Summary
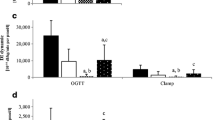
Glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and insulin sensitivity were evaluated in 8 asymptomatic patients with primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) before and at least 8 weeks after surgical correction of PHPT by means of the hyperglycemic clamp technique. In addition, 15 sex- and agematched control subjects were investigated for comparative reasons by the same technique. Glucose metabolized (M) during the hyperglycemic clamp was not significantly (NS) different between patients with PHPT and controls (7.9±2.3 vs. 6.3±1.9 mg/kg/min). However, insulin secretion (I) was significantly elevated in patients with PHPT compared to controls (87±17 vs. 45±12 μU/ml,P<0.05). The calculated insulin sensitivity index, (M/I) was significantly reduced in PHPT compared to controls (11.0±2.1 vs. 15.2±1.4 mg/kg/min per μU/ml×100,P<0.05). Comparing patients with PHPT before and after surgery, the M value, which is a measure of glucose tolerance, was not significantly different (7.9±2.3 vs. 7.8±1.5 mg/kg/min). However, insulin secretion was significantly lower after surgical correction of PHPT compared to the preoperative situation (48±9 μU/ml vs. 87±17 μU/7 ml,P<0.01). The calculated M/I rose significantly after surgery compared to the preoperative value (11±2.1 vs. 17.6±2.7 mg/kg/min per μU/ml ×100,P<0.001). We conclude that disturbed carbohydrate metabolism such as insulin hypersecretion and insulin resistance, in patients with PHPT is an early finding in this disease and that these early disturbances in glucose metabolism are, however, fully reversible. Correction of disturbed carbohydrate metabolism in PHPT might be a distinct argument for early surgical intervention in this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dent CE (1962) Some problems of hyperparathyroidism. Br Med J 2:1419–1425
Ljunghall S, Palmer M, Akerstrom G, Wide L (1983) Diabetes mellitus, glucose tolerance and insulin response to glucose in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism before and after parathyroidectomy. Eur J Clin Invest 13:373–377
Werner S, Hjern B, Sjoberg HJ (1974) Primary hyperparathyroidism. Analysis of findings in a series of 128 patients. Acta Chir Scand 140:618–625
Cheung PSY, Thompson NW, Brothers ThE, Vinik AI (1986) Effect of hyperparathyroidism on the control of diabetes mellitus. Surgery 100:1039–1047
Birge (1969) Clinopathologic conference: multiple endocrine adenomatosis. Am J Med 47:608–617
Kim H, Kalkhoff RK, Costrini NV, Cerletti JM, Jacobson M (1971) Plasma insulin disturbances in primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Invest 50:2596–2605
Yasuda K, Hurukawa Y, Okuyama M, Kikuchi M, Yoshinaga K (1975) Glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in patients with parathyroid disorders. Effect, of serum calcium on insulin release. N Engl J Med 292:501–504
Harter HR, Santiago JV, Rutherford WE, Slatopolsky E, Klahr S (1976) The relative roles of calcium phosphorus and parathyroid hormone in glucose and tolbutamide-mediated insulin release. J Clin Invest 58:359–367
Prager R, Kovarik J, Schernthaner G, Woloszczuk W, Willvonseder R (1983) Peripheral insulin resistance in primary hyperparathyroidism. Metabolism 32:800–805
Prager R, Schernthaner G, Kovarik J, Cichini G, Klaushofer K, willvonseder R (1984) Primary hyperparathyroidism is associated with decreased insulin receptor binding and glucose intolerance. Calcif Tissue Int 36:253–258
Walsh CH, Soler NG, Malins JM (1975) Diabetes mellitus and primary hyperparathyroidism. Postgrad Med J 51:446–449
Akgun S, Ertel NH (1978) Hyperparathyroidism and coexisting diabetes mellitus: altered carbohydrate metabolism. Arch Intern Med 138:1500–1502
De Fronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R (1979) Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol 273:214–223
National Diabetes Data Group (1979) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance. Diabetes 28:1039–1057
De Fronzo RA, Lang R (1980) Hypophosphatemia and glucose intolerance. Evidence for tissue insensitivity to insulin. N Engl J Med 303:1259–1263
Bygrave FL (1967) The ionic environment and metabolic control. Nature 214:667–670
Manery JF (1966) Effect of calcium ion on membranes. Fed Proc 25:1804–1809
Bevilacqua S, Barret E, Ferranini E, Gusberg R, Stenhart A, Richardson L, Smith D, De Fronzo R (1981) Lack of effect of parathyroid hormone on hepatic glucose metabolism in the dog. Metabolism 30:469–474
Levy J, Gavin JR, Hammerman MR, Avioli LV (1986) Ca2+MG2+ ATPase activity in kidney basolateral membrane in noninsulin-dependent rats: effect of insulin. Diabetes 35:899–905
Levy J, Stern Z, Gutman A, Naparstek Y, Gavin JR, Avioli V (1986) Plasma calcium and phosphate levels in an adult noninsulin-dependent diabetic population. Calcif Tissue Int 39:316–318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prager, R., Schernthaner, G., Niederle, B. et al. Evaluation of glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and insulin action in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism before and after surgery. Calcif Tissue Int 46, 1–4 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02555816
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02555816