Abstract
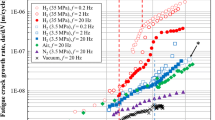
Fracture mode transition in hydrogen-assisted cracking (HAC) of AISI 4340 steel has been studied from an equilibrium aspect at room temperature with 8.6-mm-thick double cantilever beam (DCB) specimens. The threshold stress intensity,K th , necessary for the occurrence of HAC and the corresponding fracture surface morphology have been determined as a function of hydrogen pressure and yield strength. The K th increases with decrease in hydrogen pressure at a given yield strength and also with decrease in yield strength at a given hydrogen pressure. AsK th increases, the corresponding HAC fracture mode changes from the intergranular (IG) and quasi-cleavage (QC) modes to the microvoid coalescence (MVC) mode. The experimental results indicate that the critical hydrogen concentration for crack extension in the IG mode is higher than that for crack extension in the MVC mode. The fracture mode transition with varying hydrogen pressure and yield strength is discussed by simultaneously considering the micromechanisms for HAC and the hydrogen pressure and yield strength dependencies ofK th .
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Takeda and C.J. McMahon, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1255–66.
Y. H. Kim and J. W. Moms, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1883–88.
M. Gao, M. Lu, and R. P. Wei:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 735–46.
C.D. Beachem:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 437–51.
W. W. Gerberich, Y. T. Chen, and C. St. John:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 1485–98.
S. K. Banerji, C.J. McMahon, Jr., and H. C. Feng:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 237–47.
W. W. Gerberich and Y. T. Chen:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 271–78.
R. Thomson:J. Mater. Sci., 1978, vol. 13, pp. 128–42.
S. V. Nair and J. K. Tien:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 2333–40.
J. Kameda:Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 867–82.
R. O. Ritchie, W. L. Server, and R. A. Wullaert:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 1557–70.
J. -K. Choi and S.-I. Pyun:J. Mater. Sci., 1990, vol. 25, pp. 246–52.
R. B. Heady:Corrosion, 1977, vol. 33 (3), pp. 98–107.
A. R. Troiano:Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 52, pp. 54–80.
R. A. Oriani and P. H. Josephic:Acta Metall., 1974, vol. 22, pp. 1065–74.
Y. Kikuta and T. Araki: inHydrogen Effects in Metals, I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., TMS-AIME, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 309–18.
K. N. Akhurst and T.J. Baker:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1059–70.
J. R. Rice and M. A. Johnson: inInelastic Behavior of Solids, M. F. Kanninen, W. G. Adler, A. R. Rosenfield, and R. I. Jaffee, eds., McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1970, pp. 641–72.
J. R. Rice:Corrosion, 1976, vol. 32 (1), pp. 22–26.
D. M. Tracey:J. Eng. Mater. Technol., Trans. ASME, Ser. H, 1976, vol. 98, pp. 146–51.
W. W. Gerberich, T. Livne, X. -F. Chen, and M. Kaczorowski:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 1319–34.
J. P. Hirth:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 861–90.
T. B. Cox and J. R. Low, Jr.:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1457–70.
A. S. Argon and J. Im:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 839–51.
A. S. Argon, J. Im, and A. Needleman:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 815–24.
A. C. MacKenzie, J. W. Hancock, and D. K. Brown:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1977, vol. 9, pp. 167–88.
H. K. Birnbaum: inAtomistics of Fracture, R. M. Latanision and J. R. Pickens, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1983, pp. 733–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pyun, SI., Lee, HK. Effect of threshold stress intensity on fracture mode transitions for hydrogen-assisted cracking in AISI 4340 steel. Metall Trans A 21, 2577–2583 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647003
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647003