Abstract
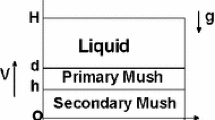
The analysis is applicable to alloy solidification which proceeds horizontally to the center of a mold. The model follows the growth of the solid-liquid zone adjacent to the chill face (the initial transient), the movement of the zone across the mold, and the region of final solidification adjacent to the centerline (the final transient). During solidification the density of the liquid varies across the twophase zone. Consequently, there is natural convection which is treated as flow through a porous medium. The equations for convection are coupled with the equation of solute redistribution between the phases in order to calculate macrosegregation after solidification is complete. Results were computed for alloys which show: (1) “inverse segregation≓ at a cooled-surface; (2) macrosegregation resulting from solidification with the initial transient, a period with a complete two-phase zone, and a final transient; and (3) macrosegregation when the width of the two-phase zone exceeds the semi-width of the mold.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
coefficient in the pressure equation, Eq. [5]
- A x,Ay :
-
components of A
- α E :
-
constant to describe temperature field, Eq. [6b]
- B :
-
parameter in the pressure equation, Eq. [5]
- B :
-
parameter in the pressure equation in the form of Eq. [18]
- b E, bE :
-
constants to describe temperature field, Eqs. [6a, b]
- C E :
-
eutectic composition
- C L :
-
composition of the interdendritic liquid vC0 composition of the bulk liquid
- C p :
-
heat capacity
- C s :
-
local average composition of the solid after solidification, Eq. [13] or [14]
- C*/s :
-
composition of the solid at the solid-liquid interface
- g :
-
gravitational constant
- g:
-
acceleration due to gravity
- g E :
-
volume fraction of eutectic liquid
- g L :
-
local volume fraction of liquid
- g s :
-
local volume fraction of solid
- H :
-
enthalpy
- K :
-
permeability
- k :
-
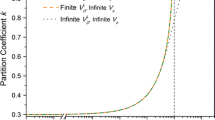
equilibrium partition ratio,Cf/CL
- L :
-
height of the ingot
- n :
-
unit vector
- p :
-
pressure
- p :
-
modified pressure, Eq. [17]
- p 0 :
-
ambient pressure
- q :
-
constant to describe temperature field, Eqs. [6a, b]
- T :
-
temperature
- T E :
-
eutectic temperature
- T L :
-
liquidus temperature
- t :
-
time
- t E, ti :
-
time at the passage of eutectic isotherm and liquidus isotherm, respectively
- U E :
-
velocity of the eutectic isotherm
- V :
-
velocity of the interdendritic liquid
- V x, Vy :
-
components of V
- W :
-
width of the solid-liquid zone
- x :
-
distance from the chill-surface
- xc :
-
semiwidth of the ingot
- x E,xL :
-
positions of the eutectic isotherm and liquidus isotherm, respectively
- x p :
-
distance to the liquid/porosity surface
- x′ x :
-
distance to the location of the final solidification of the entire ingot
- y :
-
distance from the bottom of the ingot
- γ :
-
permeability coefficient, Eq. [3]
- η:
-
vertical coordinate in the computational domain
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- Ώ :
-
viscosity
- ξ:
-
horizontal coordinate in the computational domain
- ρ:
-
density
- ρL,ρS :
-
density of the interdendritic liquid and primary solid, respectively
- ρLE, ρSE :
-
density of the eutectic liquid and the eutectic solid, respectively
- ρ LO :
-
density of the liquid at the liquidus isotherm
- Τ:
-
time in the computational domain
References
A. L. Maples and D. R. Poirier: Report No. 80HV007, vol. I, General Electric Company, Huntsville, AL, 1980.
A. L. Maples and D. R. Poirier: Report No. 80HV007, General Electric Company, Huntsville, AL, 1980, vol. II.
A. L. Maples and D. R. Poirier: Report No. 80HV007, General Electric Company, Huntsville, AL, 1980, vol. III.
A. L. Maples and D. R. Poirier: Report No. 81HV001, vol. I, General Electric Company, Huntsville, AL, 1981.
A. L. Maples and D. R. Poirier: Report No. 81HV001, General Electric Company, Huntsville, AL, 1981., vol. II.
R. Mehrabian, M. Keane, and M. C. Flemings:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1209–20.
T. Fujii, D.R. Poirier, and M.C. Flemings:Metall. Trans. B, 1979, vol. 10B, pp. 331–39.
M. C. Flemings and G. E. Nereo:Trans. TMS-A1ME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 1449–61.
M.C. Flemings: Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1974, pp. 134-76.
S. Kou, D.R. Poirier, and M.C. Flemings:Electric Furnace Proceedings, Iron and Steel Society of AIME, New York, NY, 1977, vol. 35, pp. 221–28.
S. Kou, D. R. Poirier, and M. C. Flemings:Metall. Trans. B, 1978, vol. 9B, pp. 711–19.
S.D. Ridder, F. C. Reyes, S. Chakravorty, R. Mehrabian, J.D. Nauman, J. H. Chen, and H. J. Klein:Metall. Trans. B, 1978, vol. 9B, pp. 415–25.
S.D. Ridder, S. Kou, and R. Mehrabian,Metall. Trans. B, 1981, vol. 12B, pp. 435–47.
C. L. Jeanfils, J. H. Chen, and H. J. Klein:Modeling of Casting and Welding Processes, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 313–32.
D. N. Petrakis, M. C. Flemings, and D. R. Poirier:Modeling of Casting and Welding Processes, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 285-312.
J.F. Thompson, FC. Thames, and C.W. Mastin:J. Comp. Phys., 1974, vol. 15, p. 299.
B. A. Carre:Computer J., 1961, vol. 4, p. 73.
E. Isaacson and H. B. Keller:Analysis of Numerical Methods, John Wiley, New York, NY, 1966, p. 468.
R. Mehrabian, M. Keane, and M. C. Flemings:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 3238–41.
D.R. Poirier, M.C. Flemings, R. Mehrabian, and H.J. Klein:Advances in Metal Processing, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 277–318.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maples, A.L., Poirier, D.R. Convection in the two-phase zone of solidifying alloys. Metall Trans B 15, 163–172 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02661075
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02661075