Abstract
Objectives
Magnetic resonance (MRI) velocity mapping was used to evaluate non-invasively the flow profiles of the ascending aorta in normal volunteers and in patients with an aortic (mechanical) valve prosthesis.
Background
In patients with artificial aortic valves the flow profile in the ascending aorta is severely altered. These changes have been associated with an increased risk of thrombus formation and mechanical hemolysis.
Methods
Velocity profiles were determined 30 mm distal to the aortic valve in six healthy volunteers and seven patients with aortic valve replacement (replacement within the last 2 years) using ECG triggered phase contrast MRI. Peak flow, mean flow and mean reverse flow were measured in intervals of 25 ms during the entire heart cycle. Systolic reverse flow, end-systolic closing and diastolic leakage volume were calculated for all subjects.
Results
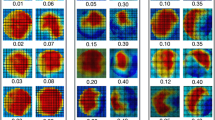
Peak flow velocity during mid-systole was significantly higher in patients with valvular prosthesis than in normals (mean±SD, 1.9±0.4 m/s vs. 1.2±0.03 m/s,P<0.001) with a double peak and a zone of reversed flow close to the inner (left lateral) wall of the ascending aorta of the patients. Closing volume was significantly larger in patients than in controls (−3.3±1.2 ml/beat vs. −0.9±0.5 ml/beat;P<0.001). There was reverse flow during systole in valvular patients amounting to 15.7±6.7% of total cardiac output compared to 2.3±1.2% in controls (P<0.001). Diastolic mean flow was negative in patients after valve replacement but not in controls (−11.0±15.2 ml/beat vs. 6.8±3.2 ml/beat;P<0.01).
Conclusions
The following three major quantitative observations have been made in the present study: (1) Mechanical valve prostheses have an increased peak flow velocity with a systolic reverse flow at the inner (left lateral) wall of the ascending aorta. (2) A double peak flow velocity pattern can be observed in patients with bileaflet (mechanical) prosthesis. (3) The blood volume required for leaflet closure and the diastolic leakage blood volume are significantly higher for the examined bileaflet valve than for native heart valves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodnar E, Yacoub M. Biologic and Bioprosthetic valves. New York: York Medical Books, 1986.
Bodnar E, Frater R. Replacement Cardiac Valves. New York: Pergamon Press, 1991.
Butchart EG, Bodnar E. Thrombosis, embolism and bleeding. UK: ICR Publishers, 1992.
Roberts WC. Choosing a substitute cardiac valve, type, size, surgeon. Am J Cardiol 1976;38:633–44.
Chandran KG, Cabell GN, Khalighi B, Chen CJ. Laser anemometry measurements of pulsatile flow past aortic valves. J Biomech 1983;16:865–73.
Chandran KG, Cabell GN, Khalighi B, Chen CJ. Pulsatile flow past aortic valve bioprosthesis in a model human aorta. J Biomech 1984;17:609–19.
Woo Y-R, Yoganathan AP. In vitro pulsatile flow velocity and turbulent shear stress measurements in the vicinity of mechanical aortic heart valve prosthesis. Life Support Syst 1985;3:283–312.
Woo Y-R, Yoganathan AP. In vitro pulsatile flow velocity and turbulent shear stress measurements in the vicinity of mechanical mitral heart valve prosthesis. J Biomech 1986;19:39–51.
Yoganathan AP, Woo Y-R, Sung H-W, Williams FP, Franch RH, Jones M. In vitro hemodynamic characteristics of tissue bioprosthesis in the aortic position. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1986;92:198–209.
Yoganathan AP, Woo Y-R, Sung H-W. Turbulent shear stress measurements in the vicinity of aortic heart valve prosthesis. J Biomech 1986;19:433–42.
Yoganathan AP, Sung H-W, Woo Y-R. In vitro velocity and turbulence measurements in the vicinity of three new mechanical aortic heart valve prostheses. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1988;95:929–39.
Schoephoerster RT, Oynes F, Nunez G, Kapadvanjwala M, Dewanjee MK. Effects of local geometry and fluid dynamics on regional platelet deposition on artificial surfaces. Arterioscler Thromb 1993;13:1806–13.
Tillmann W, Reul H, Herold M, Bruss KH, Van Gilse J. In-vitro wall shear stress measurements at aortic valve prosthesis. J Biomech 1984;17:263–79.
Hasenkam JM, Giersiepen M, Reul H. Three-dimensional visualization of velocity fields downstream of six mechanical aortic valves in a pulsatile flow model. J Biomech 1988;21:647–61.
Hasenkam JM, Westphal D, Nygaard H, Reul H, Giersiepen M, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H. In vitro stress measurements in the vicinity of six mechanical aortic valves using hot-film anemometry in steady-flow. J Biomech 1988;21:235–47.
Hasenkam JM, Pedersen EM, Østergaard JH, Nygaard P, Paulsen PK, Johannsen G, Schurizek BA. Velocity fields and turbulent stresses downstream of biological and mechanical aortic valve prosthesis implanted in pigs. Cardiovasc Res 1988;22:472–83.
Grigg L, Fulop J, Daniel L, Weisel R, Rakowski H. Doppler echocardiography assessment of prosthetic heart valves. Echocardiography 1990;7(2):97–114.
Walker PG, Pedersen EM, Oyre S, Flepp L, Ringaard S, Heinrich RS, Walton SP, Hasenkam JM, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H, Yoganathan AP. Magnetic resonance velocity imaging: a new method for prosthetic heart valve study. J Heart Valve Dis 1995;4:296–307.
Fontaine AA, Heinrich R, Walker PG, Pedersen EM, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P, Walton SP, Yoganathan AY. Comparison of MRI and LDA velocity measurements downstream of prosthetic heart valves: Implications for in vivo assessment of prosthetic valve function. J Heart Valve Dis 1996;5:66–73.
Paulsen PK, Hasenkam JM, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H, Albrechtsen O. Three-dimensional visualization of velocity profiles in the ascending aorta in humans with normal aortic valves and after insertion of St Jude Medical and Starr-Edwards Silastic Ball valves in the aortic position. Int J Artif Organs 1988;11(4):277–92.
Nygaard H, Paulsen PK, Hasenkam JM, Kromann-Hansen O, Pedersen EM, Rovsing PE. Quantitation of the turbulent shear stress distribution downstream of normal, diseased and artificial aortic valves in humans. Cardiothorac Surg 1992;6:609–17.
Houlind K, Eschen O, Pedersen EM, Jensen T, Hasenkam JM, Paulsen PK. Magnetic resonance imaging of blood velocity distribution around St Jude Medical aortic valves in patients. J Heart Valve Dis 1996;5:511–7.
Kilner PJ, Yang ZY, Mohiaddin RH, Firmin DN, Longmore DB. Helical and retrograde secondary flow patterns in the aortic arch studied by three-dimensional magnetic resonance velocity mapping. Circulation 1993;88:2235–47.
Nayler GL, Firmin DN, Longmore DB. Blood flow imaging by cine magnetic resonance imaging. J Comp Assist Tomogr 1986;12:715–22.
Stahlberg F, Thomsen C, Sondergaard L, Henriksen O. Pulse sequence design for MR velocity mapping of complex flow: notes on the necessity of low echo times. Magn Reson Imaging 1994;12(8):1255–62.
Botnar R, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. Quantification of blood flow patterns in human vessels by magnetic resonance imaging. Technol Health Care 1996;4:97–112.
Botnar R, Ringaard S, Hirt F, Pedersen EM, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. Assessment of velocity fields downstream of prosthetic heart valves by magnetic resonance imaging. in-vivo and in-vitro studies. Proceedings, Fourth Scientific Meeting, New York, Berkeley, CA, Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 1996, p. 696
Yoganathan AP. Cardiac valve prostheses. In: Bronzino JD, editor. The Biomedical Engineering Handbook. Boca Raton: CRC, 1995:1847–70.
Reisner SA, Meltzer RS. Normal values of prosthetic valve Doppler echocardiographic parameters: a review. J Am Soc Echo 1988;1:201–10.
Goldrath N, Zimes R, Vered Z. Analysis of Doppler-obtained velocity curves in functional evaluation of mechanical prosthetic valves in the mitral and aortic positions. J Am Soc Echo 1988;1:211–25.
Wiseth R, Samstad S, Rossvoll O, Torp HG, Skjaerpe T, Hatle L. Cross-sectional left ventricular outflow tract velocities before and after aortic valve replacement: a comperative study with two-dimensional Doppler ultrasound. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1993;6:279–85.
Spielmann RP, Schneider O, Thiele F, Heller M, Bücheler E. Appearance of poststenotic jets in MRI: dependence on flow velocity and imaging parameters. Magn Reson Imag 1991;9:67–72.
Ståhlberg F, Søndergaard L, Thomsen C, Henriksen O. Quantification of complex flow using MR phase imaging-a study of parameters influencing the phase/velocity relation. Magn Reson Imag 1992;10:13–23.
Urchuk SN, Plewes DB. Mechanisms of flow-induced signal loss in MR-angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 1992;4:453–62.
Botnar R, Ringgaard S, Hirt F, Pedersen EM, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. Assessment of velocity fields downstream of prosthetic heart valves: in-vivo and in-vitro studies. In: Proceedings, ISMRM. Fourth Annual Meeting, New York, 1996, p. 696.
Kozerke S, Scheidegger MB, Pedersen EM, Boesiger P. Heart motion adapted cine phase contrast flow measurements through the aortic valvc. In: Proceedings, ISMRM, Sixth Annual Meeting, Sydney, 1998, p. 277.
Chatzimavroudis GP, Walker PG, Oshinski JN, Franch RH, Pettigrew RI, Yoganathan AP. Slice location dependence of aortic regurgitation measurements with phase velocity mapping. Magn Res Med 1997;37:545–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Botnar, R., Nagel, E., Scheidegger, M.B. et al. Assessment of prosthetic aortic valve performance by magnetic resonance velocity imaging. MAGMA 10, 18–26 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02613108
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02613108