Summary
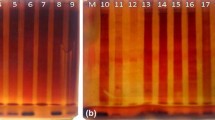
Four leaf enzymes malate dehydrogenase (MDH), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGD), peroxidase (PX) and aspartate aminotransferase (AAT) of 17 walnut cultivars and two pollen enzymes malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGD) of 15 walnut cultivars were analysed using horizontal starch gel electrophoresis. Walnut cultivars of different origin exhibited different numbers of electrophoretic bands and also different relative mobility. Different activity levels and phenotypic groups were detected in studied enzyme systems. Pollen enzymes revealed higher variability than enzymes extracted from the leaves. 15 walnut cultivars were classified into 10 malate dehydrogenase phenotypic groups and 14 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase phenotypic groups based on pollen analyses. 17 cultivars were classified into 9 peroxidase phenotypic groups and 7 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase phenotypic groups based on analyses of leaves. All of the 15 walnut cultivars could be identified and distinguished with electrophoretic analyses of MDH and 6PGD from the pollen while only 10 cultivars were distinguishable with analyses of 6PGD and PRX from the leaves. No variability useful for cultivar identification was observed in MDH and AAT from the leaves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleta, N., Olarte, C., Truco, M. J. & Arus, P (1990). Identification of walnut cultivars by isozyme analysis. Acta Horticulturae 284: 91–96.
Aleta, N., Rovira, M., Ninot, A. & Arus, P. (1991). Inheritance of four isozymes in walnut. Acta Horticulturae 311:62–65.
Arulsekar, S., Parfitt, D. E. & McGranahan, G. H. (1985). Isozyme gene markers inJuglans species. The Journal of Heredity 76:103–106.
Arulsekar, S., and Parfitt, D. E. (1986). Isozyme analysis procedures for stone fruits, almond, grape, walnut, pistachio and fig. Hort Science 21(4):928–933.
Arulsekar, S., McGranahan, G. H. & Parfitt, D. E. (1986). Inheritance of phosphoglucomutase and esterase isozymes in Persian walnut. The Journal of Heredity 77:220–221.
Chandler, W.H. (1947). Decidious Orchards. Philadelphia, ZDA, 388.
Cheng, S. and Yang, W. (1987). Taxonomic studies of ten species of the genusJuglans based on isozymic zymograms. Acta Horticulturae Sinica 14(2):90–96.
Germain, E., Jalinat, J. & Marchou, M. (1981). Divers aspects de la biologie florale du noyer. In: Bergougnoux, F & Grospierre, P: Le Noyer, 13–27.
Germain, E., Hanquier, I. & Monet, R. (1993). Identification of eightJuglans sp. and some inter-specific hybrids by isoenzyme patterns. Acta Horticulturae 311:73–81.
Korać, M. (1986). Orah. Nolit, Beograd, 7,8.
Kuhns, L.J. and Fretz, T.A. (1978). Distinguishing rose cultivars by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. I. Extraction and storage of protein and active enzymes from rose leaves. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 103(4):503–508.
Malvolti, M.E., Paciucci, M., Cannata, F. & Fineschi, S. (1993). Genetic variation in Italian populations ofJuglans regia L. Acta Horticulturae 311:86–91.
Manganaris, A.G. and F.H. Alston (1992). Inheritance and linkage relationships of peroxidase isoenzymes in apple. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83:392–399.
McGranahan, G.H., Tulecke, W., Arulsekar, S. & Hansen, J.J. (1986). Intergeneric Hybridization in the Juglandaceae:Pterocarya sp. xJuglans regia. J.Amer. Soc.Hort.Sci. 114:627–630.
Peirce, L.C. & Brewbaker, J.L. (1973). Applications of Isozyme Analysis in Horticultural Science. Hort Science 8(1):17–22.
Scandalios, J.G. (1969). Genetic Control of Multiple Molecular Forms of Enzymes in Plants. A review. Biochem. Genet. 3:37–79.
Shields, C.R., Orton, T.J. & Stuber, C.W. (1983). An outline of general resource needs and procedures for the electrophoresic separation of active enzymes from plant tissue. In: Tanksley, S. D., Orton, T. J.: Isozymes in Plant Genetics and Breeding. Part A, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 443–468.
Solar, A., Smole, J., Štampar, F. (1993). Identification of Walnut Cultivars by Pollen Isozymes. Acta Horticulturae 311:95–100.
Vallejos, C.E. (1983). Enzyme activity staining. In: Tanksley, S. D., Orton, T.J.: Isozymes in plant genetics and breeding. Part A, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 469–516.
Weeden, N.F. & Lamb, R.C. (1985). Identification of Apple Cultivars by Isozyme Phenotypes. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 110:509–515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solar, A., Smole, J., Štampar, F. et al. Characterization of isozyme variation in walnut(Juglans regia L.) . Euphytica 77, 105–112 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02551471
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02551471