Abstract
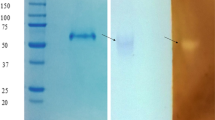
A novel exocellular glucoamylase produced by a thermophilic fungus,Cephalosporium eichhorniae, was purified by a combination of membrane filtration and Sephadex chromatography. The enzyme was a glycoprotein, 28% carbohydrate by weight. It was composed of a single polypeptide chain with a molecular weight of 26,850. The enzyme was thermostable with optimum activity between 45 and 62°C. It had a substrate preference of amylose>amylopectin. Analysis by thin-layer and gas-liquid chromatography showed the major hydrolytic product of starch was glucose, classifying this enzyme as a thermophilic glucoamylase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Cherevenka, C. H. 1970. A manual of methods for the analytical ultracentrifuge. Palo Alto, Calif.: Spinco Division, Beckman Instruments.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. A., Rebers, P. A., Smith, F. 1956. Colorimetric method for the determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry28:350–356.
Gregory, K. F., Reade, A. E., Santos-Nunez, J., Alexander, J. C., Smith, R. E., MacLean, S. J. 1977. Further thermotolerant fungi for the conversion of cassava starch to protein. Animal Feed Science and Technology2:7–19.
Hale, W. S., Rawlins, L. C. 1951. Amylases ofBacillus marcerans. Cereal Chemistry28:49–58.
King, N. J. 1967. The glucoamylase ofConiophora cerebella. Biochemical Journal105:577–583.
Leonard, J. 1970. Protein and glycolipid components of human erythrocyte membranes. Biochemistry9:1129–1132.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. C., Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the folin-phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry193:265–275.
Martin, R. G., Ames, B. N. 1961. A method for determining the sedimentation behaviour of enzymes: Application to protein mixtures. Journal of Biological Chemistry236:1372–1379.
Pazur, J. H. 1972. Glucoamylase fromAspergillus niger, pp. 931–934. In: Ginsberg, V. (ed.), Methods in enzymology, vol. 28. New York: Academic Press.
Pazur, J. H., Ando, T. 1959. The action of an amyloglucosidase ofAspergillus niger on starch and malto-oligosaccharides. Journal of Biological Chemistry234:1966–1970.
Pazur, J. H., Kleppe, K., Ball, E. M. 1963. The glycoprotein nature of some fungal carbohydrases. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics103:515–516.
Pazur, J. H., Okada, S. 1967. Properties of the glucoamylase fromRhizopus delemar. Carbohydrate Research4:371–379.
Phillips, L. L., Caldwell, M. L. 1951. A study of the action of gluc amylase, a glucose-producing amylase, formed by the moldRhizopus delemar. Journal of the American Chemical Society73:3563–3568.
Smiley, K. L. 1971. Continuous conversion of starch to glucose with immobilized glucoamylase. Biotechnology and Bioengineering13:309–322.
Tsuboe, A., Yamasaki, K., Suzuki, T. 1974. Two forms of glucoamylase fromMucor rouxianus. I. Purification and crystallization. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry38:543–550.
Wadman, W. H., Thomas, G. I., Pardee, A. B. 1954. Quantitative method using paper chromatography for the estimation of reducing oligosaccharides. Analytical Chemistry26:1192–1195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Day, D.F. A thermophilic glucoamylase fromCephalosporium eichhorniae . Current Microbiology 1, 181–184 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02601674
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02601674