Abstract
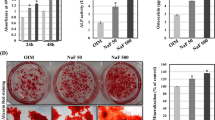
Zinc is an important mineral that is required for normal bone development. However, the direct effects of zinc on the mineralization of bone cells of human origin are not clear. The objective of this study was to determine the effects of zinc on the differentiation of SaOS-2 human osteoblast-like cells and the formation of mineralized bone nodules. Cells were cultured for 8 d and then transferred to zinc-free medium and treated with varying concentrations (0–50 μM) of zinc. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was used as a measure of osteoblast differentiation, and bone nodules were detected by von Kossa staining. After 4, 6, and 8 d of treatment, zinc increased ALP activity at 1 and 10 μM, but decreased activity at 50 μM. After 9 d of treatment, zinc increased both the number and area of mineralized bone nodules at low concentrations (1 and 10 μM), but decreased both at higher concentrations (25 and 50 μM). These findings demonstrate that zinc has biphasic effects on the differentiation and mineralization of human osteoblast-like cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Pandel and R. M. Francis, Osteoporosis in men, Best Pract Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 15, 415–427 (2001).
R. Eastell, I. T. Boyle, and J. Compston, Management of male osteoporosis: report of the UK consensus group, Q. J. Med. 91, 71–92 (1998).
C. Christodoulou and C. Cooper, What is osteoporosis? Postgrad. Med. J. 79, 133–138 (2003).
K. M. Hambidge, C. E. Casey, and N. F. Krebs, Zinc, in Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, W. Metz, ed., Academic, Orlando, FL, pp. 1–37 (1986).
R. Cousins, Zinc, in Present Knowledge in Nutrition, E. E. Ziegler and L. J. Filer, ed., ILSI Press, Washington DC, pp. 293–306 (1996).
A. Cerovic, I. Miletic, S. Sobajic, et al., Effect of dietary zinc on the levels and distribution of fatty acids and vitamin A in blood plasma chylomicrons. Biol. Trace Element Res. 112, 145–158 (2006).
R. S. MacDonald, The role of zinc in growth and cell proliferation, J. Nutr. 130, 1500S-1508S (2000).
A. S. Prasad, J. A. Halsted, and M. Nadim, Syndrome of iron deficiency anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, hypogonadism, dwarfism and geophagia, Am. J. Med. 31, 532–546 (1961).
J. C. Wallwork and H. H. Sandstead, Zinc, in Nutrition and Bone Development, D. J. Simmons, ed., Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 313–339 (1990).
R. M. Angus, P. N. Sambrook, N. A. Pocock, and J. A. Eisman, Dietary intake and bone mineral density, Bone Miner. 4, 265–277 (1988).
A. Gur, L. Colpan, and K. Nas, The role of trace minerals in the pathogenesis of postmenopausal osteoporosis and a new effect of calcitonin, J. Bone Miner. Metab. 20, 39–43 (2002).
J. P. McClung, C. H. Stahl, L. J. Marchitelli, et al., Effects of dietary phytase on body weight gain, body composition and bone strength in growing rats fed a low-zinc diet, J. Nutr. Biochem. 17, 190–196 (2006).
L. Rossi, S. Migliaccio, A. Corsi, M. Marzia, P. Bianco, and A. Teti, Reduced growth and skeletal changes in zinc-deficient growing rats are due to impaired growth plate activity and inanition. J. Nutr. 131, 1142–1146 (2001).
I. Diamonde and L. S. Hurley, Histopathology of zinc-deficient fetal rats. J. Nutr. 100, 325–329 (1970).
M. Yamaguchi and T. Matsui, Stimulatory effect of zinc-chelating dipeptide on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells, Peptides 17, 1207–1211 (1996).
M. Yamaguchi, H. Oishi, and Y. Suketa, Stimulatory effects of zinc on bone formation in tissue culture, Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 4007–4012 (1987).
S. L. Hall, H. P. Dimai, and J. R. Farley, Effects of zinc on human skeletal alkaline phosphatase activity in vitro. Calcif. Tissue. Int. 64, 163–172 (1996).
S. Epstein, Serum and urinary markers of bone remodeling: assessment of bone turnover, Endocrine Rev. 9, 437–438 (1988).
R. H. Christenson, Biochemical markers of bone metabolism: an overview, Clin. Biochem. 30, 573–593 (1997).
Y. Sugawara, K. Suzuki, M. Koshikawa, M. Ando, and J. Iida, Necessity of enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase for mineralization of osteoblastic cells, Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 88, 262–269 (2002).
B. J. Lian, G. S. Stein, E. Canalis, P. G. Robey, and A. L. Boskey, Bone formation: osteoblast lineage cells, growth factors, matrix proteins and the mineralization process, in: Primer on the Metabolic Bone Disease and Disorder of Mineral Metabolism, M. J. Favus, ed., Lippincott Wiliams & Wiliams, Philadelphia (1999).
L. G. Rao, L. J. Liu, T. M. Murray, E. McDermott, and X. Zhang, Estrogen added inter-mittently but not continuously, stimulates differentiation and bone formation in SaOS-2 cells, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 26, 936–945 (2003).
N. W. Tietz, ed., Study group on alkaline phosphatase. A reference method for measurement of alkaline phosphatase activity in human serum. Clin. Chem. 29, 751 (1983).
M. M. Bradfod, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976).
L. F. Bonewald, S. E. Harris, J. Rosser, S. L. Dallas, and N. P. Camacho, Von kossa staining alone is not sufficient to confirm that mineralization in vitro represents bone formation, Calcif. Tissue. Int. 72, 537–547 (2003).
G. Oner, B. Bhaumick, and R. M. Bala, Effects of zinc deficiency on serum somatomedin levels and skeletal growth in young rats, Endocrinology 114, 1860–1863 (1984).
M. Yamaguchi and R. Yamaguchi, Action of zinc on bone metabolism in rats. Increases in alkaline phosphatase activity and DNA content, Biochem. Pharmacol. 35, 773–777 (1986).
M. S. Cooper, M. Hewison, and P. M. Stewart, Glucocorticoid activity, inactivity and the osteoblast, J. Endocrinol. 163, 159–164 (1999).
X. Wu, N. Itoh, T. Taniguchi, T. Nakanishi, and Y. Tatsu, Zinc induced sodium dependent vitamin C transporter 2 expression: potent roles in osteoblast differentiation, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 420, 114–120 (2003).
A. Prasad, D. Oberleas, P. Wolf, and J. P. Horwitz, Studies on zinc deficiency: changes in trace elements and enzyme activities in tissues of zinc-deficient rats, J. Clin. Invest. 46, 217–224 (1967).
P. Dimai, S. Hall, and J. Farley, Effects of dietary zinc on bone formation and resorption indices in adult female mice, J. Bone Miner. Res. 11(Suppl. 1), s228 (1996).
W. H. Fishman, Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes: recent progress, Clin. Biochem. 23, 99–104 (1990).
J. C. King and C. L. Keen, Zinc, in Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, M. E. Shils, J. A. Olson, and M. Shike, ed., Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia (1994).
J. E. Aubin, F. Liu, L. Malaval, and A. K. Gupta, Osteoblast and chondroblast differentiation, Bone 17, 77S-83S (1995).
B. A. Watkins, H. E. Lippman, L. L. Bouteiller, Y. Li, and M. F. Seifert, Bioactive fatty acids: role in bone biology and bone cell function, Progr. Lipid Res. 40, 125–148 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cerovic, A., Miletic, I., Sobajic, S. et al. Effects of zinc on the mineralization of bone nodules from human osteoblast-like cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 116, 61–71 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685919
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685919