Abstract
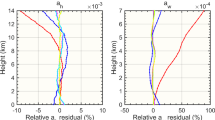
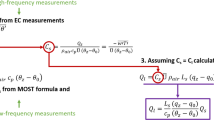
Based on unstability of inversion algorithms of the lidar equation caused by molecular scattering, a new algorithm to derive both the aerosol extinction to backscatter ratio and the extinction coefficient profile is proposed in this paper. As shown in numerical experiments, in case of a ground-based lidar, the error in the aerosol optical depth solution can be less than 10%, and the error of < 6.7 in the aerosol extinction to backscatter ratio can be obtained if the error in the lidar constant is < 6%; and in the case of a spaceborne lidar, the present method can be used to de-termine the lidar constant at a short wavelength with an accuracy of being better than 1%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elterman, L. (1964), Parameters for attenuation in the atmospheric windows for fifteen wavelengths,Appl. Opt.,3: 745–749.
Fernald, F. G. (1984), Analysis of Atmospheric Lidar Observations: Some Comments,Appl Opt. 23: 652–653.
Kaestner, M. (1986), Lidar inversion with variable backscatter/ extinction ratios,Appl. Opt.,25: 833–835.
Klett, J. D. (1981), Stable analytical inversion solution for processing lidar returns,Appl. Opt.,20: 211–220.
McClatchey, R. A., et al. (1972), Optical properties of the Atmosphere, AFCRL-72-0497,108p.
McCormick M. P., et al. (1993), Scientific Investigations Planned for the Lidar In-space Technology Experiment (LITE),Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,74: 205–214.
Qiu Jinhuan (1988), Sensitivity of Lidar Equation Solution to Boundary Values and Determination of the Values,Adv. Atmos. Sci.,5: 229–230.
Qiu Jinhuan and Lu Daren (1991), On lidar application for remote sensing of the atmosphere,Adv. Atmos. Sci.,8: 369–378.
Qiu Jinhuan and Lu Daren (1993), A Study of Inversion Algorithm for Determining Atmospheric Aerosol Profile from Simulated Spaceborne Lidar Signals, In:Frontiers in Atmospheric Sciences, Allerton Press, INC. / New York, 322–338.
Sasano Y. and H. Nakane (1984), Significance of the Extinction / backscatter Ratio and the Boundary Value Term in the Solution for the Two-component Lidar Equation,Appl. Opt.,23: 11–13.
Spinhirne,J.D., J. A. Reagan and B. M. Herman (1980), Vertical Distribution of Aerosol Extinction Cross Section and Inference of Aerosol Imaginary Index in the Troposphere by Lidar Technique,J. Appl. Meteor.,19: 426–427.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jinhuan, Q. Two-wavelength lidar measurement of Cloud-aerosol optical properties. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 12, 177–186 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656830
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656830