Summary
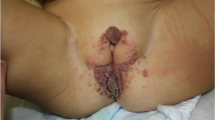
There are many technics for treating condyloma acuminatum. None is entirely satisfactory. The viral etiology and the probable venereal transmission make most methods difficult at best. Our method of using bichloracetic acid has given us a more satisfactory cure rate, with a minimum of discomfort, no scarring, and less prolonged convalescence. Future improvement in the management of condyloma acuminatum will depend upon the development of a suitable vaccine based on the positive identification of these growths as specific infectious lesions caused by a virus. Oral or injectable medication would attack the lesion directly, be easier to apply, be less painful, and allow vectors to be treated more easily. However, until such a vaccine is introduced, the clinician will continue to see condyloma acuminatum and will need therapeutic tools that cause few complications and minimum discomfort and have a reasonable degree of success in removing the warts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng, S. F., and R. J. Veenema: Topical application of thio-TEPA to penile and urethral tumors. J. Urol.94: 259, 1965.
Culp, O. S., and I. W. Kaplan: Condylomata acuminata: Two hundred cases treated with podophyllin. Ann. Surg.120: 251, 1944.
Gold, J. D.: Liquid air and carbonic acid snow: Therapeutic results obstained by the dermatologist. New York J. Med.92: 1276, 1910.
Graber, E. A., H. R. K. Barber, and J. J. O'Rourke: Simple surgical treatment for condyloma acuminatum of the vulva. Obstet. Gynec.29: 247, 1967.
Grace, D. A., J. A. Ochsner, C. R. McLain, and J. P. Smith: Vulvar condyloma acuminata in prepubertal females. J.A.M.A.201: 151, 1967.
Hall, A. F.: Advantages and limitations of liquid nitrogen in the therapy of skin lesions. Arch. Dermat.82: 9, 1960.
Halverstadt, D. B., and W. L. Parry: Thiotepa in the management of intraurethral condyloma acuminata. J. Urol.101: 729, 1969.
Lewis, G. M., and C. E. Wheeler, Jr.: Practical Dermatology. Ed. 3. Philadelphia, W. B. Saunders Company, 1967, 679 pp.
Lyell, A.: Management of warts. Brit. Med. J.2: 1576, 1966.
Marino, A. W. M., Jr.: Proctologic lesions observed in male homosexuals. Dis. Colon Rectum.7: 121, 1969.
Morgan, H. A., and P. C. Balduzzi: Propagation of an intranuclear inclusion-forming agent from human condyloma acuminatum. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA52: 1561, 1964.
Murphy, J. C., and S. Petty: Chloroquine treatment of warts: A double-blind clinical study. Rocky Mountain Med. J.62: 25, (Jan.) 1965.
Nahra, K. S., S. L. Moschella, and N. W. Swinton, Sr.: Condyloma acuminatum treated with liquid nitrogen: Report of five cases. Dis. Colon Rectum.12: 125, 1969.
Rowe, R. J., and J. M. Gray: Ultrasound treatment of plantar warts. Arch. Phys. Med.46: 273, 1965.
Smith, K. O., E. Dougherty, J. L. Melnick, and F. Rapp: Fine structure of unassembled viral subunits from human warts. J. Bact.90: 278, 1965.
Walter, E. L., Jr., D. L. Walker, and G. A. Cooper: Localization of specific antigen in human warts. Arch. Path.79: 419, 1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Swerdlow, D.B., Salvati, E.P. Condyloma acuminatum. Dis Colon Rectum 14, 226–231 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02553191
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02553191