Abstract
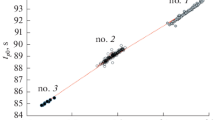
Eleven PASSCAL broadband digital seismic stations were employed in the Tibetan Plateau by the Sino-US team from September, 1991 to June, 1992. Seven of them were distributed along the Qinghai-Tibet highway, others in Maqin and Yushu of Qinghai Province, Linzhi and Xigatze of Tibet. The data included 31 local earthquakes recorded by these stations from July, 1991 to January, 1992. Considering the characters of digital data, we identified the seismic phases carefully in several methods using SAC softwares (Seismic Analysis Code) in SUN workstation. We compared the seismic phases after converting the seismograms of the single stations to the seismic profiles; analyzed the first arrivals of P waves in the incident planes by rotating 3 component seismic records; identified the seismic phases from the particle motion pictures. The Pn apparent velocities were calculated in the distance range of 230–1200 km from Linzhi earthquakes, western Changtang earthquakes, Xitieshan and Gonghe earthquakes and the earthquakes in India. The results show that the Pn velocities change slightly in the Tibetan Plateau (8.0–8.1 km/s). These values near the velocities at the uppermost mantle of the normal continents. The Moho undulation in the Tibetan Plateau was also studied by using Pn data by the time-term method. The primary results indicate that the Moho beneath the Tibetan Plateau is flat, and its depths are 67–70 km.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barazangi, M., and J. Ni, 1982. Velocities and propagation characteristics of Pn and Sn beneath the Himalayan arc and Tibetan Plateau: Possible evidence for underthrusting of Indian continental lithosphere beneath Tibet.Geology,10, 179–185.
Beghoul, N., and M. Barazangi, 1989. Contrasting upper mantle velocity structure beneath the basin and range province and Tibetan Plateau,EOS.70, 402.
Chen, G. Y., Zhen, R. S., An, C. Q., Su, X. L. and Wu, F. T., 1992. The lateral variation studies of the deep structures for the Tibetan Plateau using phase velocities of Rayleigh waves.Acta Seismologica Sinica,14, Supplement I 565–572. (in Chinese).
Chen, W. P., and P. Molnar, 1981. Constrains on the seismic wave velocity structure beneath the Tibetan Plateau and their implications,J. Geophys. Res.,85, 5937–5962.
Hirn, A., Lepine, J., Jobert, G., Sapin, M., Wittlinger, G., Xu, Z. X., Gao, E. Y., Wang, X. J., Teng, J. W., Xiong, S. B., Pandey, M. R. and Tater, J. M., 1984 Crustal structure and variability of the Himalayan border of Tibet.Nature,307, 23–25.
Hirn, A., 1988. Features of the curst-mantle structured of Himalayas-Tibet: a comparison with seismic traverses of Alpine, Pyrenean and Vanscan belts.Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., A326, 17–32.
Holt, W. E., and T. C. Wallace, 1990. Crustal thickness and upper mantle velocities in the Tibetan Plateau region from the inversion of regional Pnl waveforms: Evidence for a thick upper mantle lid beneath southern Tibet.J. Geophys. Res.,95, B8, 12499–12525.
Jia, S. J., Chao, X. F., and Yan, J. Q., 1981. The P wave travel times and upper mantle structure of the Tibetan Plateau.North western Seismological Journal,3, 3, 27–34 (in Chinese).
Lu, D. Y., Wang, X. J., 1990. The crustal structure and deep internal processes in the Tuotuohe-Golmud area of the north Qinghai-Xizang Plateau.Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,21, 227–237 (in Chinese).
Molnar, P., 1988. A review of geophysical constrains on the deep structure of the Tibetan Plateau, the Himalaya and the Karakoram, and their tectonic implications.Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., A326, 33–88.
Ni, J. and M. Barazangi, 1983. High frequency seismic wave propagation beneath the Indian shield, Himalayan arc, Tibetan Plateau and surrounding regions: high uppermost mantle velocities and efficient Sn propagation beneath Tibet.Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc.,72, 665–689.
Xiong, S., Teng, J. and Yin, Z., 1985. The crustal thicknesses and the undulation of the Moho in the Tibetan Plateau.Acta Geophysica Sinica,28, Supplement I, 16–27 (in Chinese).
Zhao, L. and D. V. Helmberger., 1991. Geophysical implications from relocations of Tibetan earthquakes; hot lithosphere.Geophys. Res. Letters,18, 12, 2205–2208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The Chinese version of this paper appeared in the Chinese edition ofActa Seismologica Sinica,14, Supp., 593–600, 1992.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, ZF., Zeng, RS. & Wu, F.T. The Pn wave velocities and the relief of Moho in the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Seismologica Sinica 6, 317–325 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650944
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650944