and erosion from agricultural management systems. USDA Conservation Research Report No. 26, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, D.C.
Lilliefors, H. W. 1967. On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown.Journal of the American Statistical Association 62:399–402.
Long, E. R., D. D. Macdonald, S. L. Smith, andF. D. Calder. 1995. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments.Environmental Management 19:81–97.
Makepeace, D. K., D. W. Smith, andS. J. Stanley. 1995. Urban stormwater quality: Summary of contaminant data.Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 25:93–139.
Matthews, K. M. 1989. Radioactive fallout in the south pacific: A history. Part 1. Deposition in New Zealand Report NRL1989/2, National Radiation Laboratory, Christchurch, New Zealand.
McGlone, M. S. andJ. M. Wilmshurst.. 1999. Dating initial Maori impact in New Zealand.Quaternary International 59:17–26.
Moore, P. D. andJ. A. Webb. 1978. An Illustrated Guide to Pollen Analysis. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Morrisey, D. J., D. S. Roper, andR. B. Williamson. 1997. Biological effects of the build-up of contaminants in sediments in urban estuaries. p. 228–250.In L. A. Roesner (ed.), Effects of Watershed Development and Management on Aquatic Ecosystems, Proceedings of an Engineering Foundation Conference. American Society of Civil. Engineers. New York.
Morrisey, D. J., R. B. Williamson, L. Van Dam, andD. J. Lee. 2000. Stormwater contamination of urban estuaries. 2. Testing a predictive model of the build-up of heavy metals in sediments.Estuaries 23:67–79.
Oldman. J. O. and A. Swales. 1999. Maungamaungaroa estuary numerical modelling and sedimentation. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Client Report ARC70224. Hamilton, New Zealand.
Olsen, C. R., H. J. Simpson, T.-H. Peng, R. F. Bopp, andR. M. Trier. 1981. Sediment mixing and accumulation rate effects on radionuclide depth profiles in Hudson estuary sediments.Journal of Geophysical Research 86:11020–11028.
Pearce, J. B. 1995. Editorial: Urban development and the marine and riparian habitat.Marine Pollution Bulletin 30:496–499.
Ritchie, J. C. andJ. R. McHenry. 1989. Application of radioactive fallout cesium-137 for measuring soil erosion and sediment accumulation rates and patterns: A review with bibliography. Hydrology Laboratory. Maryland.
Robbins, J. A. andD. N. Edgington. 1975. Determination of recent sedimentation rates in Lake Michigan using210Pb and137Cs.Geochimica, et Cosmochimica Acta 39:285–304.
Roper, D. S., R B. Williamson, M. A. Weatherhead, and R. D. Pridmore. 1994. Effects of future urbanisation in the catchment of the Upper Waitemata Harbour: Ecological impacts. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Client Report ARC100. Hamilton, New Zealand.
Stuvier, M. andH. A. Polach. 1977. Discussion: Reporting of14C data.Radiocarbon 19:355–363.
Swales, A. 1989. The effects of urbanisation and consequent sediment generation on the upper Pakuranga estuary, Auckland. M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Geography, University of Auckland, New Zealand.
Swales, A., T. M. Hume, J. W. Oldman, and M. O. Green. 1997. Holocene sedimentation and recent human impacts in a drowned valley estuary, p. 895–900.In J. Lumsden, Proceedings of the 13th Australian Coastal and Ocean Engineering Conference, Centre for Advanced Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand.
Valette-Silver, N. J. 1993. The use of sediment cores to reconstruct historical trends in contamination of estuarine and coastal sediments.Estuaries 16:577–588.
Vant, W. N., R. B. Williamson, T. M. Hume, and T. J. Dolphin. 1993. Effects of future urbanisation in the catchment of the Upper Waitemata Harbour. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Client Report ARC220. Hamilton, New Zealand.
Wallbrink, P. J. andA. S. Murray. 1993. Use of fallout radionuclides as indicators of erosion processes.Hydrological Processes 7:297–304.
Walling, D. E. andQ. He. 1993. Towards improved interpretation of137Cs profiles in lake sediments, p. 31–53.In J. McManus and R. W. Duck (eds.), Geomorphology and Sedimentology of Lakes and Reservoirs. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Williamson, R. B. 1993. Urban runoff data book: A manual for the preliminary evaluation of urban stormwater impacts on water quality. Water Quality Centre Publication No. 20. Hamilton, National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, Hamilton, New Zealand.
Williamson, R. B. andD. J. Morrisey. 2000. Stormwater contamination of urban estuaries. 1. Predicting the build-up of heavy metals in sediments.Estuaries 23:56–66.
Williamson, R. B., D. J. Morrisey, andA. Swales. 1999. The build up of contaminants in urbanised estuaries. Proceedings of the Comprehensive Stormwater and Aquatic Ecosystem Management Conference, Auckland, February 1999 1: 59–66. New Zealand Water and Wastes Association, Auckland, New Zealand.
Williamson, R. B. andR. J. Wilcock. 1994. The distribution and fate of contaminants in estuarine sediments: Recommendations for monitoring and environmental assessment. Environment and Planning Division Technical Publication No. 47. Auckland Regional Council, Aukland, New Zealand.
Wilmshurst, J. M., D. N. Eden, andP. C. Froggatt. 1999. Late Holocene forest disturbance in Gisborne, New Zealand: A comparison of terrestrial and marine pollen records.New Zealand Journal of Botamy 37:523–540.
Wise, S. 1977. The use of radionuclides210Pb and137Cs in estimating denudation rates and in soil erosion measurement. Occasional Paper No. 7. University of London, King's College, Department of Geography, London.
Source of Unpublished Materials
Basher, L. R. unpublished data. Landcare Research, P. O. Box 69, Lincoln, New Zealand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swales, A., Williamson, R.B., Van Dam, L.F. et al. Reconstruction of urban stormwater contamination of an estuary using catchment history and sediment profile dating. Estuaries 25, 43–56 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02696048
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02696048