Abstract
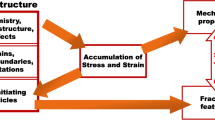
Two microscopic ductile fracture processes have been established in a fracture tough superalloy, Inconel 718, aged to five strength levels. At yield strengths less than 800 MPa, the mechanism is a slow tearing process within large pockets of inhomogeneous carbides and nitrides, giving rise to plane strain fracture toughness (K IC)values greater than 120 MPa-m1/2. At yield strengths greater than 900 MPa, the mechanism involves fracture initiation at carbides and nitrides followed by off crack plane void sheet growth nucleated at the Laves (σ) phases. Here, the fracture toughness drops to about 80 MPa-m1/2. A Mode I normal strain growth model for low yield strength conditions and a shear strain void sheet model for high yield strength ones are shown to model KIC data obtained from a J-integral evaluation of compact tension results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. R. Rice and M. A.Johnson:Inelastic Behavior of Solids, Institute of Materials Science Colloquia, pp. 641-72, 1969.
F. A. McClintock:Ductility, American Soc. for Metals, pp. 255-77, 1967.
F. A. McClintock, S. M. Kaplan, and C. A. Berg:Int. J. FractureMech., 1966, vol. 2, pp. 614–27.
J. R. Rice and D. M. Tracy:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1969, vol. 17, pp. 201–17.
F. A. McClintock:Int. J. Fracture Mech., 1968, vol. 4, pp. 107–29.
F. A. McClintock:Physics of Strength and Plasticity, pp. 307-26, M.I.T. press, 1969.
H. C. Rogers:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1960, vol. 218, pp. 363–71.
T. B. Cox and J. R. Low, Jr.:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1457–70.
D. F. Paulonis, J. M. Oblak, and D. S. Duvall:Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp. 611–22.
J. M. Oblak, D. F. Paulonis, and D. S. Duvall:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 143.
H.J.Wagner and A. M. Hall: DMIC Report 217, 1965.
P. S. Kotval:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, p. 1764.
I. Kirman and D. H. Warrington:Met. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, p. 2667.
R. F. Decker and J. R. Mikalisin:Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, p. 487.
C. P. Sullivan and M. J. Donochi, Jr.:Metals Eng. Quar., 1971, vol. 11, p. 1.
C. P. Sims and W. C. Hagel:The Superalloys, pp. 113-43, John Wiley & Sons, 1972.
J. D. Landis and J. A. Begley: ASTM STP 560, pp. 170-86, 1974.
F. A. McClintock:J. Appl. Mech., 1968, vol. 35, pp. 363–71.
A. J. Wang:Quar. Appl. Math., 1953,vol. 11,p.427.
D. M. Tracy: Ph.D. Thesis, Brown University, 1973.
J.W. Hutchinson:.J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1968, vol. 16, pp. 13–31.
J. W. Hutchinson:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1968, vol. 16 pp. 337–47.
P. D. Hilton and J. W. Hutchinson:Eng. Fract. Meeh., 1971, vol. 3, pp. 435–51.
J. R. Rice, P. C.Paris, and J. G. Merkle: ASTM STP 536, pp. 231-45, 1973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stout, M.G., Gerberich, W.W. Structure/property/continuum synthesis of ductile fracture in inconel alloy 718. Metall Trans A 9, 649–658 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02659922
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02659922