Abstract
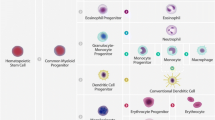
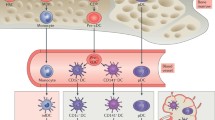
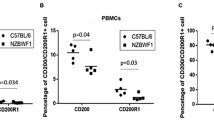
Over the last decade, the role of dendritic cells (DCs) in the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has become apparent. As unique mediators of both tolerance and immunity, aberrant myeloid and plasmacytoid DC function can promote autoimmune responses via a number of mechanisms and proinflammatory pathways. This review provides an overview of DC function, the potential role of DCs in promoting autoimmune responses in SLE, and how other abnormalities in lupus can lead to an enhanced engagement of DCs in immune responses. How medications used to treat SLE and other autoimmune conditions may exert effects on DCs is also explored.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herrmann M, Voll RE, Kalden JR: Etiopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol Today 2000;21:424–426.
Nagy G, Koncz A, Perl A: T- and B-cell abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. Crit Rev Immunol 2005;25:123–140.
Kaplan MJ, Lewis EE, Shelden EA, et al: The apoptotic ligands TRAIL, TWEAK, and Fas ligand mediate monocyte death induced by autologous lupus T cells. J Immunol 2002;169:6020–6029.
Shlomchik MJ, Craft JE, Mamula MJ: From T to B and back again: positive feedback in systemic autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2001;1:147–153.
Zielinski CE, Jacob SN, Bouzahzah F, Ehrlich BE, Craft J: Naive CD4+ T cells from lupus-prone Fasintact MRL mice display TCR-mediated hyperproliferation due to intrinsic threshold defects in activation. J Immunol 2005;174:5100–5109.
Tsokos GC, Mitchell JP, Juang YT: T cell abnormalities in human and mouse lupus: intrinsic and extrinsic. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003;15:542–547.
Wenzel J, Henze S, Brahler S, Bieber T, Tuting T: The expression of human leukocyte antigen-DR and CD25 on circulating T cells in cutaneous lupus erythematosus and correlation with disease activity. Exp Dermatol 2005;14:454–459.
Tsai HF, Lai JJ, Chou AH, Wang TF, Wu CS, Hsu PN: Induction of costimulation of human CD4 T cells by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand: possible role in T cell activation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:629–639.
Calvani N, Richards HB, Tucci M, Pannarale G, Silvestris F: Up-regulation of IL-18 and predominance of a Th1 immune response is a hallmark of lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol 2004;138:171–178.
Gomez D, Correa PA, Gomez LM, Cadena J, Molina JF, Anaya JM: Th1/Th2 cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: is tumor necrosis factor alpha protective? Semin Arthritis Rheum 2004;33:404–413.
Tyrrell-Price J, Lydyard PM, Isenberg DA: The effect of interleukin-10 and of interleukin-12 on the in vitro production of anti-double-strand DNA antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 2001;124:118–125.
Llorente L, Zou W, Levy Y, et al: Role of interleukin 10 in the B lymphocyte hyperactivity and autoantibody production of human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med 1995;181:839–844.
Palucka AK, Banchereau J, Blanco P, Pascual V: The interplay of dendritic cell subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol Cell Biol 2002;80:484–488.
Kono DH, Baccala R, Theofilopoulos AN: Inhibition of lupus by genetic alteration of the interferon-alpha/beta receptor. Autoimmunity 2003;36:503–510.
Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, et al: Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2000;18:767–811.
Jego G, Pascual V, Palucka AK, Banchereau J: Dendritic cells control B cell growth and differentiation. Curr Dir Autoimmun 2005;8:124–139.
Liu YJ: Dendritic cell subsets and lineages, and their functions in innate and adaptive immunity. Cell 2001;106:259–262.
Steinbach F, Henke F, Krause B, Thiele B, Burmester GR, Hiepe F: Monocytes from systemic lupus erythematous patients are severely altered in phenotype and lineage flexibility. Annu Rheum Dis 2000;59:283–288.
Koller M, Zwolfer B, Steiner G, Smolen JS, Scheinecker C: Phenotypic and functional deficiencies of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Int Immunol 2004;16:1595–1604.
Colonna L, Dinnall JA, Shivers DK, Frisoni L, Caricchio R, Gallucci S: Abnormal costimulatory phenotype and function of dendritic cells before and after the onset of severe murine lupus. Arthritis Res Ther 2006;8:R49.
Ding D, Mehta H, McCune WJ, Kaplan MJ: Aberrant phenotype and function of myeloid dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2006;177:5878–5889.
Decker P, Kotter I, Klein R, Berner B, Rammensee HG: Monocyte-derived dendritic cells over-express CD86 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:1087–1095.
Zhu J, Liu X, Xie C, et al: T cell hyperactivity in lupus as a consequence of hyperstimulatory antigen-presenting cells. J Clin Invest 2005;115:1869–1878.
Georgiev M, Agle LM, Chu JL, Elkon KB, Ashany D: Mature dendritic cells readily break tolerance in normal mice but do not lead to disease expression. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:225–238.
Cederblad B, Blomberg S, Vallin H, Perers A, Alm GV, Ronnblom L: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have reduced numbers of circulating natural interferon-alpha- producing cells. J Autoimmun 1998;11:465–470.
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, Pascual V, Banchereau J: Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 2001;294:1540–1543.
Gill MA, Blanco P, Arce E, Pascual V, Banchereau J, Palucka AK: Blood dendritic cells and DC-poietins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol 2002;63:1172–1180.
Migita K, Miyashita T, Maeda Y, et al: Reduced blood BDCA-2+(lymphoid) and CD11c+(myeloid) dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 2005;142:84–91.
Scheinecker C, Zwolfer B, Koller M, Manner G, Smolen JS: Alterations of dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: phenotypic and functional deficiencies. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44:856–865.
Kalled SL, Cutler AH, Burkly LC: Apoptosis and altered dendritic cell homeostasis in lupus nephritis are limited by anti-CD154 treatment. J Immunol 2001;167:1740–1747.
Adachi Y, Taketani S, Toki J, et al: Marked increase in number of dendritic cells in autoimmune-prone (NZW × BXSB)Fl mice with age. Stem Cells 2002;20:61–72.
Asselin-Paturel C, Brizard G, Chemin K, et al: Type I interferon dependence of plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation and migration. J Exp Med 2005;201:1157–1167.
Blomberg S, Eloranta ML, Cederblad B, Nordlin K, Alm GV, Ronnblom L: Presence of cutaneous interferon-alpha producing cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2001;10:484–490.
Farkas L, Beiske K, Lund-Johausen F, Brandtzaeg P, Jahnsen FL: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (natural interferon-alpha/beta-producing cells) accumulate in cutaneous lupus erythematosus lesions. Am J Pathol 2001;159:237–243.
Meller S, Winterberg F, Gilliet M, et al: Ultraviolet tadiation-induced injury, chemokines, and leukocyte recruitment: An amplification cycle triggering cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:1504–1516.
Bogdan C: The function of type I interferons in antimicrobial immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 2000;12:419–424.
Cerutti A, Qiao X, He B: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells and the regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain class switching. Immunol Cell Biol 2005;83:554–562.
Ronnblom L, Eloranta ML, Alm GV: The type I interferon system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:408–420.
Siegal FP, Kadowaki N, Shodell M, et al: The nature of the principal type 1 interferon-producing cells in human blood. Science 1999;284:1835–1837.
Hooks JJ, Moutsopoulos HM, Geis SA, Stahl NI, Decker JL, Notkins AL: Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med 1979;301:5–8.
Dall’era MC, Cardarelli PM, Preston BT, Witte A, Davis JC, Jr: Type I interferon correlates with serological and clinical manifestations of SLE. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:1692–1697.
Zhuang H, Narain S, Sobel E, et al: Association of antinucleoprotein autoantibodies with upregulation of Type I interferon-inducible gene transcripts and dendritic cell maturation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol 2005;117:238–250.
Bennett L, Palucka AK, Arce E, et al: Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. J Exp Med 2003;197:711–723.
Crow MK, Kiron KA, Wohlgemuth J: Microarray analysis of interferon-regulated genes in SLE. Autoimmunity 2003;36:481–490.
Peterson KS, Huang JF, Zhu J, et al: Characterization of heterogeneity in the molecular pathogenesis of lupus nephritis from transcriptional profiles of laser-captured glomeruli. J Clin Invest 2004;113:1722–1733.
Gota C, Calabrese L: Induction of clinical autoimmune disease by therapeutic interferon-alpha. Autoimmunity 2003;36:511–518.
Gresser I, Maury C, Tovey M, Morel-Maroger L, Pontillon F: Progressive glomerulonephritis in mice treated with interferon preparation at birth. Nature 1976;263:420–422.
Adam C, Thoua Y, Ronco P, Verroust P, Tovey M, Morel-Maroger L: The effect of exogenous interferon: acceleration of autoimmune and renal diseases in (NZB/W) F1 mice. Clin Exp Immunol 1980;40:373–382.
Santiago-Raber ML, Baccala R, Haraldsson KM, et al: Type-I interferon receptor deficiency reduces lupus-like disease in NZB mice. J Exp Med 2003;197:777–788.
Hu Y, Ivashikiv LB: Costimulation of chemokine receptor signaling by matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates enhanced migration of IFN-alpha dendritic cells. J Immunol 2006;176:6022–6033.
Bave U, Vallin H, Alm GV, Ronnblom L: Activation of natural interferon-alpha producing cells by apoptotic U937 cells combined with lupus IgG and its regulation by cytokines. J Autoimmun 2001;17:71–80.
Tucci M, Calvani N, Richards HB, Quatraro C, Silvestris F: The interplay of chemokines and dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Ann NY Acad Sci 2005;1051:421–432.
Lin Q, Dong C, Cooper MD: Impairment of T and B cell development by treatment with a type I interferon. J Exp Med 1998;187:79–87.
Pascual V, Banchereau J, Palucka AK: The central role of dendritic cells and interferon-alpha in SLE. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003;15:548–556.
Llorente L, Richaud-Patin Y: The role of interleukin-10 in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 2003;20:287–289.
Hron JD, Peng SL: Type I IFN protects against murine lupus. J Immunol 2004;173:2134–2142.
Li J, Liu Y, Xie C, Zhu J, Kreska D, Morel L, Mohan C: Deficiency of type I interferon contributes to Sle 2-associated component lupus phenotypes. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:3063–3072.
Vallin H, Perers A, Alm GV, Ronnblom L: Anti-doublestranded DNA antibodies and immunostimulatory plasmid DNA in combination mimic the endogenous IFN-alpha inducer in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 1999;163:6306–6313.
Ronnblom L, Alm GV: The natural interferon-alpha producing cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol 2002;63:1181–1193.
Means TK, Luster AD: Toll-like receptor activation in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann NY Acad Sci 2005;1062:242–251.
Lovgren T, Eloranta ML, Bave U, Alm GV, Ronnblom L: Induction of interferon-alpha production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells by immune complexes containing nucleic acid released by necrotic or late apoptotic cells and lupus IgG. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:1861–1872.
Suen JL, Chuang YH, Chiang BL: In vivo tolerance breakdown with dendritic cells pulsed with U1A protein in non-autoimmune mice: the induction of a high level of autoantibodies but not renal pathological changes. Immunology 2002;106:326–335.
Zandman-Goddard G, Shoenfeld Y: Infections and SLE. Autoimmunity 2005;38:473–485.
Goodnow CC: Immunology. Discriminating microbe from self suffers a double toll. Science 2006;312:1606–1608.
Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S: Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 2003;21:335–376.
Hornung V, Rothenfusser S, Britsch S, et al: Quantitative expression of toll-like receptor 1–10 mRNA in cellular subsets of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and sensitivity to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. J Immunol 2002;168:4531–4537.
Barrat FJ, Meeker T, Gregorio J, et al: Nucleic acids of mammalian origin can act as endogenous ligands for Toll-like receptors and may promote systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med 2005;202:1131–1139.
Lenert PS: Targeting Toll-like receptor signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and autoreactive B cells as a therapy for lupus. Arthritis Res Ther 2006;8:203.
Boule MW, Broughton C, Mackay F, Akira S, Marshak-Rothstein A, Rifkin IR: Toll-like receptor 9-dependent and -independent dendritic cell activation by chromatin-immunoglobulin G complexes. J Exp Med 2004;199:1631–1640.
Means TK, Latz E, Hayashi F, Murali MR, Golenbock DT, Luster AD: Human lupus autoantibody-DNA complexes activate DCs through cooperation of CD32 and TLR9. J Clin Invest 2005;115:407–417.
Lian ZX, Kikuchi K, Yang GX, Ansari AA, Ikehara S, Gershwin ME: Expansion of bone marrow IFN-alpha-producing dendritic cells in New Zealand Black (NZB) mice: high level expression of TLR9 and secretion of IFN-alpha in NZB bone marrow. J Immunol 2004;173:5283–5289.
Christensen SR, Kashgarian M, Alexopoulon L, Flavell RA, Akira S, Shlomchik MJ: Toll-like receptor 9 controls anti-DNA autoantibody production in murine lupus. J Exp Med 2005;202:321–331.
Vollmer J, Tluk S, Schmitz C, et al: Immune stimulation mediated by autoantigen binding sites within small nuclear RNAs involves Toll-like receptors 7 and 8. J Exp Med 2005;202:1575–1585.
Savarese E, Chae OW, Trowitzsch S, et al: U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein immune complexes induce type I interferon in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Blood 2006;107:3229–3234.
Kelly KM, Zhuang H, Nacionales DC, et al: “Endogenous adjuvant” activity of the RNA components of lupus autoantigens Sm/RNP and Ro 60. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:1557–1567.
Pisitkun P, Deane JA, Difilippantonio MJ, Tarasenko T, Satterthwaite AB, Bolland S: Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science 2006;312:1669–1672.
Berghofer B, Frommer T, Haley G, Fink L, Bein G, Hackstein H: TLR7 ligands induce higher IFN-alpha production in females. J Immunol 2006;177:2088–2096.
Casciola-Rosen LA, Anhalt G, Rosen A: Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med 1994;179:1317–1330.
Kaplan MJ: Apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol 2004;112:210–218.
Sheriff A, Gaipl US, Voll RE, Kalden JR, Herrmann M: Apoptosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2004;30:505–527, viii–ix.
Jin O, Sun LY, Zhou KX, et al: Lymphocyte apoptosis and macrophage function: correlation with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 2005;24:107–110.
Ren Y, Tang J, Mok MY, Chan AW, Wu A, Lau CS: Increased apoptotic neutrophils and macrophages and impaired macrophage phagocytic clearance of apoptotic neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:2888–2897.
Shoshan Y, Shapira I, Toubi E, Frolkis I, Yaron M, Mevotach D: Accelerated Fas-mediated apoptosis of monocytes and maturing macrophages from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: relevance to in vitro impairment of interaction with iC3b-opsonized apoptotic cells. J Immunol 2001;167:5963–5969.
Denny MF, Chandaroy P, Killen PD, et al: Accelerated macrophage apoptosis induces autoantibody formation and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2006;176:2095–2104.
Baumann I, Kolowos W, Voll RE, et al: Impaired uptake of apoptotic cells into tingible body macrophages in germinal centers of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:191–201.
Albert ML, Pearce SF, Francisco LM, et al: Immature dendritic cells phagocytose apoptotic cells via alphavbeta5 and CD36, and cross-present antigens to cytotoxic Tlymphocytes. J Exp Med 1998;188:1359–1368.
Inaba K, Turley S, Yamaide F, et al: Efficient presentation of phagocytosed cellular fragments on the major histocompatibility complex class II products of dendritic cells. J Exp Med 1998;188:2163–2173.
Rovere P, Manfredi AA, Vallinoto C, et al: Dendritic cells preferentially internalize apoptotic cells opsonized by anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies. J Autoimmun 1998;11:403–411.
Frisoni L, McPhie L, Colonna L, et al: Nuclear autoantigen translocation and autoantibody opsonization lead to increased dendritic cell phagocytosis and presentation of nuclear antigens: a novel pathogenic pathway for autoimmunity? J Immunol 2005;175:2692–2701.
Bondanza A, Zimmermann VS, Dell’Antonio G, et al: Requirement of dying cells and environmental adjuvants for the induction of autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:1549–1560.
Tzeng TC, Suen JL, Chiang BL: Dendritic cells pulsed with apoptotic cells activate self-reactive T-cells of lupus mice both in vitro and in vivo. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:1230–1237.
Sauter B, Albert ML, Francisco L, Larsson M, Somersan S, Bhardwaj N: Consequences of cell death: exposure to necrotic tumor cells, but not primary tissue cells or apoptotic cells, induces the maturation of immunostimulatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med 2000;191:423–434.
Stuart LM, Lucas M, Simpson C, Lamb J, Savill J, Lacy-Hulbert A: Inhibitory effects of apoptotic cell ingestion upon endotoxin-driven myeloid dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol 2002;168:1627–1635.
Ma L, Chan KW, Trendell-Smith NJ, et al: Systemic autoimmune disease induced by dendritic cells that have captured necrotic but not apoptotic cells in susceptible mouse strains. Eur J Immunol 2005;35:3364–3375.
Ip WK, Lau YL: Distinct maturation of, but not migration between, human monocyte-derived dendritic cells upon ingestion of apoptotic cells of early or late phases. J Immunol 2004;173:189–196.
Rovere P, Vallinoto C, Bondanza A, et al: Bystander apoptosis triggers dendritic cell maturation and antigen-presenting function. J Immunol 1998;161:4467–4471.
Shodell M, Shah K, Siegal FP: Circulating human plasmacytoid dendritic cells are highly sensitive to corticosteroid administration. Lupus 2003;12:222–230.
Piemonti L, Monti P, Allavena P, et al: Glucocorticoids affect human dendritic cell differentiation and maturation. J Immunol 1999;162:6473–6481.
Mehling A, Grabbe S, Voskort M, Schwarz T, Luger TA, Beissert S: Mycophenolate mofetil impairs the maturation and function of murine dendritic cells. J Immunol 2000;165:2374–2381.
Lund JM, Alexopoulou L, Sato A, et al: Recognition of single-stranded RNA viruses by Toll-like receptor 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:5598–5603.
Bayry J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Delignat S, et al: Intravenous immunoglobulin abrogates dendritic cell differentiation induced by interferon-alpha present in serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:3497–3502.
Botsios C: Safety of tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1 blocking agents in rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev 2005;4:162–170.
Palucka AK, Blanck JP, Bennett L, Pascual V, Banchereau J: Cross-regulation of TNF and IFN-alpha in autoimmune diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005;102:3372–3377.
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Nagata S: Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature 1992;356:314–317.
Nauta AJ, Castellano G, Xu W, et al: Opsonization with C1q and mannose-binding lectin targets apoptotic cells to dendritic cells. J Immunol 2004;173:3044–3050.
Lang TJ: Estrogen as an immunomodulator. Clin Immunol 2004;113:224–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monrad, S., Kaplan, M.J. Dendritic cells and the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol Res 37, 135–145 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685895
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685895