Abstract
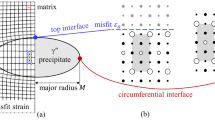
The elastic-plastic accommodation energy generated by the formation of a plate-shaped inclusion in an effectively infinite solid is calculated using two-dimensional (2-D) and three-dimensional (3-D) finite element techniques. A typical example of the occurrence of such an inclusion, modeled in detail in this article, is the formation of a zirconium hydride platelet in a zirconium alloy. To verify the finite element models, initial calculations were based on a linear elastic model of the inclusion and the surrounding matrix material, plus elastic-plastic solutions of an isotropically misfitting spherical inclusion expanding within an elastic/perfectly plastic, infinite solid. Good agreement with the corresponding exact analytical results was found. The finite element analysis was used to determine the accommodation energy of isotropically and anisotropically misfitting oblate spheroids contained in an elastic/perfectly plastic medium. Calculations were carried out for oblate spheroids with aspect ratios (semiminor to semimajor axes) of 0.75, 0.5, 0.25, and 0.1. In contrast to the elastic result, the elastic-plastic accommodation energy values increased with decreasing aspect ratio. This result is due to an increase in the hydrostatic component of the stress in the matrix and a consequent loss in ability to decrease the misfit stresses by plastic deformation. Three-dimensional analyses of cuboidal inclusions expanding into infinite elastic and elastic/plastic solids were also performed. The results depended on mesh density, but reasonable values could be obtained at moderate mesh densities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. R.L. Beck and W.M. Mueller: inMetal Hydrides, W.M. Mueller, J.P.L. Blackledge, and G.G. Libowitz, eds., Academic Press, New York, NY, 1968, p. 312.
L.A. Simpson and M.P. Puls:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 1093–1105.
J.D. Eshelby:Proc. R. Soc. London A, 1957, vol. 241, pp. 376–96.
J.D. Eshelby: inSolid State Physics, F. Seitz and D. Turnbull, eds., Academic Press, New York, NY, 1966, vol. 3, pp. 89–140.
D.M. Barnett, J.K. Lee, H.I. Aaronson, and K.C. Russell:Scripta Metall., 1974, vol. 8, p. 1447.
M. Shibata and K. Ono:Acta Metall., 1978, vol. 26, p. 921.
G.J.C. Carpenter, J.F. Warters, and R.W. Gilbert:J. Nucl. Mater., 1973, vol. 48, p. 267.
G.J.C. Carpenter and J.F. Watters:J. Nucl. Mater., 1978, vol. 73, p. 190.
J.K. Lee, Y.Y. Earmme, H.I. Aaronson, and K.C. Russell:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 1837–47.
M.P. Puls:Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, pp. 1961–81.
M.P. Puls:Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 1259–69.
M.P. Puls:J. Nucl. Mater., 1989, vol. 165, pp. 128–41.
M.P. Puls:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 2905–17.
G.P. Tandon and G.J. Weng:ASME J. Appl. Mech., 1986, vol. 53, p. 511.
R.D. Cook:Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1981.
G.J.C. Carpenter:J. Nucl. Mater., 1973, vol. 48, p. 264.
K.G. Barraclough and C.J. Beevers:J. Mater. Sci., 1969, vol. 4, pp. 518–25.
C.J. Beevers and K.G. Barraclough:J. Mater. Sci., 1969, vol. 4, pp. 802–08.
M.P. Puls and J. Rabier: AECL Research, Whiteshell Laboratories, Pinawa, MB, Canada, unpublished research, 1991.
G. Faivre:Phys. Status Solidi A, 1964, vol. 35, p. 249.
J.K. Lee and W.C. Johnson:Phys. Status Solidi A, 1978, vol. 46, p. 267.
W.C. Johnson, Y.Y. Earmme, and J.K. Lee:ASME J. Appl. Mech., 1980, vol. 47, p. 781.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leitch, B.W., Puls, M.P. Finite element calculations of the accommodation energy of a misfitting precipitate in an elastic-plastic matrix. Metall Trans A 23, 797–806 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02675557
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02675557