Abstract
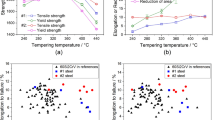
The effects of nitride (Cr2N) precipitation on the tensile, impact, and hardness properties of a typical high-nitrogen, low-carbon austenitic stainless steel (SS), nominally Fe-19Cr-5Mn-5Ni-3Mo-0.024C0.69N, were determined. Annealed and cold-rolled (20 pct reduction in thickness) specimens were isothermally aged at 700 °C and 900 °C for times ranging from 0.1 to 10 hours. Only grain boundary Cr2N precipitation occurred in annealed materials aged at 700 °C. Precipitation at 900 °C occurred sequentially at grain boundaries, by cellular precipitation, and, finally, by transgranular precipitation within the matrix. Nitride precipitation had little effect on yield and ultimate strengths but reduced tensile ductility and impact toughness. Embrittlement occurred due to grain boundary separation (700 °C and 900 °C) and fracture through cellular precipitate regions, initiated at nitrides (900 °C). Prior deformation increased precipitation kinetics and had a controlling influence on nitride morphology, enhancing grain boundary and transgranular Cr2N and retarding cellular precipitation. Nitride structures produced in cold-rolled materials were just as detrimental to material plasticity as those produced in annealed materials, but prior deformation increased the kinetics of embrittlement. Due to strain recovery, the yield and ultimate strengths of cold-rolled materials decreased with aging time and temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Menzel, G. Stein, and P. Dahlmann:High-Nitrogen Steels 1990, G. Stein and H. Witulski, eds., Verlag Stahleisen mbH, Dusseldorf, Germany, 1990, pp. 365–71.
J.C. Rawers, N.A. Gokcen, and R.D. Pehlke:Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 73–82.
M.O. Speidel:High-Nitrogen Steels 1988, J. Foct and A., eds., Institute of Metals, London, 1989, pp. 92–96.
E. Werner:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1988, vol. 101, pp. 93–98.
PJ. Uggowitzer and M. Harzenmoser:High-Nitrogen Steels 1988, J. Foct and A. Hendry, eds., Institute of Metals, London, 1989, pp. 174–79.
R.P. Reed:JOM, 1989, Mar., pp. 16-21.
M.O. Speidel and R.M. Pedrazzoli:Mater. Performance, 1992, vol. 31 (9), pp. 59–61.
P. Gumpel and T. Ladwein:High-Nitrogen Steels 1988, J. Foct and A. Hendry, eds., Institute of Metals, London, 1989, pp. 151–58.
R.E. Stoltz and J.B. Vander Sande:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 1033–37.
M. Grujicic, J.-O. Nilsson, W.S. Owen, and T. Thorvaldsson:High- Nitrogen Steels 1988, J. Foct and A. Hendry, eds., The Institute of Metals, London, 1989, pp. 151–58.
J. Sassen, A.J. Garratt-Reed, and W.S. Owen:High-Nitrogen Steels 1988, J. Foct and A. Hendry, eds., Institute of Metals, London, 1989, pp. 159–62.
M.L.G. Byrnes, M. Grujicic, and W.S. Owen:Acta Metall, 1987, vol. 35 (7), pp. 1853–62.
M. Kikuchi, M. Kajihara, and K. Frisk:High-Nitrogen Steels 1988, J. Foct and A. Hendry, eds., Institute of Metals, London, 1989, pp. 63–74.
M. Kikuchi, M. Kajihara, and S.K. Choi:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1991, vol. A146, pp. 131–50.
J.W. Simmons: Ph.D. Dissertation, Oregon Graduate Institute of Science and Technology, Beaverton, OR, 1993.
R. Presser and J.M. Silcock:Met. Sci., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 241–47.
H. Chandra Holm, P.J. Uggowitzer, and M.O. Speidel:Scripta Metall, 1987, vol. 21, pp. 513–18.
J.W. Simmons and D.G. Atteridge:Microstructural Science, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1993, vol. 20, pp. 311- 25.
D.B. Rayaprolu and A. Hendry:Mater. Sci. Technol, 1988, vol. 4, pp. 136–45.
ASTM Book of Standards, E23-88, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1989, vol. 3.01, p. 198.
G.V. Samsonov:Press Handbooks of High-Temperature Materials, No. 2, Properties Index, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1964, p. 185.
J.W. Simmons:Scripta Metall, 1995, vol. 32 (2), pp. 265–70.
A.R. Rosenfield, G.T. Hahn, and J.D. Embury:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 2797–2804.
L.E. Miller and G.C. Smith:J. Iron Steel Inst, 1970, vol. 208, p. 998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simmons, J.W. Mechanical properties of isothermally aged high-nitrogen stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 2579–2595 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669416
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669416