Abstract
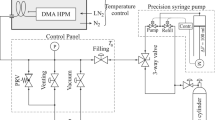
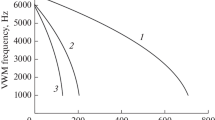
A new version of a vibrating tube flow densitometer has been designed permitting measurements of density differences between two fluids in the temperature range from 298 to 723 K and at pressures up to 40 MPa. The instrument is equipped with a Pt/Rh20 vibrating tube (1.6-mm o.d.) and a Pt/Rh10 transporting tube (1.2-mm o.d.) permitting measurements with highly corrosive liquids. The period of oscillation of the tube is about 7.5 ms, with a typical stability better than 10−4% over about a 1-h period over the entire temperature interval. The calibration constantK at room temperature is about 530 kg·m−3·ms−2, with a temperature coefficient of approximately −0.13kg·m−3·ms−2·K−1, and is practically pressure independent. It can be determined by calibration with a reproducibility generally better than 0.1%. The instrument was tested with NaCl(aq) solutions in the temperature range from 373 to 690 K for density differences between sample and reference liquid ranging from 200 to 2 kg·m−3; the corresponding errors are believed to be below 0.3 and 5%, respectively. A highly automated temperature control maintains the temperature of the tube stable to within ±0.02 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Kratky, H. Leopold, and H. Stabinger,Z. Agew. Phys. 27:273 (1969).
D. R. Defibaugh and G. Morrison,J. Chem. Eng. Data 37:107 (1992).
L. A. Galicia-Luna, D. Richon, and H. Renon,J. Chem. Eng. Data. 39:424 (1994).
C. Bouchot, Ph.D. thesis (École de Mines, Paris, 1995).
J. M. Simonson, C. S. Oakes, and R. J. Bodnar,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 26:345 (1994).
C. S. Oakes, J. M. Simonson, and R. J. Bodnar,J. Solut. Chem. 24:897 (1995).
H. J. Albert and R. H. Wood,Rev. Sci. Instrum. 55:589 (1984).
V. Majer, J. A. Gates, A. Inglese, and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 20:949 (1988).
R. H. Wood, C. W. Buzzard, and V. Majer,Rev. Sci Instrum. 60:493 (1989).
V. Majer, A. Inglese, and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 21:321 (1989).
V. Majer, A. Inglese, and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 21:397 (1989).
H. R. Corti, R. F. Prini, and F. Svarz,J. Solut. Chem. 19:793 (1990).
R. F. Chang, and M. R. Moldover,Rev. Sci. Instrum. 67:in press (1996).
L. Hnedkovsky, I. Cibulka, and V. Hynek, in preparation.
V. Majer, R. Crovetto, and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 23:333 (1991).
R. Crovetto, R. H. Wood, and V. Majer,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 23:1139 (1991).
V. Majer, Lu Hui, R. Crovetto, and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 23:213 (1991).
V. Majer, Lu Hui, R. Crovetto, R. H. Crovetto, and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 23:365 (1991).
V. Majer and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 26:1143 (1994).
L. Hnedkovsky, V. Majer, and R. H. Wood,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 27:801 (1995).
L. Hnedkovsky, R. H. Wood, and V. Majer,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 26:125 (1996).
D. G. Archer,J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 21:793 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hynek, V., Obšil, M., Quint, J. et al. A vibrating tube flow densitometer for measurements with corrosive solutions at temperatures up to 723 K and pressures up to 40 MPa. Int J Thermophys 18, 719–732 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02575130
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02575130