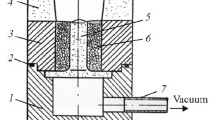
Abstract
A new process for the preparation and casting of metal-particulate non-metal composites is described. Particulate composites of ceramic oxides and carbides and an Al-5 pet Si-2 pct Fe matrix were successfully prepared. From 10 to 30 wt pct of A12O3, SiC, and up to 21 wt pct glass particles, ranging in size from 14 to 340 ώ were uniformly distributed in the liquid matrix of a 0.4 to 0.45 fraction solid slurry of the alloy. Initially, the non-wetted ceramic particles are mechanically entrapped, dispersed and prevented from settling, floating, or agglomerating by the fact that the alloy is already partially solid. With increasing mixing times, after addition, interaction between the ceramic particles and the liquid matrix promotes bonding. Efforts to mix the non-wetted particles into the liquid alloy above its liquidus temperature were unsuccessful. The composite can then be cast either when the metal alloy is partially solid or after reheating to above the liquidus temperature of the alloy. End-chilled plates and cylindrical slugs of the composites were sand cast from above the liquidus temperature of the alloy. The cylindrical slugs were again reheated and used as starting material for die casting. Some of the reheated composites possessed “thixotropy.” Distribution of the ceramic particles in the alloy matrix was uniform in all the castings except for some settling of the coarse, 340ώ in size, particles in the end-chilled cast plates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. B. Spencer, R. Mehrabian, and M. Flemings:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 1925.
R. Mehrabian and M. Flemings:Trans. AFS, 1972, vol. 80, p. 173.
E. F. Fascetta, R. G. Riek, R. Mehrabian, and M. Flemings:Trans. AFS, 1973, vol. 81, p. 81.
F. A. Badia:Trans. AFS, 1971, vol. 79, p. 347.
F. A. Badia, D. F. MacDonald, and J. R. Pearson:Trans. AFS, 1971, vol. 79, p. 265.
F. A. Badia and P. K. Rohtagi:Trans. AFS, 1969, vol. 77, pp. 402–406.
D. Herald and D. M. Scruggs:Method of Producing Dispersion Strengthened Metals, U.S. Patent No. 3,468,658, September 23, 1969.
G. Imich:Method of Preparing Composite Products Containing Metallic and Non-Metallic Materials, U.S. Patent No. 2,793,949, May 28,1957.
J. E. Restall, A. BUrwood-Smith, and K. F. Walles:Metals Mater., 1970, vol. 4, pp. 467–73.
A. E. Standage and M. S. Gani: J.Amer. Ceram Soc, 1967, vol. 50, pp. 101–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrabian, R., Riek, R.G. & Flemings, M. Preparation and casting of metal-particulate non-metal composites. Metall Trans 5, 1899–1905 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644158
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644158