Summary
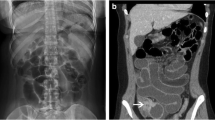
“Pseudo-obstruction of the colon” refers to a condition in which physical and radiologic findings identical to those associated with mechanical obstruction of the large bowel are found, but in which no organic cause of colonic distention can be identified. These cases may involve progressive proximal large-intestinal dilatation to the point of cecal perforation or necrosis.
Two cases of spontaneous perforation of the cecum and one case of gangrene of the cecum secondary to proximal distention of the right colon that followed pseudoobstruction of the colon are presented.
Various etiologic factors reported in the medical literature are discussed and analyzed, and an anatomicophysiologic explanation of a possible mechanism, based on sympathetic-parasympathetic neurostimulatory imbalance, is offered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers JH, Smith LL, Carter R: Perforation of the cecum. Ann Surg 143: 251, 1956
Brobeck JR (ed). Best and Taylor's Physiological Basis of Medical Practice. Ninth edition. Baltimore, The Williams and Wilkins Company, 1973, section 2, pp 8–9
Bryk D, Soong KY: Colonic ileus and its differential roentgen diagnosis. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 101: 329, 1967
Carrasquilla C, Arbulu A, Fromm S, et al: Cecal perforation due to adynamic ileus. Dis Colon Rectum 13: 252, 1970
Dragstedt CA, Lang VF, Millet RF: The relative effects of distention in different portions of the intestine. Arch Surg 18: 2257, 1929
Eckman WG, Wenzke F, Abramson W: Perforation of the cecum complicating adynamic ileus. Am J Surg 96: 718, 1958
Evison G, Samuel E: Pseudo-volvulus of the colon. Clin Radiol 16: 256, 1965
Hirsch MI: Spontaneous rupture of the caecum: Report of a case. Cent Afr J Med 7: 49, 1961
Lowman RM, Davis L: An evaluation of cecal size in impending perforation of the cecum. Surg Gynecol Obstet 103: 711, 1956
McCune WS, Keshishian JM: Postoperative intestinal obstruction. Surg Gynecol Obstet 96: 567, 1953
Meier-Ruge W, Hunziker O: Extrinsic parasympathetic innervation of the distal colon. Abdom Surg 61: 139, 1974
Millar DR, Ovlisen B: Two cases of spontaneous perforation of the caecum following caesarian section. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 45: 254, 1966
Moore CE, Koman GM: Impending cecal perforation secondary to a crushing injury of the pelvis. Arch Surg 79: 1044, 1959
Morton JH, Schwartz SI, Gramiak R: Ileus of the colon. Arch Surg 81: 425, 1960
Murphy JB: Ileus. JAMA 26: 72, 1896
Norton L, Young D, Scribner R: Management of pseudo-obstruction of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet 138: 595, 1974
Ogilvie H: Large-intestine colic due to sympathetic deprivation: A new clinical syndrome. Br Med J 2: 671, 1948
Robertson JA, Eddy WA, Vosseler AJ: Spontaneous performation of the cecum without mechanical obstruction: Review of literature and case report. Am J Surg 96: 448, 1958
Rothwell-Jackson RL: Idiopathic large-bowel obstruction. Br J Surg 50: 797, 1963
Stephens FO: The syndrome of intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Br Med J 1: 1248, 1962
Stephens FO: Intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Med J Aust 1: 1026, 1966
Van Zwaienburg C: Strangulation resulting from distention of hollow viscera: Its bearing upon appendicitis, strangulated hernia and gall-bladder disease. Ann Surg 46: 780, 1907
Wanebo H, Mathewson C, Conolly B: Pseudoobstruction of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet 133: 44, 1971
Wojtalik RS, Lindenauer SM, Kahn SS: Perforation of the colon associated with adynamic ileus. Am J Surg 125: 601, 1973
Yeo R: Spontaneous perforation of the caecum: Case reports and a review of the literature. Postgrad Med J 43: 65, 1967
Zimmerman LM: Spastic ileus. Surg Gynecol Obstet 50: 721, 1930
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Spira, I.A., Wolff, W.I. Gangrene and spontaneous perforation of the cecum as a complication of pseudo-obstruction of the colon: Report of three cases and speculation as to etiology. Dis Colon Rectum 19, 557–562 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02590953
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02590953