Abstract
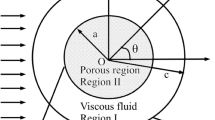
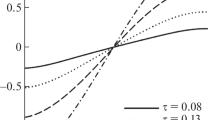
A compact economical description of transient mass transport in Krogh tissue cylinders is devised. It is based on extensions of the Gill-Subramanian dispersion technique and Sturm-Liouville theory to two-phase systems and takes into account the following aspects of convective mass transfer simultaneously: radial and axial diffusion in both blood and tissue, a localized mass-transfer resistance at the capillary membrane, and an axial diffusion barrier at each end of the cylinder. Numerical examples are provided for two situations of physiological interest: (i) Small lipid-soluble solutes encountering no localized barrier at the capillary membrane, and (ii) hydrophilic solutes, which encounter a very substantial barrier. It is shown that existing one-dimensional chromatographic models are satisfactory for the lipophilic solutes, for what is generally considered a satisfactory set of parameters for describing Krogh cylinders. However, the limitations on this treatment are emphasized, and it is shown how convective dispersion may complicate this picture. For the hydrophilic solutes Taylor dispersion is shown to be much more important than hitherto believed. It appears that existing methods of estimating capillary membrane permeabilities should be revised in the light of these findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aris, R. On the dispersion of a solute in a fluid flowing through a tube.Proc. Roy. Soc. 1956,A235, 67–77.
Aris, R.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A 1959,252, 538.
Aroesty, J., and Gross, J. F., Convection and diffusion in the microcireulation.Microvascular Research 1970,2, 247–267.
Bassingthwaighte, J. B., Knopp, T. J., and Hazelrig, J. B. Concurrent flow model for capillarytissue exchanges. In C. Crone and N. A. Lassen (Eds.),Capillary permeability, Alfred Benzon Symposium II. Copenhagen: Munksgaard, 1970. Pp. 60–80.
Bassingthwaighte, J. B. A concurrent flow model for extraction during transcapillary passage.Circulation Research 1974,35, 483–503.
Baz, A., Tepper, R. S., Lightfoot, E. N., and Lanphier, E. H. The risk of isobaric bubble formation in shifts of breathing medium.Federation Proceedings 1977,36, Abst. No. 1627, 579.
Brenner, H. The diffusion model of longitudinal mixing in beds of finite length.Chemical Engineering Science 1962,17, 229–243.
Crone, C. Permeability of capillaries in various organs as determined by use of the ‘indicator diffusion’ method.Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 1963,58, 292–305.
Gill, W. N., and Sankarasubramanian, R. Exact analysis of unsteady convective diffusion.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A 1970,316, 341.
Goresky, C. A., Ziegler, W. H., and Bach, G. G. Capillary exchange modeling: Barrier-limited and flow-limited distribution.Circulation Research 1970,27, 739–764.
Guller, B., Ypintsoi, T., Orvis, A. L., and Bassingthwaighte, J. B. Myocardial sodium extraction at varied coronary flows in the dog.Circulation Research 1975,37, 359–378.
Johnson, J. A., and Wilson, T. A. Model for capillary exchange.American Journal of Physiology 1966,210, 1299–1303.
Kindwall, E. P., Baz, A., Lightfoot, E. N., Lanphier, E. H., and Seireg, A. Nitrogen elimination in man during decompression.Undersea Biomedical Research 1975,2, 171–183.
Lanphier, E. H., Tepper, R. S., and Lightfoot, E. N. New approaches to decompression modelling.Proc. of European Undersea Biomed. Soc., 3rd annual scientific mtg., Toulon, France, July 15 and 16, 1977.
Lee, H. L., and Lightfoot, E. N. Preliminary report on ultrafiltration induced polarization chromatography—An analog of field flow fractionation.Separation Science 1976,11, 417.
Lee, H. L. A study of the synthesis and development of separations processes and specifically ultra-filtration induced polarization chromatography. Ph.D. thesis, Chem. Eng., Univ. of Wisconsin, 1976.
Lee, J. S., and Fronek, A. Analysis on the exchange of indicators in single capillaries.Microvascular Research 1970,2, 302–318.
Levitt, D. G. Capillary-tissue exchange kinetics: An analysis of the Krogh cylinder model,Journal of Theoretical Biology 1972,34, 103–124.
Lightfoot, E. N., Baz, A., Lanphier, E. H., Kindwall, E. P., and Seireg, A. The role of bubble growth kinetics in decompression.Proc. Sixth Symposium on Underwater Physiology, San Diego, California, July 6–10, 1975.
Perl, Wm., and Chinard, F. P. A convective-diffusion model of indicator transport through an organ.Circulation Research 1968,22, 273–298.
Perl, W., Interpolation model for evaluating permeability from indicator dilution curves. In C. Crone and N. A. Lassen (Eds.)Capillary permeability, Alfred Benzon Symposium II, Copenhagen: Munksgaard, 1970. Pp. 185–201.
Ramkrishna, D., and Amundson, N. R. Transport in composite materials: Reduction to a selfadjoint formalism.Chemical Engineering Science 1974,29, 1457–1464.
Reis, J. F. G., Ramkrishna, D., and Lightfoot, E. N. Convective mass transfer in the presence of polarizing fields: Dispersion in hollow-fiber electropolarization chromatography.American Institute of Chemical Engineering Journal 1978,24, 679–686.
Renkin, E. M. Transport of Potassium-42 from blood to tissue in isolated mammalian skeletal muscles.American Journal of Physiology 1959,197, 1205–1210.
Sangren, W. C., and Sheppard, C. W. Mathematical derivation of the exchange of a labeled substance between a liquid flowing in a vessel and an external compartment.Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 1953,15, 387–394.
Schmidt, G. W. Mathematical theory of capillary exchange as a function of tissue structure.Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 1952,14, 229–263.
Taylor, G. I. Dispersion of soluble matter in solvent flowing slowly through a tube.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A 1953,219, 186.
Taylor, G. I. Conditions under which dispersion of a solute in a stream of solvent can be used to measure molecular diffusion.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A 1954,223, 446.
Tepper, R. S., Lanphier, E. H., and Lightfoot, E. N. Mixed-gas pharmaco-kinetics,Annual scietific meeting, Undersea medical society, Toronto, May 13–17, 1977.
Tepper, R. S. Ph.D. thesis, Dept. of Chem. Eng., Univ. of Wisconsin, 1978.
Tepper, R. S., Hobbs, S. H., Lanphier, E. H., and Lightfoot, E. N. The pharmaco-kinetics of inert gases. In D. O. Cooney (Ed.),Handbook of chemical engineering in medicine. Dekker, New York, 1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tepper, R.S., Lee, H.L. & Lightfoot, E.N. Transient convective mass transfer in Krogh tissue cylinders. Ann Biomed Eng 6, 506–530 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02584553
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02584553