Abstract
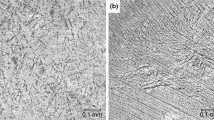
The microstructure and relative amounts of fcc and bcc phases have been studied for rapidly solidified Type 304 stainless steel powders produced by vacuum gas atomization (VGA) and centrifugal atomization (CA). The VGA powder solidifies with a cellular microstructure while the CA powder has a dendritic microstructure. The volume fraction of fcc phase in the CA powder is found to increase from 40 Pct to 97 Pct with increasing particle size from 30 to 125 µm. In the VGA powder, the volume fraction of fcc phase is found to decrease from about 90 Pct to 77 Pct over the same range of particle sizes. The origins of the fcc and bcc phases in each powder are considered. It is concluded that bcc is present as both a primary crystallization phase in the smaller CA particles (<75 µm) and as compositionally stabilized eutectic ferrite at the cell walls of particles of both CA and VGA powders in which fcc was the primary crystallization phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kou and Y. Le:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1141–52.
T. F. Kelly, M. Cohen, and J. B. Vander Sande:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 819–33.
J. M. Vitek, A. Dasgupta, and S. A. David:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1833–41.
L.V. Azaroff:Elements of X-ray Crystallography, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1968, pp. 517–18.
R. J. Patterson:Rapidly Solidified Amorphous and Crystalline Alloys, B.H. Kear, B.C. Giessen, and M. Cohen, eds., Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc., 1982.
S. David:Welding J., April 1981, vol. 60, pp. 63s-71s.
J. A. Brooks: Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 1981.
N.J. Grant:J. Metal., 1983, vol. 35, pp. 20–27.
R. Mehrabian:International Metallurgical Reviews, 1982, vol. 27, pp. 184–208.
H. Fredriksson:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 2989–97.
I. Masumoto, K. Tamaki, and M. Kutsuna:J. Japan Welding Soc, 1972, vol. 41, pp. 1306–14.
T. Tsuk, M. Hubert, and C. Messager:Revue de Metallurgie, 1971, vol. 68, pp. 829–37.
J. H. Perepezko:Proceedings of the MRS Symposium on Alloy Phase Diagrams, L.H. Bennett, T.B. Massalski, and B.C. Giessen, eds., North Holland, New York, NY, 1983.
R.E. Cech:J. Metal., 1956, vol. 8, pp. 585–89.
M.J. Cieslak, A.M. Ritter, and W. F. Savage:Welding J., Jan. 1982, pp. ls-8s.
J. A. Brooks, J. C. Williams, and A.W. Thompson:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 23–31.
J.A. Brooks, J. C. Williams, and A.W. Thompson:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1271–81.
C. E. Lyman, P. E. Mennings, D. J. Duquette, and E. Hall:Scanning Electron Microscopy, 1978, vol. 1, pp. 213–20.
T. F. Kelly and J.B. Vander Sande:Chemistry and Physics of Rapidly Solidified Materials, B. J. Berkowitz and R.O. Scattergood, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1982, pp. 35–47.
D. B. Moharil, I. Jin, and G. R. Purdy:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 59–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, R.N., Flinn, J.E., Korth, G.E. et al. The microstructure and phase relationships in rapidly solidified type 304 stainless steel powders. Metall Trans A 19, 2399–2405 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645467
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645467