Abstract
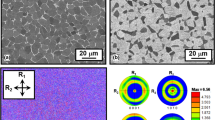
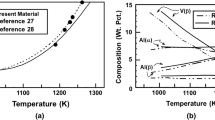
The effect of cooling conditions, giving estimated cooling rates in the range 104 °C per second to 107 °C per second, on the microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V has been evaluated. The microstructures of as-solidified particulates were martensitic, with the martensite lath length decreasing with beta grain size,L, which in turn decreased with increasing cooling rate. For material alpha + beta heat-treated or vacuum hot pressed, the alpha morphology was dependent on the prior cooling rate. For materials cooled at <5 × 105 °C per second martensite transformed to lenticular alpha, while material cooled at >5 × 105 °C per second developed an equiaxed alpha morphology. This change in morphology was explained in terms of high dislocation density or grain size refinement, both of which result from the high cooling rate. When the beta grain size (L) was plottedvs section thickness (z), and estimated cooling rate (T), power law relationships analogous to those reported for secondary dendrite arm spacing were found:L = 1.3 ± 0.4z089±006 (thin, chill-substrate quenched),L = 0.17 ± 0.05z0.86±0.01(thick, convection-cooled material), andL = 3.1 × 106 T−0.93±0.12 (all material), whereL and z are in μm andT is in K/s. The last relationship is in agreement with the 0.9 exponent predicted using a model developed for the effect of grain size on cooling rate assuming classical homogeneous nucleation and isotropic linear growth during solidification. The first two relationships were rationalized by assuming that the two materials cooled under near-Newtonian conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Duwez, R. H. Willens, and W. Klement:J. Appl. Phys., 1960, vol. 31, pp. 1136, 1137, and 1500.
H. Jones:Rapid Solidification of Metals and Alloys, Monograph No. 8, The Institution of Metallurgists, London, 1982.
R. Mehrabian:Int. Met. Rev., 1982, vol. 27, no. 4, p. 185.
Rapid Solidification Processing: Principles and Technologies II, R. Mehrabian, ed., Claitor’s Publishing Division, Baton Rouge, LA, 1980.
F. H. Froes and J. R. Pickens:JOM, 1984, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 14–28.
F. H. Froes, D. Eylon, G. E. Eichelman, and H. M. Burte:JOM, 1980, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 47–54.
E. J. Dulis, V. K. Chandhok, F. H. Froes, and L. P. Clark: Proceed- ings 10th National SAMPE Technical Conference, 1978, pp. 316-29.
D. Eylon, F. H. Froes, and L. D. Parsons: Proceedings of the AIAA83, 24th Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Lake Tahoe, NV, May 1983, pp. 586-93.
L. D. Parsons, J. Bruce, J. Lane, and F. H. Froes:Metal Progress, September 1984, vol. 126, no. 4, pp. 83–94.
F. H. Froes, D. Eylon, and G. Friedman:Metals Handbook, 9th ed., vol. 7, Powder Metallurgy, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1984, pp. 748–55.
S. M. L. Sastry, T. C. Peng, P. J. Meschter, and J. E. O’Neal:JOM, 1983, vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 21–28.
S.M. L. Sastry, P.J. Meschter, and J. E.O’Neal: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1451–63.
S. M. L. Sastry, T. C. Peng, and L. P. Beckerman:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1465–74.
A. G. Jackson, T. F. Broderick, F. H. Froes, and J. Moteff:Third International Conference on Rapid Solidification Processing, held at National Bureau of Standards, Gaithersburg, MD, December 1982, R. Mehrabian, ed., p. 585.
A. G. Jackson: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 1983.
S. Krishnamurthy, R. G. Vogt, D. Eylon, and F. H. Froes:Progress in Powder Metallurgy 1983, H. S. Nayar, S.M. Kaufman, and K. E. Meiners, eds., MPIF, Princeton, NJ, 1984, vol. 39, pp. 603–23.
S. Krishnamurthy, R.G. Vogt, D. Eylon, and F.H. Froes:Rapidly Solidified Metastable Materials, B. H. Kear and B. C. Giessen, eds., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc., New York, NY, 1984, vol. 28, pp. 361–66.
D. G. Konitzer, R. Kirchheim, and H. L. Fraser:Rapidly Solidified Metastable Materials, B.H. Kear and B.C. Giessen, eds., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc., New York, NY, 1984, vol. 28, pp. 381–85.
M. C. Flemings:Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1974, p. 148.
H. Jones:Rapid Solidification Processing: Principles and Tech- nologies, R. Mehrabian, B.H. Kear, and M. Cohen, eds., Claitor’s Publishing Division, Baton Rouge, LA, 1978, p. 28.
L. Katgerman:Scripta Met., 1980, vol. 14, p. 861.
J. I. Nurminen and H. D. Brody:Titanium Science and Technology, R. I. Jaffee and H. M. Burte, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, vol. 3, pp. 1893–914.
T. F. Broderick, F. H. Froes, and A. G. Jackson:Rapidly Solidified Metastable Materials, B. H. Kear and B. C. Giessen, eds., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc., New York, NY, 1984, vol. 28, pp. 345–51.
P. G. Boswell and G. A. Chadwick:Scripta Met., 1977, vol. 11, pp. 459–65.
A. F. Belov and I. S. Polkin: German Metallurgical Society Workshop, University of Nuremberg, Erlangen, July 12, 1982.
E. J. Kosinski:Progress in Powder Metallurgy 1982, James G. Bewley and Sherwood W. McGee, eds., MPIF, Princeton, NJ, 1982, vol. 38, pp. 491–502.
R. E. Maringer, C. E. Mobley, and E. W. Collings:AIChE J., 1978, vol. 74, no. 180, pp. 111–16.
S. M. L. Sastry, T. C. Peng, P. J. Meschter, and J. E. O’Neal: “Dispersion-Strengthened Powder-Metallurgy Titanium Alloys,” Air Force Wright Aeronautical Laboratories Technical Report No. AFWAL-TR-83-4092, Wright-Patterson AFB, OH, December 1982.
S. J. Savage and F. H. Froes:JOM, 1984, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 20–33.
C. F. Yolton, F. H. Froes, and R. F. Malone:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 132–34.
H. I. Aaronson: Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, private communication, 1983.
J. P. Hirth: The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, private com- munication, 1983.
D. Eylon and F. H. Froes:Titanium Alloys in Surgical Implants, H. A. Luckey and F. Kubli, Jr., eds., ASTM Publications, Philadelphia, PA, 1983, pp. 43–58.
F. H. Froes, D. Eylon, G. Wirth, K-J. Grundhoff, and W. Smarsly:Progress in Powder Metallurgy 1982, James G. Bewley and Sherwood W. McGee, eds., MPIF, Princeton, NJ, 1982, vol. 38, pp. 503–20.
I. Weiss, G. E. Welsch, F. H. Froes, and D. Eylon: “Mechanism of Microstructural Refinement in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy”, presented at the Fifth International Conference on Titanium, Munich, West Germany, 10–14 September 1984 and to be published by the German Metal- lurgical Society, 1985.
P. Roberts: Nuclear Metals, Inc., Concord, MA, private commu- nication, 1984.
Y. S. Touloukian and C. Y. Ho:Thermophysical Properties of Matter, IFI Plenum, New York, NY, 1970.
American Institute of Physics Handbook, 3rd ed., D.E. Gray, ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1972.
T. W. Clyne and A. Garcia:J. Mater. Sci., 1981, vol. 16, pp. 1643–53.
B. Cantor:Rapidly Solidified Amorphous and Crystalline Alloys, B.H. Kear, B. C. Giessen, and M. Cohen, eds., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc., New York, NY, 1982, pp. 317–30.
Rapid Solidification Processing: Principles and Technologies, R. Mehrabian, ed., Claitor’s Publishing Division, Baton Rouge, LA, 1978, pp. 9–27.
H. A. Davies:Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Rapidly Quenched Metals, S. Steeb and H. Warlimont, eds., Elsevier, North Holland, New York, NY, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broderick, T.F., Jackson, A.G., Jones, H. et al. The effect of cooling conditions on the microstructure of rapidly solidified Ti-6Al-4V. Metall Trans A 16, 1951–1959 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02662396
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02662396