Summary
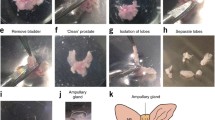
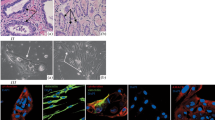
Sustained growth of mouse ventral and anterior prostatic epithelial cells embedded within collagen gel matrix was achieved in a serum-free medium composed of Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium and Ham's F12 medium, 1∶1 (vol/vol), supplemented with bovine serum albumin fraction V, epidermal growth factor, transferrin, cholera toxin, prolactin, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, cortisol, putrescine, fibroblast growth factor, and a trace element mixture. Three-dimensional growth of prostatic epithelial cells occurred inside the collagen gel matrix. This serum-free medium allowed cell growth greater than sevenfold over 10 d in culture. Tissue recombination and cell culture techniques were integrated to demonstrate that cultured cells retained prostatic characteristics. Following 10 d of culture, epithelial colonies from mouse ventral and anterior prostatic epithelial cell cultures were isolated and combined with rat fetal urogenital sinus mesenchyme and grown for 4 wk under the renal capsule of intact athymic male mice. These tissue recombinants showed distinctive prostatic histologic characteristic (alveoli and ducts lined with cuboidal or columnar epithelium surrounded by stroma). When histologic sections of recombinants were stained with the Hoechst 33258, epithelial cells of mouse origin were distinguishable from stromal cells of rat origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins, J. F.; Lewis, J. B.; Anderson, C. W., et al. Enhanced differential synthesis of proteins in a mammalian cell-free system by addition of polyamines. J. Biol. Chem. 250:5688–5695; 1975.
Barnes, D.; Sato, G. Methods for growth of cultured cells in serum-free medium. Anal. Biochem. 102:255–270; 1980.
Burleigh, D.; Reich, E.; Strickland, S. The culture of hormone-dependent cells from the rat ventral prostate. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 19:183–196; 1980.
Carmena, M. J.; Fernandez, M. D.; Prieto, J. C. Characterization of insulin-receptors in isolated epithelial cells from rat ventral prostate: effect of fasting. Cell Biochem. Funct. 4:19–24; 1986.
Chevalier, S.; Bleau, G.; Roberts, K. D., et al. Proliferation and differentiation of canine prostatic epithelial cells in culture. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 24:195–208; 1981.
Coffey, D. S.; Isaacs, J. T. Control of prostate growth. Urology (Suppl.) 17:17–24; 1981.
Cohen, S. S.; Hoffner, N.; Jansen, M., et al. Polyamines, RNA synthesis and streptomycin. Lethality in a relaxed mutant ofE. coli strain 15 TAU. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 57:721–728; 1967.
Cooke, P. S.; Uchima, F.-D. A.; Fujii, D. K., et al. Restoration of normal morphology and estrogen responsiveness in cultured vaginal and uterine epithelia transplanted with stroma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:2109–2113; 1986.
Crabb, J. W.; Armes, L. G.; Carr, S. A., et al. The complete primary structure of prostatropin, a prostate epithelial cell growth factor. Biochemistry 25:4988–4993; 1986.
Cristofalo, V. J.; Rosner, B. A. Glucocorticoid modulation of cell proliferation. In: Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol. 57. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1981:208–209.
Cunha, G. R. Epithelio-mesenchymal interactions in primordial gland structures which become responsive to androgenic stimulation. Anat. Rec. 172:179–196; 1972.
Cunha, G. R. The dual origin of vaginal epithelium. Am. J. Anat. 143:387–392; 1975.
Cunha, G. R.; Chung, L. W. K.; Shannon, J. M., et al. Stromal-epithelial interactions in sex differentiation. Biol. Reprod. 22:19–42; 1980.
Cunha, G. R.; Donjacour, A. A.; Cooke, P. S., et al. The endocrinology and developmental biology of the prostate. Endocrin. Rev. 8:338–362; 1987.
Cunha, G. R.; Fujii, H.; Neubauer, B. L., et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in prostatic development. I. Morphological observations of prostatic induction by urogenital sinus mesenchyme in epithelium of the adult rodent urinary bladder. J. Cell Biol. 96:1662–1670; 1983.
Cunha, G. R.; Lung, B. The possible influences of temporal factors in androgenic responsiveness of urogenital tissue recombinants from wild-type and androgen-insensitive (Tfm) mice. J. Exp. Zool. 205:181–194; 1978.
Cunha, G. R.; Vanderslice, K. D. Identification in histological sections of species origin of cells from mouse, rat and human. Stain Technol. 59:7–12; 1984.
Ekblom, P.; Thesleff, I.; Saxen, L., et al. Transferrin as a fetal growth factor: acquisition of responsiveness related to embryonic induction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:2651–2655; 1983.
Fanger, B. O.; Viceps-Madore, D.; Cidlowski, J. A. Regulation of high- and low-affinity epidermal growth factor receptors by glucocorticoids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 235:141–149; 1984.
Farnsworth, W. E. Prolactin effect on the permeability of human benign hyperplastic prostate to testosterone. Prostate 12:221–229; 1988.
Gospodarowicz, D. Growth factors and their action in vivo and in vitro. J. Pathol. 141:201–233; 1983.
Gospodarowicz, D.; Neufeld, G.; Schweigerer, L. Fibroblast growth factor: structural and biological properties. J. Cell. Physiol. (Suppl.) 5:15–26; 1987.
Hinegardner, R. T. An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal. Biochem. 39:197–201; 1971.
Iguchi, T.; Uchima, F.-D. A.; Ostrander, P. L., et al. Growth of normal mouse vaginal epithelial cells in and on collagen gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:3743–3747; 1983.
Iguchi, T.; Uchima, F.-D. A.; Ostrander, P. L., et al. Proliferation of normal mouse uterine luminal epithelial cells in serum-free collagen gel culture. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B. 61:292–295; 1985.
Imagawa, W.; Spencer, E. M.; Larson, L., et al. Somatomedin-C substitutes for insulin for the growth of mammary epithelial cells from normal virgin mice in serum-free collagen gel cell culture. Endocrinology 119:2695–2699; 1986.
Imagawa, W.; Tomooka, Y.; Nandi, S. Serum-free growth of normal and tumor mouse mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:4074–4077; 1982.
Johnson, C. C.; Dawson, W. E.; Turner, J. T. Regulation of rat ovarian cell growth and steroid secretion. J. Cell Biol. 86:483–489; 1980.
Kan, M.; Yamane, I. Effects of ferrous iron and transferrin on cell proliferation of human diploid fibroblasts in serum-free culture. In Vitro 20:89–94; 1984.
Kawamura, H.; Ichihara, I. Primary culture of epithelial cells derived from the rat ventral prostate: formation of three-dimensional acinus-like structure in collagen gel. Prostate 10:153–161; 1987.
Landschulz, W.; Thesleff, I.; Ekblom, P. A lipophilic iron chelater can replace transferrin as a stimualtor of cell proliferation and differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 98:596–601; 1984.
Lechner, J. F.; Kaighn, M. E. Nutrition of prostate cells. In: Murphy, G. P., ed. Models for prostate cancer. New York: Alan R. Liss, Inc.; 1980:217–232.
Lewis, R. W.; Kaack, B. Nonhuman primate prostate culture. In: Murphy, G. P., ed. Models for prostate cancer. New York: Alan R. Liss, Inc.; 1980:39–65.
McKeehan, W. L.; Adams, P. S. Heparin-binding growth factor/prostatropin attenuates inhibition of rat prostate tumor epithelial cell growth by transforming growth factor type beta. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 24:243–246; 1988.
McKeehan, W. L.; Adams, P. S.; Rosser, M. P. Modified nutrient medium MCDB 151, defined growth factors, cholera toxin, pituitary factors, and horse serum support epithelial cell and suppress fibroblast proliferation in primary cultures of rat ventral prostate cells. In Vitro 18:87–91; 1982.
McKeehan, W. L.; Adams, P. S.; Rosser, M. P. Direct mitogenic effects of insulin, epidermal growth factor, glucocorticoid, cholera toxin, unknown pituitary factors and possibly prolactin, but not androgen, on normal rat prostate epithelial cells in serum-free, primary cell culture. Cancer Res. 44:1998–2010; 1984.
Michalopoulos, G.; Pitot, H. C. Primary culture of parenchymal liver cells on collagen membranes. Exp. Cell Res. 94:70–78; 1975.
Moss, J.; Vaughn, M. Activation of adenylate cyclase by choleragen. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 48: 581–600; 1979.
Murphy, L. J.; Sutherland, R. L.; Stead, B., et al. Progestin regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor in human mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 46:728–734; 1986.
Nishi, N.; Matuo, Y.; Nakamoto, T., et al. Proliferation of epithelial cells derived from rat dorsolateral prostate in serum-free primary cell culture and their response to androgen. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 24:778–787; 1988.
Norman, J. T.; Cunha, G. R.; Sugimura, Y. The induction of new ductal growth in adult prostatic epithelium in response to an embryonic prostatic inductor. Prostate 8:209–220; 1986.
O'Conner, T.; Sinha, D. K. Characterization of rat ventral prostatic epithelial cells in collagen gel culture. Prostate 7:305–319; 1985.
Orlowski, J.; Bird, C. E.; Clark, A. F. Preparation of epithelial and stromal cell fractions from immature rat prostatic tissue using Percoll gradients. J. Androl. 3:232–240; 1982.
Peehl, D. M.; Stamey, T. A. Serum-free growth of adult prostatic epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 22:82–90; 1986.
Ruberstein, M.; Anderson, K. M. Isolation of viable rat ventral prostate epithelial and nonepithelial cells. Endocrinology 106:530–540; 1980.
Schuurmans, A. L. G.; Boalt, J.; Mulder, E. Androgens stimulate both growth rate and epidermal growth factor receptor activity of the human prostate tumor cell LNCaP. Prostate 12:55–63; 1988.
Stahler, M. S.; Pansky, B.; Budd, G. C. Immunocytochemical demonstration of insulin or insulin-like immunoreactivity in the rat prostate gland. Prostate 13:189–198; 1988.
Straus, D. S. Effects of insulin on cellular growth and proliferation. Life Sci. 29:2131–2136; 1981.
Tomooka, Y.; Bern, H. A.; Nandi, S. Growth of mammary epithelial cells from neonatally sex hormone-exposed mice in serum-free collagen gel culture. Cancer Lett. 20:255–261; 1983.
Uchima, F.-D. A.; Edery, M.; Mills, K. T., et al. Estrogen and progestin receptors in mouse vaginal epithelium and fibromuscular wall. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 841:135–138; 1985.
Waymouth, C.; Ward, P. F.; Blake, S. L. Mouse prostatic epithelial cells in defined culture media. In: Sato, G. H.; Pardee, A. B.; Sirbasku, D. A., eds. Growth of cells in hormonally defined media, vol. 9. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1982:1097–1108.
Yang, J.; Flynn, D.; Larson, L., et al. Growth in primary culture of mouse submandibular epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. In Vitro 18:435–442; 1982.
Yang, J.; Larson, L.; Flynn, D., et al. Serum-free primary culture of human normal mammary epithelial cells in collagen gel matrix. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 6:969–975; 1982.
Yang, J.; Nandi, S. Growth of cultured cells using collagen as substrate. Int. Rev. Cytol. 81:249–286; 1983.
Yang, J.; Richards, J.; Bowman, P., et al. Sustained growth and three-dimensional organization of primary mammary tumor epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:3401–3405; 1979.
Yang, J.; Richards, J.; Guzman, R., et al. Sustained growth in primary culture of normal mammary epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:2088–2092; 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Aided by grants CA-05388 and CA-09041 from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, and by M. A. R. C. fellowship GM08730 to T. T.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turner, T., Bern, H.A., Young, P. et al. Serum-free culture of enriched mouse anterior and ventral prostatic epithelial cells in collagen gel. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 26, 722–730 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624429
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624429