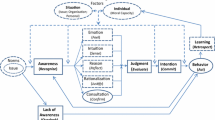
Summary
This is a paper about problem-solving styles in Environmental Management and the specific deficiencies in these styles that might be groupd under the label ‘tunnel vision’. The latter, a form of selective attention, contributes to inadequate problem-formulation, partial solutions to complex problems and to the generation of even more intractable, additional problems. Examples of tunnel vision in military and environmental decision-making are discussed, together with the situational, personal and educational factors that exacerbate its influence. The paper concludes with some recommendations for changes in professional education that might help to recduce the occurrence of tunnel vision.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskerville, G. (1976) Report of the task-force for evaluation of budworm control alternatives. Cabinet Committee on Economic Development, Province of New Brunswick, Canada, 1976.
Bennett, P. and Dando, M. (1979) Complex strategic analysis: A hypergame study of the Fall of France,Journal of the Operational Research Society, 30, pp. 23–32.
Berresford, A. and Dando, M. (1979) Operational research for strategic decision-making: The role of world-view,Journal of the Operational Research Society, 29, pp. 137–146.
Bissett, R. (1978) Quantification, decision-making and environmental impact assessment in the United Kingdom,Journal of Environmental Management, 7, pp. 43–58.
Conacher, A. (1980) Environmental problem-solving and land-use management: a proposed structure for Australia,Environmental Management, 4, pp. 391–405.
Dixon, N. (1976)On the Psychology of Military Incompetence, Jonathan Cape Ltd.
Ehrenfeld, D. (1978)The Arrogance of Humanism, Oxford University Press
Festinger, L., Riecken, H. and Schacter, S. (1964)When Prophecy Fails, Harpper and Row.
Getzels, J. (1979) Problem-finding and research in educational administration. In G. Immegart and W. Boyd (eds.),Problem Finding in Educational Administration, Lexington Books.
Henning, D. (1974)Environmental Policy and Administration, New York, American Elsevier.
Henning, D. (1980) In-service training for environmental personnel: a critical analysis with innovations,Journal of Environmental Education, 11, pp. 4–10.
Hoh, A. (1981) Concensus building: a creative approach to resolving conflicts,Management Review, 70, pp. 52–54.
Hollick, M. (1981) The role of quantitative decision-making methods in environmental impact assessment,Journal of Environmental Management, 12, pp. 65–78.
Horowitz, I. (1969) Engineering and sociological perspectives on development: interdisciplinary constraints in social forecasting,International Social Science Journal, 21, pp. 545–556.
Hudson, L. (1966)Contrary Imaginations, Penguin Books.
Huxham, C. and Dando, M. (1981) Is bounded-vision an adequate explanation of strategic decision-making failures,Omega: International Journal of Management Science, 9, pp. 371–379.
Huxham, C., Bennett, P., Lozowski, M. and Dando, M. (1981) The study of human decision-making: A cautionary tale from the world of experimental gaming,Journal of the Operational Research Society, 32, pp. 173–185.
Ignizio, J. (1980). Solving large-scale problems: A venture into a new dimension,Journal of the Operational Research Society, 31, pp. 217–225.
Janis, I. (1972)Victims of Groupthink, Houghton Mifflin.
Keen, P. (1977) Cognitive style and career specialization. In J. an Maanen (ed.),Organizational Careers: Some New Perspectives, Wiley.
Kendall, S. and MacKintosh, E. (1978)Management Problems of Polydisciplinary Environmental Research Projects in the University Setting, Publication No. 86, Centre for Resources Development, University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada.
Leckie, G. (1975)Interdisciplinary Research in the University Setting, Occasional paper No. 9, Centre for Settlement Studies, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
Lowe, J. and Lewis, D. (1981) Environmental choice and public decision-making,Omega: The International Journal of Management Science, 9, pp. 297–305.
Lyles, M. and Mitroff, I. (1980) Organizational problem formulation: An empirical study,Administrative Science Quarterly, 25, pp. 102–119.
Martin, B. (1977) Academics and the Environment,Ecologist, pp. 224–232.
Maslow, A. (1966)The Psychology of Science: A Reconnaissance, Harper and Row.
Mason, R. (1978) The critical potential of knowledge: Environmental studies and the matrix of power, Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Toronto.
Mason, R. O. and Mitroff, I. (1979) Assumptions of majestic metals: strategy through dialectics,California Management Review, 22, pp. 80–88.
Miller, A. (1981a) Psychosocial factors in environmental problem-solving,Environmental Management, in press.
Miller, A. (1981b) Conceptual matching models and interactional research in education.Review of Educational Research, 51, pp. 33–84.
Miller, A. (1981c) Irrational processes in man-environment interactions: Implications for environmental studies,International Journal of Environmental Studies, in press.
Miller, A. (1982) Information search and environmental decision-making, unpublished paper, University of New Brunswick.
Mitroff, I. and Emshoff, J. (1979) On strategic assumption-making: A dialectical approach to policy and planning,Academy of Management Review, 4, pp. 1–12.
Mitroff, I. and Kilmann, R. (1978)Methodological Approaches to Social Science, Jossey-Bass.
Mitroff, I., Emshoff, J. and Kilmann, R. (1978) Assumptional analysis: A methodology for strategic problems-solving,Management Science, 25, pp. 583–593.
Murnighan, J. (1981) Group decision making: What strategies should you use?Management Review, 70, pp. 55–62.
Parker, L. (1980) Evaluating group decision-making in the corporate environment,Management Decision, 18, pp. 35–44.
Petak, W. (1980) Environmental planning and management: The need for an integrative perspective,Environmental Management, 4, pp. 287–295.
Pidd, M. and Wooley, R. Four views on problem structuring,Interfaces,10, pp. 51–54.
Rice, G. (1980) But how do managemers make decisions?Management Decision, 18.
Schroder, H., Driver, M. and Streufer, S. (1967)Human Information Processing, New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Stoppard, J. and Miller, A. (1981) Cognitive matching in psychotherapy, unpublished paper, University of New Brunswick.
Stromberg, R. (1975)After Everything: Western Intellectual History since 1945, New York: St. Martin's Press.
Walton, R. (1979) A problem-solving workshop on border conficts in Eastern Africa. In L. Goodstein, B. Lubin and A. Lubin,Organizational Change Sourcebook 2: Cases in Conflict Management, LaJolla, California: University Associates.
Witkin, H., Moore, C., Oltman, P., Goodenough, D., Friedman, F., Owen, D. and Raskin, E. (1977) Role of field independent and field dependent cognitive styles in academic evolution: a longitudinal study,Journal of Educational Psychology, 69, pp. 197–211.
Witkin, H., Goodenough, D. and Oltman, P. (1979) Psychological differentiation: Current status,Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37, pp. 1127–1145.
Woolley, R. and Pidd, M. (1981) Problem structuring—A literature review,Journal of the Operational Research Society, 32, pp. 197–206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dr Alan Miller who is now associate professor at the University of New Brunswick received his training in biology (in England) and ecology (in Canada). He then spent several years pursuing research at the Northwest Institute for Medical Research in Chicago, USA. A growing interest in the human aspects of environmental and medical problems led to a further graduate study in psychology, followed by teaching positions in Ireland and Canada. His current interests include: the education of environmental professional; the psychosocial problems involved in environmental management, and, the problems inherent in interdisciplinary project groups.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, A. Tunnel vision in environmental management. Environmentalist 2, 223–231 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02603102
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02603102