Abstract
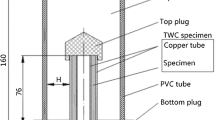
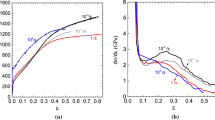
The evolution of adiabatic shear localization in an annealed AISI 316L stainless steel has been investigated and was reported in Part I of this paper (Met. Trans. A, 2006, Vol. 37A, pp. 2435–446). In the present research (Part II), a comprehensive transmission electron microscopy (TEM) examination was conducted on the microstructural evolution of shear localization in this material at different loading stages. The TEM results indicate that elongated subgrain laths and an avalanche of dislocation cells are the major characteristics in an initiated band. Development of the substructures within shear bands is controlled by dynamic recovery and continuous dynamic recrystallization. The core of shear bands was found to consist of fine equiaxed subgrains. Well-developed shear bands are filled with a mixture of equiaxed, rectangular, and elongated subgrains. The equiaxed subgrains, with a typical size less than 100 nm, are postulated to result from either the breakdown and splitting of subgrain laths or the reconstruction of subcells.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
H.C. Rogers:Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1979, vol. 9, pp. 283–311.
Y.L. Bai and B. Dodd:Adiabatic Shear Localization, Occurrence, Theories and Applications, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1992, p. 24.
M.E. Backman and S.A. Finnegan: inMetallurgical Effects at High Strain Rates, R.W. Rohde, B.M. Butcher, J.R. Holland, and C.H. Karnes, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, pp. 531–43.
R.F. Recht:ASME(E) J. Appl. Mech. Trans., 1964, vol. 31, pp. 189–93.
R.J. Clifton: inMaterial Response to Ultra-High Loading Rates, NMAB-356, National Advisory Board (NRC), Washington, DC, 1980, Chapter 8.
T.W. Wright and J.W. Walter:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1987, vol. 35, pp. 701–20.
J.S. Costin, E.E. Crisman, R.H. Hawley, and J. Duffy: inProceedings of the Second Conference on the Mechanical Properties of Materials at High Rates of Strain, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. No. 47, Oxford, 1979, pp. 90–100.
K.A. Hartley, J. Duffy, and R.H. Hawley:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1987, vol. 35, pp. 283–301.
A. Marchand and J. Duffy:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1988, vol. 36, pp. 251–83.
Y.L. Bai, Q. Xue, Y.B. Xu, and L.T. Shen:Mech. Mater., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 155–64.
M. Zhou, A.J. Rosakis, and G. Ravichandran:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1996, vol. 44, pp. 981–1006.
J.J. Mason, A.J. Rosakis, and G. Ravichandran:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1994, vol. 42, pp. 1679–97.
H.C. Rogers and C.V. Shastry: inShock Waves and High Strain Rate Phenomena in Metals, M.A. Meyers and L.E. Murr, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 285–98.
R.E. Winter:Philos. Mag., 1975, vol. 31, pp. 765–73.
M.A. Meyers, G. Subhash, B.K. Kad, and L. Prasad:Mech. Mater., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 175–93.
M.A. Meyers, Y.B. Xu, Q. Xue, M.T. Perez-Prado, and T.R. McNelley:Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 1307–25.
J.V. Craig and T.A.C. Stock:J Aust. Inst. Metals, 1970, vol. 15, pp. 1–5.
T.A.C. Stock and K.R.L. Thompson:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 219–24.
A.L. Wingrove:J Aust. Inst. Metals, 1971, vol. 16, pp. 67–70.
R.C. Glenn and W.C. Leslie:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2945–47.
K. Cho, S. Lee, S.R. Nutt, and J. Duffy:Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 923–32.
Y.B. Xu, Y.L. Bai, Q. Xue, and L.T. Shen:Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 1917–26.
Y. Me-Bar and D. Shechtman:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1983, vol. 58, pp. 181–88.
H.A. Grebe, H.-R. Pak, and M.A. Meyers:Metall. Trans., 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 761–75.
M.A. Meyers and H.-R. Pak:Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 2493–99.
K.H. Hartman, H.D. Kunze, and L.W. Meyer: inShock Waves and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Metals, M.A. Meyers and L.E. Murr, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 325–37.
C. Zener and J.H. Hollomon:J. Appl. Mech., 1944, vol. 15, pp. 22–32.
M.C. Mataya, M.J. Carr, and G. Krauss:Metall. Trans., 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1263–74.
U. Andrade, M.A. Meyers, K.S. Vecchio, and A.H. Chokshi:Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 3183–95.
M.A. Meyers, L.W. Meyer, J. Beatty, U. Andrade, K.S. Vecchio, and A.H. Chokshi: inShock Waves and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Materials, M.A. Meyers, L.E. Murr, and K.P. Staudhammer, eds., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY, 1992, p. 529.
J.H. Beatty, L.W. Meyer, M.A. Meyers, and S. Nemat-Nasser: inShock Waves and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Materials, M.A. Meyers, L.E. Murr, and K.P. Staudhammer, eds., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY, 1992, p. 645.
C.O. Mgbokwere, S.R. Nutt, and J. Duffy:Mech. Mater., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 97–110.
K.A. Hartley, J. Duffy, and R.H. Hawley:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1987, vol. 35, pp. 283–301.
A. Marchand and J. Duffy:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1988, vol. 36, pp. 251–83.
J. Duffy and Y.C. Chi:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, vol. A157, pp. 195–210.
A. Marchand, K. Cho, and J. Duffy:The Formation of Adiabatic Shear Bands in an A1S1 1018 Cold-Rolled Steel, Brown University Technical Report, October 1988.
M.A. Meyers, D.J. Benson, O. Vöhringer, B.K. Kad, Q. Xue, and H.-H. Fu:Mater. Sci. Eng., 2002, vol. A322, pp. 194–216.
B. Derby:Acta Metall., 1991, vol. 39, pp. 955–62.
J. Wang, Z. Horita, M. Furukawa, M. Nemoto, N. Tsenev, R. Valiev, Y. Ma, and T.G. Langdon:J. Mater. Res., 1993, vol. 8, pp. 2810–18.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly:Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Pergamon, Oxford, U.K., 2002, pp. 127–72
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov:Prog. Mater. Sci., 2000, vol. 45, pp. 103–89.
Y.T. Zhu and T.C. Lowe:Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, vol. A291, pp. 46–53.
Y.T. Zhu, J.Y. Huang, J. Gubicza, T. Ungár, Y.M. Wang, E. Ma, and R.Z. Valiev:J. Mater. Res., 2003, vol. 18, pp. 1908–17.
Q. Wei, D. Jia, K.T. Ramesh, and E. Ma:Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, vol. 81, pp. 1240–42.
D. Jia, K.T. Ramesh, and E. Ma:Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 3495–509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Q., Gray, G.T. Development of adiabatic shear bands in annealed 316L stainless steel: Part II. TEM studies of the evolution of microstructure during deformation localization. Metall Mater Trans A 37, 2447–2458 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02586218
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02586218