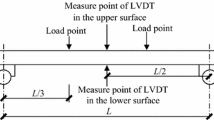
Abstract
Extensive bending creep experiments were made to measure the viscoelattic and mechano-sorptive properties of pine wood. It is observed that under constant, similar to ordinary indoor environment, creep is linearly related to the loads when the loads are below 30% of the ultimate strength, and the relation becomes nonlinear when the loads are higher. Wood of small elastic modulus creeps more than that of large elastic modulus under the same load. The mechano-sorptive effect is stronger for heavily loaded wood than that for lightly loaded. It is stronger for wood with lower elastic modulus and vice versa. The mechano-sorptive effect is negligibly small at low moisture content and it gets very large at high moisture content. It depends therefore not only on the variation range and rate of the moisture content, but also on its magnitude value.
Zusammenfassung
In umfangreichen Experimenten wurden viskoelastische und Sorptionseigenschaften von Kiefernholz gemessen. Bei konstantem Innenraumklima ist der Kriecheffekt bis ca. 30% der Bruchlast linear von der Belastung abhängig; bei höherer Belastung wird die Beziehung nicht-linear. Holz mit niedrigem Elastizitätsmodul verformt sich unter gleicher Last stärker als Holz mit höherem E-Modul. Sorptionseffekte sind unter starker Belastung ausgeprägter als unter geringer Belastung; sie sind auch stärker bei niedrigem E-Modul. Bei niedriger Feuchte sind sie vernachlässigbar, bei hoher Feuchte erreichen sie hohe Ausmaße. Mechanische Sorptionseffekte hängen somit nicht nur von der Spannweite und dem Zeitzyklus des Wechselklimas ab, sondern auch von der Größe des Feuchtegehalts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, L. D.: Deformation of wood in compression during moisture movement, Wood Sci. 5 (2) (1972) 81–86
Bach, L.: Reiner-Weisenberg’s theory applied to time-dependent fracture of wood subjected to various modes of mechanical loading. Wood Sci. 5 (3) (1973) 161–171
Bodig, J. and Jayne, B. A. Mechanics of wood and wood composites, Van Nostrand Reinhold Compony New York (1982)
Boyd, J. D., A anatomical explanation for viscoelastic and mechanosorptive creep in wood, and effects of loading rate on strength, (in New Perspective in Wood Anatomy, Ed. Baas, P., Martinus Nijhoff), Dr. W. Junk Publishers: 171–222, Hague (1982)
Dinwoodie, J. M.; B. H., Paxton; J. S.Higgins; and D. J., Robson: Creep in chipboard, Part 10: The effect of variable cliamate on the creep behaviour of a range of chipboards and one waferboard, Wood Sci. Technol., 26 (1) (1991) 39–51
Grossmann, P. U. A.: Requirements for a model that exhibits mechano-sorptive behaviour, Wood Sci. Technol., 10 (1976) 163–168
Liu, T. and Ödeen K.: Rheological behaviour of wood and wood structures-Review of literature, theories and research needs, Report TRITA-BYMA 1883:3, Department of Building Materials, the Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm (1989a)
Liu, T. and Ödeen, K.: A nonlinear viscoelastic equation for the deformation of wood and wood structures, Report TRITA-BYMA 1889:4, Department of Building Mateials, the Royal Institute of Technology, Stokholm (1989b)
Ranta-Maunus, A.: Conclusion of the workshop, COST 508—Wood Mechanics, Proceeding of the Workshop on Fundamental Aspects on Creep in Wood, March 20–21, 1991, Department of structural Engineering, Lund University, Sweden (1991)
Schniewind, A. P.: Recent progress in the study of the rheology of wood, Wood Sci. Technol., 2 (1968) 188–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T. Creep of wood under a large span of loads in constant and varying environments. Holz als Roh-und Werkstoff 51, 400–405 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02628237
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02628237