Abstract
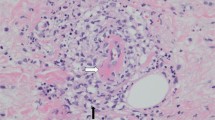
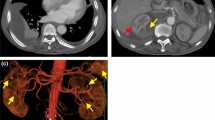
Following reports of hemorrhage from renal microaneurysms caused by renal biopsy, renal arteriography has been used increasingly as a screening procedure prior to renal biopsy as well as for diagnostic investigation. The incidence of renal microaneurysms has been documented in a group of 40 cases of suspected polyarteritis nodosa, of whom 15 were confirmed, and only 2 had microaneurysms. Both subjects with microaneurysms had more florid clinical disease. In view of the low incidence of microaneurysms it is suggested that renal angiography should be used as a diagnostic investigation only in cases with florid clinical disease and not as a screening procedure prior to renal biopsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meany TF (1958) Observations concerning renal circulation (angiography of kidneys removed from hypertensive or normotensive patients). Cleveland Clin Q 25:21–28
Fleming RT, Stern LZ (1965) Multiple intraparenchymal renal aneurysms in polyarteritis nodosa. Radiology 84:100–103
Curran RE, Steinberg I, Magstrom JWC (1967) Arteriovenous fistula complicating percutaneous renal biopsy in polyarteritis nodosa. Am J Med 43:465–470
Travers RC, Allison DJ, Brettle RP, Hughes GRV (1979) Polyarteritis nodosa: A clinical and angiographic analysis of 17 cases. Semin Arthritis Rheum 8:184–199
Vazquez JJ, San Martin P, Barbado FJ, Gil A, Guerra J, Arnalich F, Garcia Puig J, Sanchez Mejias F (1981) Angiographic findings in systemic necrotizing vasculitis. Angiology 32:773–779
Ronco P, Verroust P, Mignon F, Kourilsky O, Vanhille P, Meyrier A, Mery J, Morel-Maroger L (1983) Immunopathological studies of polyarteritis nodosa and Wegener's granulomatosis: A report of 43 patients with 51 renal biopsies. Q J Med (n.s. L11) 206:212–223
Moore TL, Zuckner J (1980) Eosinophilic fasciitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 9:228–235
Cohen RD, Conn DL, Ilstrup DM (1980) Clinical features, prognosis and response to treatment in polyarteritis. Mayo Clin Proc 55:146–155
Fisher RG (1981) Renal aneurysms in polyarteritis nodosa: A multi-episodic phenomenon. AJR 136:983–985
D'Elia JA, Gleason RE, Alday M, Malarick C, Godley K, Warram J, Kaldany A, Weinrauch LA (1982) Nephrotoxicity from angiographic contrast material. Am J Med 72:719–725
Bookstein JJ, Goldstein HM (1973) Successful management of post biopsy arteriovenous fistula with selective arterial embolization. Radiology 109:535–536
Clark RA, Gallant TE, Alexander ES (1983) Angiographic management of traumatic arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical results. Radiology 147:9–13
Scott DGI, Bacon PA, Elliot PJ, Tribe CR, Wallington TB (1982) Systemic vasculitis in a District General Hospital 1972–80: Clinical and Laboratory features, classification and prognosis of 80 cases. Q J Med 51:292–311
Travers RL (1979) Connective tissue disorders, polyarteritis nodosa and related disorders. Br J Hosp Med 1979:38–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sellar, R.J., Mackay, I.G. & Buist, T.A.S. The incidence of microaneurysms in polyarteritis nodosa. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 9, 123–126 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577919
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577919