Abstract
Seventeen male subjects, aged nineteen to twenty, went through a protocol including, while supine, relaxation at rest (10 min) and mental stress (MS) by a Kraepelin (arithmetic) test (5 min), as part of a larger study. With a polygraphic analog recording set-up we also collected a 1 ms - digital facsimile of a lead II-like thoracic ECG with maximum T-wave (Codas, Dataq Instr). Twenty-three stress responses were assigned to three classes according to known cardiotacho-, plethysmo-, and pneumo-graphic marks of “concentrated attention mainly,” “emotion,” or still “high emotion.” During each setting the most stationary 3 min RR epoch in cardiotachogram was selected for joint RR & QT beat-by-beat variability study. RR and QT intervals were detected using a published algorithm. Conventional RR and QT Fourier autospectra were computed while using RR*QT mean square coherence spectrum we detached the RR-independent, idioventricular (IV) fraction of QT low frequency (LF: 0.04–0.15 Hz) power of variability (IV QT-LF).
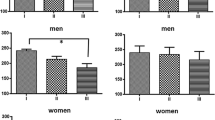
IV QT-LF responded consistently to varieties of mental stress that confuse RR-LF or let QT-LF unchanged, best witnessing the cortically-issued ventricular adrenergic strain. Indeed, while emotion propels the same way all spectral variables above, concentrated attention increased (Wilcoxon) significantly IV QT-LF only (0.54–0.80 ms2) and decreased RR-LF (715–465 ms2). Findings hold promise of a non-invasive, high resolution Holter based monitoring of sympathetic status of myocardium, robust vis-à-vis of confusion caused by the autonomic interplay at sino-atrial node.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athyros, V., Didangelos, T., et al. (1996). Effect of quinapril on heart rate variability in patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy.European Heart Journal 17:383.
Bigger, J.T., Fleiss, J.L., Rolnitzky, L.M., and Steinman, R.C. (1993). The ability of several short-term measures of RR variability to predict mortality after myocardial infarction.Circulation 88(3):927–934.
De Boer, R.W. and Karemaker, J.M. (1985). Relationship between short-term blood pressure fluctuations and heart-rate variability in resting subjects: a spectral analysis approach.Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 23:352.
Badilini, F., Maison-Blanche, P., Pinoteau, C. and Coumel, P. (1997). Rate independent influences on ventricular repolarization.European Heart Journal (Proceedings ESC Congress, Stockholm), CD-ROM, P631.
Corley, K.C., Mauck, H.P., Shiel, F.O.M., et al. (1979). Myocardial dysfunction and pathology associated with environmental stress in squirrel monkey: Effect of vagotomy and propranolol.Psychophysiology, Amsterdam: Excp. Med. Abstract. 16:554.
Dinca-Panaitescu, S., Ionescu, D-D., Filcescu, V., and Negoescu, R. (1996). Spectral RR*QT coherence can spot the sympathetic-drive-to-ventricles fraction of QT power spectrum.European Heart Journal 17:102.
Eckberg, D.L. (1995).Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia and Other Human Cardiovascular Neural Periodicities. Regulation of breathing (Dempsey, J.A., Pack, A.I., eds.).
Huang, MH., Ebey, J., and Wolf, S. (1991). Heart rate-QT interval Relationship During Postural Change and Exercise. A possible connection to cardiac contractility.Integrative Physiology and Behavioral Science 26:5–17.
Huang, MH., Ebey, J., and Wolf, S. (1989). Response of the QT interval of the Electrocardiogram During Emotional Stress.Psychosomatic Medicine 51:419–427.
Ionescu, D.-D., Dinca-Panaitescu, S. and Negoescu, R. (1998). Comparative time delays of QT interval adjustment to heart rate during autonomic blockade and after fixed rate atrial pacing in young normal subjects.Journal of American College of Cardiology (Proceedings ACC Congress).
Maliani, A., Pagani, M., Lombardi, F., and Cerutti, S. (1991). Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain.Circulation 84:482–492.
McEwen, B.S. (1998). Protective and Damaging Effects of Stress Mediators.Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Deaconess M.C. 338:171–179.
Members of the Task Force (1996). Heart Rate Variability. Standards of measurements, physiological interpretation, and clinical use.European Heart Journal 17:354–381.
Negoescu, R., Csiki, I.E., and Pafnote, M. (1989).Stabilizing the rate—a straight cortical repercussion upon the heart. Proceed. IEEE-EMBS Ann. Int. Conf. Seattle, pp. 147–148.
Negoescu, R. and Csiki, I.E. (1991). The weight of the cortical inflow against medullary reflexes as enlightened by spectral analysis of HR and SP waves.Romanian Journal of Physiology 28:17–22.
Negoescu, R., Porges, S.W., Goddart, P., Richardson, D.C., and Carlton, B. (1992).Short term oscillations in systolic time intervals. Proceed. IEEE-EMBS Ann. Int. Conf. Paris, France 14:506–507.
Negoescu, R., Csiki, I.E., Pafnote, M., and Wolf, S. (1993). Cortical control of sinus arrhythmia in man studied by spectral analysis.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 28:226–238.
Negoescu, R., Skinner, J., and Wolf, S. (1993).QT interval beat-by-beat fluctuations studied by spectral and dimensional methods. Proc. 15th Ann. Int. IEEE-EMBS, 15: #866, San Diego, CA.
Negoescu, R., Porges, S., Goddard, P., and Wolf, S. (1993).Measuring systolic time-intervals at the nearest ms. Proc. 28th Convention AAMI., 66, Boston.
Negoescu, R., Filcescu, V., Ionescu, D.D., and Dinca-Panaitescu, S. (1995).Spectral dynamics of QT intervalunder mental stress with stable RR interval by vagal blockade or atrial pacing (abstract).Rom. Heart J. 5: 126.
Negoescu, R., Dinca-Panaitescu, S., Filcescu, V., and Ionescu, D.D. (1996).QT spectral power within 0.1 Hz band is relatedto sympathetic messages to atrial and ventricular targets as a function of situation (abstract).European Heart Journal 17:282.
Negoescu, R., Dinca-Panaitescu, S., Ionescu, D.D., and Filcescu, V. (1997). Mechanism of 0.1 Hz modulation of QT interval by mental stress is adrenergicEuropean Heart Journal (XIX Congress of the European Society of Cardiology, Stockholm), CD-ROM D2136.
Negoescu, R. (1998).Psycho-social stress as arrhythmia risk factor enters quantitative era by means of Holter QT-variability. Proceedings XIX Congress of the European Society for Noninvasive Dynamics, Gent, Belgium.
Pagani, M., Mazzuero, G., Ferrari, A., Liberati, D., et al. (1991).Sympatovagal interaction during mental stress, a study using spectral analysis of heart rate variability in healthy control subjects and patients witha prior myocardial infarction. Supplement IICirculation 83:43–51.
Perini, R., Orizio, C., Baselli, G., Cerutti, S., and Veicsteinans, A. (1990).The influence of exercise intensity onthe power spectrum of heart rate variability.European Journal of Applied Physiology 61:153–160.
Singh, L.P., Johnston, J., Sleigh, P., Marinho, M., Casadei, B., and Hart, F. (1996).Waking hour QT intervaldynamics in normal subjects: implications for the circadian pattern of sudden cardiac death.European Heart Journal 17:279.
Verrier, R.L. and Hohnloser, S.H. (1987).How is the nervous system implicated in the genesis of cardiac arrhythmias? New York, Raven Press, pp. 153–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dincą-Panaitescu, S., Dincą-Panaitescu, M., Achim, A. et al. Idioventricular low frequency oscillation in QT interval responds univocally to RR confusing kinds of mental stress. Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 34, 10–18 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688706
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688706