Abstract
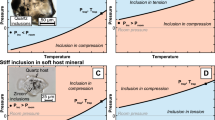
Experimental reequilibration of synthetic 10 wt% NaCl-H2O inclusions in natural quartz reveals that reequilibration textures show distinct differences depending upon the P-T path followed by the inclusion after formation. These differences combined with other geological information may be used to determine whether the sample (rock) followed a dominantly isothermal or isobaricP-T path following entrapment. The intensity and style of inclusion reequilibration features is related to the direction and magnitude of the departure of theP-T path from the original isochore for the inclusion. Thus, fluid inclusion reequilibration textures not only permit inclusionists to determine whether the rocks followed an isothermal or isobaric retrogradeP-T path, but also the magnitude of departure of this path from one that is isochoric.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker RJ, Jansen JBH (1991) Experimental post-entrapment water loss from synthetic CO2−H2O inclusions in natural quartz. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:2215–2230.
Bakker RJ, Jansen JBH (1994) A mechanism for preferential H2O leakage from fluid inclusions in quartz, based on TEM observations. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 116:7–20.
Bodnar RJ, Bethke PM (1979). Systematics of stretching of fluid inclusions. I. Fluorite and sphalerite at 1 atmosphere confining pressure. Econ Geol 79: 141–161.
Bodnar RJ, Sterner SM (1987). Synthetic fluid inclusions. In: Barnes HL, Ulmer GC (eds). Hydrothermal experimental techniques. Wiley and Sons. New York, pp 423–457.
Bodnar RJ, Vityk MO (1994) Interpretation of microthermometric data for NaCl−H2O fluid inclusions. In: De Vivo B, Frezzotti ML (eds) Fluid inclusions in minerals: methods and applications. Virginia Polytechnic Inst State Univ. Blacksburg, VA, pp 117–131.
Bodnar RJ, Binns PR, Hall DL (1989) Synthetic fluid inclusions. VI. Quantitative evaluation of the decrepitation behavior of fluid inclusions in quartz at one atmosphere confining pressure. J Metamorphic Geol 7:229–242.
Boullier AM, Michot G, Pêcher A, Barres O (1989) Diffusion and plastic deformation around fluid inclusions in synthetic quartz. In: Bridgwater D (ed) Fluid movements-element transport and the composittion of the deep crust. (NATO ASI series 281) Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 345–360.
Boullier AM, France-Lanord C, Dubessy J, Adamy J, Champenois M (1991). Linked fluid and tectonic evolution in the High Himalayan Mountains (Nepal). Contrib Mineral Petrol 107:358–372.
Chapman DS, Furlong KP (1992) Thermal state of the continental lower crust. in Fountain DM, Arculus R, Kay RW (eds) Continental lower crust. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 179–199.
Cordier P, Doukhan JC, Ramboz C (1994). Influence of dislocations on water leakage from fluid inclusions in quartz: a quantitative reappraisal. Eur J Mineral 6:745–752.
Darimont A, Burke E, Touret J (1988). Nitrogen-rich metamorphic fluids in Devonian metasediments from Bastogne, Belgium. Bull Mineral 111: 321–330.
Engelder T (1993) Stress regimes in the lithosphere. Princeton University Press. Princeton, New Jersey
Evans B, Dresen G (1991) Deformation of earth materials: six easy pieces. (Reviews in Geophysics) quadriennial Rep IUGG, Suppl, pp 823–843
Gratier JP, Jenatton L (1984). Deformation by solution-deposition and reequilibration of fluid inclusions in crystals depending on temperature, internal pressure, and stress. J Struct Geol 6:189–200.
Griggs DT (1974) A model of hydrolytic weakening in quartz. J Geophys Res 79:1655–1661.
Hall DL, Bodnar RJ (1989). Comparison of fluid inclusion decrepitation and acoustic emission protile of Westerly granite and Sioux quartzite. Tectonophysics 168:283–296.
Hall DL, Bodnar RJ (1990). Methane in fluid inclusions from granulites: a product of hydrogen diffusion? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54: 641–652.
Hall DL, Sterner SM (1993) Preferential water loss from synthetic fluid inclusions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 114:489–500.
Hall DL, Bodnar RJ, Craig JR (1991) Fluid inclusion constraints on the uplift history of the metamorphosed massive sulfide deposits at Ducktown, Tenessee. J Metamorphic Geol 9:551–565.
Harley SL (1989) The origin of granulites: a metamorphic perspective. Geol Mag 126: 215–247.
Herms P, Schenk V (1992) Fluid inclusions in granulite-facies metapelites of the Hercynian ancient lower crust of the Serre, Calabria, Southern Italy. Contrib Mineral Petrol 112:393–404.
Hirth G, Tullis J (1992) Dislocation creep regimes in quartz aggregates. J Struct Geol 14:145–159
Hollister LS (1990) Enrichment of CO2 in fluid inclusions in quartz by removal of H2O during crystal-plastic deformation. J Struct Geol 12:895–901
Hollister LS, Burruss RC, Henry DL, Hendel EM (1979) Physical conditions during uplift of metamorphic terranes, as evidenced by fluid inclusions. Bull Soc Fr Mineral Cristallogr 102:555–561.
Hurai V, Horn E (1992) A boundary layer-induced immiscibility in naturally re-equilibrated H2O−CO2−NaCl inclusions from metamorphic quartz (Western Carpathians, Czechoslovakia). Contrib Mineral Petrol 112:414–427.
Kalyuzhnyi VA (1982) Principles and knowledge about mineralforming fluids (in Russian). Naukova Dumka Press, Kiev
Kerkhof AM, van den, Berh HJ (1994). Cathodoluminescence studies of quartz as a tool for interpretation of fluid inclusion transposition (abstract). PACROFI V, Cuernavaca, Mexico, May, pp 108
Kerrich R (1976) Some effects of tectonic recrystallization on fluid inclusions in vein quartz. Contrib Mineral Petrol 59:195–202.
Klemd R (1989)P-T evolution and fluid inclusion characteristics of retrograded eclogites, Münchberg Gneiss Complex, Germany. Contrib Mineral Petrol 102:221–229
Kotel'nikova ZA (1994) The response of fluid inclusions to changes in physicochemical parameters in the external medium (in Russian). Geokhimia 4:476–485
Kreulen R (1977) CO2-rich fluids during regional metamorphism on Naxos, a study of fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. PhD thesis, Univ Utrecht
Lamb WM (1990) Fluid inclusions in granulites: peak versus. retrograde formation. In: Vielzeuf D, Vidal P (eds) Granulites and crustal evolution. Kluwer Acad Publ, The Netherlands, pp 419–433
Lamb W, Valley JW (1984) Metamorphism of reduced granulites in a low-CO2 vapor-free environment. Nature 312:56–58
Leroy J (1979) Contribution à l'étalonnag de la pression interne des inclusions fluides lors de leur décrépitation. Bull Soc Fr Miněral et Cristallogr 102:584–593
Lomov SB, Vityk MO (1990) Cracking halos around fluid inclusions in Carpathian “Marmarosh Diamonds”. Geochem Int 7:125–129
Mavrogenes JA, Bodnar RJ (1994) Hydrogen movement into and out of fluid inclusions in quartz: experimental evidence and geologic implications. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:141–148
Morgan GB, Chou I-Ming, Pasteris JD, Olsen, SN (1993) Re-equilibration of CO2 fluid inclusions at controlled hydrogen fugacities. J Metamorphic Geol 11:155–164
Mullis J (1987) Fluid inclusion studies during very low-grade metamorphism. In: Frey M (ed.) Low temperature metamorphism. Blackie, Glasgow, pp 162–199
Olsen SN, Ferry JM (1995) A comparative fluid inclusion study of the Waterville and Sangerville (Vassalboro) Formations, south-central Maine. Contrib Mineral Petrol 118:396–413
Pasteris JD (1987) Fluid inclusions in mantle xenoliths. In: Nixon PH (ed) Mantle xenoliths. J Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 691–707
Paterson MS (1978) Experimental rock deformation the brittle field. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Paterson MS (1987) Problems in the extrapolation of laboratory rheological data. Tectonophysics 133:33–43
Pêcher A (1981) Experimental decrepitation and reequilibration of fluid inclusions in synthetic quartz. Tectonophysics 78:567–583.
Pêcher A, Boullier AM (1984) Evolution À pression et température élevées d'inclusions fluides dans un quartz synthétique. Bull Mineral 107:139–153
Philippot P (1993) Fluid-melt-rock interaction in mafic eclogites and coesite-bearing metasediments: constraints on volatile recycling during subduction. Chem Geol 108:93–112
Philippot P, Selverstone J (1991) Trace-element-rich brines in eclogite veins: implications of fluid composition and transport during subduction. Contrib Mineral Petrol 106:417–430
Roedder E (1984) Fluid inclusions. (Reviews in mineralogy 12) Mineral Soc Am, Washington, DC
Selverstone J (1985) Petrologic constraints on imbrication, metamorphism, and uplift in the SW Tauern Window, Eastern Alps. Tectonics 4:687–704
Sisson VB, Lovelace RW, Maze WB, Bergman SC (1993) Direct observation of primary fluid-inclusion formation. Geology 21:751–754
Spear FS (1993) Metamorphic phase equilibria and pressure-temperature-time paths. Mineral Soc Am, Washington, DC
Sterner SM, Bodnar RJ (1984) Synthetic fluid inclusions in natural quartz: I. Compositional types synthesized and application to experimental geochemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:2659–2668
Sterner SM, Bodnar RJ (1989) Synthetic fluid inclusions. VII. Reequilibration of fluid inclusions in quartz during laboratory simulated metamorphic burial and uplift. J Metamorphic Geol 7:243–260
Swanenberg HEC (1980) Fluid inclusions in high-grade metamorphic rocks from S.W. Norway. Geol Ultraiectina 25
Touret JLR (1977) The significance of fluid inclusions in metamorphic rocks. In: Fraser DG (ed) Thermodynamics in geology. Reidel Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 203–227
Touret JLR (1992) Fluid inclusions in subducted rocks. In: LePichon X, Touret JLR, van Hinte J (eds) Le rôle des fluides dans les zones de subduction. Maison Descartes, Amsterdam, pp 385–403
Touret JLR, Hartel THD (1990) Synmetamorphic fluid inclusions in granulites. In: Vielzeuf D, Vidal Ph (eds) Granulites and crustal evolution. Kluwer Acad Pub, The Netherlands, pp 397–418.
Touret JLR, Marquis J (1994) Fluides profonds et conductivité électrique de la croûte continentale inferieure. C R Acad Sci Paris 318:1469–1482
Tullis J (1990) Experimental studies of deformation mechanisms and microstructures in quartzo-feldspathie rocks. In: Barber DJ, Meredith PG (eds) Deformation processes in minerals, ceramics and rocks. Unwin Hyman Press, London, pp 190–227
Vityk MO, Bodnar RJ (1994a) Applications of fluid inclusions in tectonic reconstruction: morphological analysis (abstract) PAC-ROFI V, Cuernavaca, Mexico, May, p 115
Vityk MO, Bodnar RJ (1994b) The effect of temperature on fluid inclusion reequilibration behavior under conditions of compresive loading (abstract). 16th IMA General Meet September, Pisa, Italy, p 430
Vityk MO, Bodnar RJ, Schmidt CS (1994) Fluid inclusions as tectonothermobarometers: relation between pressure-temperature history and reequilibration morphology during crustal thickening. Geology 22:731–734.
Voznyak DK, Kalyuzhnyi VA (1976) Utilization of decrepitated inclusions for reconstruction ofPT conditions of mineral formation (on example of pegmatitic quartz from Volyn) (in Russian). Mineral Sb 30:31–40
Wanamaker BJ, Wong TF, Evans B (1990) Decrepitation and crack healing of fluid inclusions in San Carlos olivine. J Geophys Res 95:15623–15641
Wilkins RWT, Barkas JP (1978) Fluid inclusion deformation and recrystallization in granite tectonites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 65:293–299
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: J. Touret
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vityk, M.O., Bodnar, R.J. Textural evolution of synthetic fluid inclusions in quartz during reequilibration, with applications to tectonic reconstruction. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 121, 309–323 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688246
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688246