Abstract
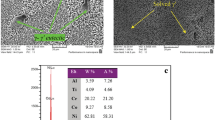
The superplastic formability of SP- lnconel 718 superalloy was evaluated using the argon blowing method. Relationships among superplastic forming parameters (forming temperature, argon pressure, and forming time) and specific dome height (dome height/workpiece diameter) were investigated, as were changes in material properties after superplastic forming. Experimental results showed the optimum forming temperature range for SP- lnconel 718 to be between 975 and 995 °C. During the superplastic forming process, 5- phase precipitates formed at grain boundaries and limited the grain growth, which is considered beneficial for superplastic deformation. On the other hand, increasing the forming deformation also increased the formation of cavities, which can be attributed to the existence of niobium- rich inclusions. This degraded the superplasticity of the superalloy. Electrochemical tests showed that the corrosion resistance of SP- lnconel 718 after superplastic forming worsened because of the existence of both S- phase precipitates and niobium- rich inclusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.H. Hamilton and G.W. Stacher, Superplastic Forming of Ti- 6A1-4V Beam Frames,Met. Prog., Vol 109 (No. 3), 1976, p 34
Y. Torisaka, Superplasticity and Internal Friction of Nickel-Base Superalloy,Acta Metall., Vol 39, 1991, p 937
M.W. Mahoney and R. Crooks, Superplastic Forming of Inconel 718,Superplasticity in Aerospace, U.C. Heikkenen and T.R. McNelley, Ed., TMS, 1988, p 331
A.R. Ragab, Thermoforming of Superplastic Sheet in Shaped Dies,Met. Technol., Vol 10, 1983, p 340
R. Cozar and A. Pineau, Morphology of γ’ and γ’’ Precipitates and Thermal Stability of Inconel 718 Type Alloys,Metall. Trans., Vol 4, 1973, p 47
M. Chang, A.K. Koul, P. Au, and T. Terada, Damage Tolerance of Wrought Alloy 718 Ni-Fe-Base Superalloy,J. Mater. Eng. Perform., Vol 3, 1994, p 356
J. Prybylowski and R. Ballinger, Influence of Microstructure on the Environmentally Assisted Cracking of Inconel 718,Corrosion, Vol 43, 1987, p 111
N. Srinivasan and Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Microstructural Control in Hot Working of IN-718 Superalloy Using Processing Map,Metall. Trans., Vol 25, 1994, p 2275
T. Sakai and J.J. Jonas, Dynamic Recrystallization: Mechanical and Microstructural Considerations,Acta Metall., Vol 32, 1984, p 189
J. Pilling and N. Ridley, Cavitation and Fracture,Superplasticity in Crystalline Solids, Institute of Metals, London, 1989, p 102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, M., Tsau, C. & Chuang, T. Evaluation of the superplastic formability of SP-inconel 718 superalloy. JMEP 5, 71–77 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647272
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647272