Abstract
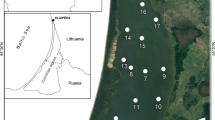
Net fluxes of respiratory metabolites (O2, dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), NH4 +, NO3 −, and NO2 −) across the sediment-water interface were measured using in-situ benthic incubation chambers in the area of intermittent seasonal hypoxia associated with the Mississippi River plume. Sulfate reduction was measured in sediments incubated with trace levels of35S-labeled sulfate. Heterotrophic remineralization, measured as nutrient regeneration, sediment community oxygen consumption (SOC), sulfate reduction, or DIC production, varied positively as a function of temperature. SOC was inversely related to oxygen concentration of the bottom water. The DIC fluxes were more than 2 times higher than SOC alone, under hypoxic conditions, suggesting that oxygen uptake alone cannot be used to estimate total community remineralization under conditions of low oxygen concentration in the water column. A carbon budget is constructed that compares sources, stocks, transformations, and sinks of carbon in the top meter of sediment. A comparison of remineralization processes within the sediments implicates sulfate reduction as most important, followed by aerobic respiration and denitrification. Bacteria accounted for more than 90% of the total community biomass, compared to the metazoan invertebrates, due presumably to hypoxic stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aller, R. 1998. Mobile deltaic and continental shelf muds as fluidized bed reactors.Marine Chemistry 61:143–155.
Alongi, D. 1997. Coastal Ecosystem Processes, CRC Press, New York.
Atwood, D., A. Bratkovich, M. Gallagher, andG. Hitchcock. 1994. Introduction to the dedicated issue.Estuaries 17: 729–731.
Bierman, Jr.,V., N. Rabalais, S. Hinz, D.-W. Zhu, R. E. Turner, andW. Wiseman. 1994. A preliminary mass balance model of primary productivity and dissolved oxygen in the Mississippi River plume/Inner Gulf shelf region.Estuaries 17:886–899.
Boesch, D. and N. Rabalais. 1991. Effects of hypoxia on continental shelf benthos: Comparisons between the New York Bight and the northern Gulf of Mexico, p. 27–34.In R. Tyson and T. Pearson (eds.), Modern and Ancient Continental Shelf Anoxia. Geological Society Special Publication Number 58, London, U.K.
Boland, G. S. andG. T. Rowe. 1991. Deep-sea benthic sampling with the GOMEX box corer.Limnology and Oceanography 36: 1015–1020.
Bratbak, G. andI. Dundas. 1984. Bacterial dry matter content and biomass estimations.Applied and Environmental Microbiology 48:755–757.
Cai, W.-J. andC. Reimers. 1995. Benthic oxygen flux, bottom water oxygen concentration and core top organic carbon content in the deep northeast Pacific Ocean.Deep-Sea Research I 42:1681–1699.
Canfield, D., B. Jorgensen, andH. Fossing. 1993. Pathways of organic carbon oxidation in three continental margin sediments.Marine Geology 113:27–40.
Carey, A., J. Pennock, J. Lehter, W. Lyons, W. Schroeder, andJ.-C. Bonzongo. 1999. The Role of the Mississippi River in Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia. Environmental Institute Publication No. 70, University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, Alabama.
Cederwall, H. andR. Elmgren. 1990. Biological effects of eutrophication in the Baltic Sea, particularly the coastal zone.Ambio 19:109–112.
Cloern, J. 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem.Marine Ecology Progress Series 210:223–253.
Diaz, R. andR. Rosenberg. 1995. Marine benthic hypoxia, A review of its ecological effects and the behavioural responses of benthic macrofauna.Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Reviews 33:245–303.
Dortch, Q., N. Rabalais, R. Turner, andG. Rowe. 1994. Respiration rates and hypoxia on the Louisiana shelf.Estuaries 17:862–872.
Eadie, B., B. McKee, M. Lansing, J. Robbins, S. Metz, andJ. Trefry. 1994. Records of nutrient enhanced coastal ocean productivity in sediments from the Louisiana continental shelf.Estuaries 17:754–765.
Fenchel, T. andB. Finlay. 1995. Ecology and Evolution in Anoxic Worlds. Oxford Press, New York.
Ferdelman, T., C. Lee, S. Pantoja, J. Harder, B. Bebout, andH. Fossing. 1997. Sulfate reduction and methanogenesis in aThioploca-dominated sediment off the coast of Chile.Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 61:3065–3079.
Fry, J. C. 1988. Determination of biomass, p. 27–71.In B. Austin (ed.), Methods in Aquatic Microbiology. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., New York.
Gardner, W., E. Escobar Briones, andG. Rowe. 1993. Ammonium excretion by benthic invertebrates and sediment-water nitrogen flux in the Gulf of Mexico near the Mississippi River outflow.Estuaries 16:799–808.
Gaston, G. 1985. Effects of hypoxia on macrobenthos of the inner shelf off Cameron, Louisiana.Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 20:603–613.
Gerlach, S., A. Hahn, andM. Schrage. 1985. Size spectra of benthic biomass and metabolism.Marine Ecology Progress Series 26:161–173.
Grant, J. andP. Schwinghamer. 1987. Size partitioning of microbial and meiobenthic biomass and respiration on Brown's Bank, southwest Nova Scotia.Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 25:647–661.
Green, M., R. Aller, andJ. Aller. 1998. The influence of carbonate dissolution on the survival of shell-bearing meiobenthos in nearshore sediments.Limnology and Oceanography 43: 18–28.
Hagerman, L., A. Josefson, andJ. Jensen. 1996. Benthic macrofauna and demersal fish, p. 155–177.In B. Jorgensen and K. Richardson (eds.), Eutrophication in Coastal Marine Ecosystems, Coastal and Estuarine Studies 52. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C.
Justić, D., N. Rabalais, andR. E. Turner. 1996. Effects of climate change on hypoxia in coastal waters: A doubled CO2 scenario for the northern Gulf of Mexico.Limnology and Oceanography 41:992–1003.
Levin, L., J. Gage, C. Martin, andP. Lamont. 2000. Macrofauna community structure within and beneath the oxygen minimum zone, NW Arabian Sea.Deep-Sea Research II 47:189–226.
Lin, S. andJ. W. Morse. 1991. Sulfate reduction and iron sulfide mineral formation in Gulf of Mexico anoxic sediments.American Journal of Science 291:55–89.
Lohrenz, S., G. Fahnenstiel, andD. Redalje. 1994. Spatial and temporal variations of photosynthetic parameters in relation to environmental conditions in coastal waters of the northern Gulf of Mexico.Estuaries 17:779–795.
Mahaut, M., M. Sibuet, andY. Shirayama. 1995. Weight-dependent respiration rates in deep-sea organisms.Deep-Sea Research 42:1575–1582.
Marvin-DiPasquale, M. C. andD. Capone. 1998. Benthic sulfate reduction along the Chesapeake Bay central channel. I. Spatial trends and controls.Marine Ecology Progress Series 168: 213–228.
Miller-Way, T., G. Boland, G. Rowe, andR. Twilley. 1994. Sediment oxygen consumption and benthic nutrient fluxes on the Louisiana continental shelf: A methodological comparison.Estuaries 117:809–815.
Morse, J. andG. Rowe. 1999. Benthic biogeochemistry beneath the Mississippi River plume.Estuaries 22:206–214.
Murrell, M. andJ. Fleeger. 1989. Meiofauna abundance on the Gulf of Mexico continental shelf affected by hypoxia.Continental Shelf Research 9:1049–1062.
Nelson, T., P. Blackwelder, T. Hood, B. McKee, N. Romer, C. Alverez-Zarikian, andS. Metz. 1994. Time-based correlation of biogenic, lithogenic and authigenic sediment components with anthropogenic inputs in the Gulf of Mexico NECOP study area.Estuaries 17:873–885.
Pakulski, J., R. Benner, T. Whitledge, R. Amon, B. Eadie, L. Cifuentes, J. Ammerman, andD. Stockwell. 2000. Microbial metabolism and nutrient cycling in the Mississippi and Atchafalaya River plumes.Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 50: 173–184.
Porter, K. G. andY. S. Feig. 1980. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora.Limnology and Oceanography 25:943–948.
Qureshi, N. 1995. The role of fecal pellets in the flux of carbon to the sea floor on a river-influenced continental shelf subject to hypoxia. Ph.D. Dissertation. Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
Rabalais, N., N. Smith, D. Harper, andD. Justić. 2001. Effects of seasonal hypoxia on continental shelf benthos, p. 211–240.In N. Rabalais and R. E. Turner (eds.), Coastal Hypoxia: Consequences for Living Resources and Ecosystems. Coastal and Estuarine Studies 58, American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C.
Rabalais, N., R. E. Turner, andD. Scavia. 2002. Beyond science into policy: Gulf of Mexico hypoxia and the Mississippi River.Bioscience 52:129–142.
Rabalais, N. N., R. E. Turner, W. J. Wiseman, Jr., and D. F. Boesch. 1991. A brief summary of hypoxia on the northern Gulf of Mexico, p. 35–47.In R. V. Tyson and T. H. Person (eds.). Modern and Ancient Continental Shelf Anoxia. Geological Society Special Publication 58, London, U.K.
Rabalais, N., W. Wiseman, Jr., andR. E. Turner. 1994. Comparison of continuous records of near-bottom dissolved oxygen from the hypoxia zone along the Louisiana coast.Estuaries 17:850–861.
Redalje, D., S. Lohrenz, andG. Fahnenstiel. 1994. The relationship between primary production and the vertical export of particulate organic matter in a river impacted coastal ecosystem.Estuaries 17:829–838.
Rowe, G. 2001. Seasonal hypoxia in the bottom water off the Mississippi River delta.Journal of Environmental Quality 30:281–290.
Rowe, G. andC. H. Clifford. 1973. Modifications of the Birge-Ekman box corer for use with SCUBA or deep submergence research vessels.Limnology and Oceanography 18:172–175.
Rowe, G. T. 1983. Biomass and production in the deep-sea benthos, p. 97–121.In G. Rowe (ed.), Deep-Sea Biology, The Sea, Volume 8. Wiley, New York.
Rowe, G., M. Sibuet, J. Deming, J. Tietjen, andA. Khripounoff. 1990. Organic carbon turnover time in deep-sea benthos.Progress in Oceanography 24:141–160.
Rowe, G. 1997. The structure and function of Arctic benthic communities: Are high-latitude ecosystems different?Korean Journal for Polar Research 8:85–95.
Schallenberg, M., J. Kalff, andJ. B. Rasmussen. 1989. Solution to problems in enumerating sediment bacteria by direct counts.Applied and Environmental Microbiology 55:1214–1219.
Schmitt, J., J. Deming, P. Jumars, andR. Keil. 1998. Constancy of bacterial abundance in surficial marine sediments.Limnology and Oceanography 43:976–982.
Tengberg, A., F. De Bovee, P. Hall, W. Berelson, D. Chadwick, G. Ciceri, P. Glud, F. Graziottin, J. Jahnke, A. Khripounoff, S. Lieberman, V. Nuppenau, O. Pfannkucke, C. Reimers, G. Rowe, A. Sahami, F. Sayles, M. Schurters, D. Smallman, B. Wehrli, andP. Dewilde. 1995. Benthic chamber and profiling landers in oceanography—A review of design, technical solutions and functioning.Progress in Oceanography 35:253–292.
Thamdrup, B., H. Fossing, andB. Jorgensen. 1994. Manganese, iron, and sulfur cycling in a coastal marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark).Geochemica Cosmochimica Acta 58:5115–5129.
Trefry, J. andB. Presley. 1982. Manganese fluxes from Mississippi delta sediments.Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 46:1715–1726.
Trefry, J., S. Metz, T. Nelson, R. Trocine, andB. Eadie. 1994. Transport of particulate organic carbon by the Mississippi River and its fate in the Gulf of Mexico.Estuaries 17:839–849.
Turner, R. E., N. Qureshi, N. Rabalais, Q. Dortch, D. Justić, R. Shaw, andJ. Cope. 1998. Fluctuating silicate:nitrate ratios and coastal plankton food webs.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95:13048–13051.
Velji, M. I. andL. J. Albright. 1986. Microscopic enumeration of attached marine bacteria of seawater, marine sediment, fecal matter, and kelp blade samples following pyrophosphate and ultrasound treatments.Canadian Journal of Microbiology 32: 121–126.
Warnken, K., G. Gill, P. Santschi, andL. Griffin. 2000. Benthic exchange of nutrients in Galveston Bay, Texas.Estuaries 23:647–661.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rowe, G.T., Kaegi, M.E.C., Morse, J.W. et al. Sediment community metabolism associated with continental shelf hypoxia, Northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries 25, 1097–1106 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02692207
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02692207