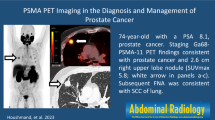
Abstract
Findings on transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS), computerized tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in local staging of prostatic carcinoma (PCa) were compared with the final pathological staging in 30 patients who underwent radical prostatectomy. We found TRUS and MRI to have the same accuracy rate (53%) in local staging, whereas CT revealed a lower accuracy rate with 47%. TRUS revealed the highest accuracy rate in detecting seminal vesicle invasion with 70%, and MRI in invasion of periprostatic tissue with 67%. Although it revealed similar efficiency as MRI, TRUS should be considered as the first line modality in local staging of PCa in light of its relatively high accuracy rate, cost effectiveness and ease in performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zincke, H.: Treatment of clinical Stage C prostate cancer with radical prostatectomy: Influence of pathologic stage dictates adjuvant treatment. In: G. Murphy, S. Khoury, C. Chatelain, L. Dennis (eds): Proceedings of 3rd International Symposium on Recent Advances in Urologic Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Paris, June 17–19, 1992, pp. 200–204.
Schroeder, F. H., Belt, E.: Carcinoma of the prostate: A study of 213 patients with Stage C tumors treated by total perineal prostatectomy.J. Urol., 114, 257 (1975).
Ebert, T., Schmitz-Draeger, B. J., Bürrig, K. F.: Accuracy of imaging modalities in staging the local extent of prostate cancer.Urol. Clin. North. Am. Urologic Oncology, 18 (3), 453 (1991).
Macoska, J. A., Micale, M. A., Sakr, W. A., Benson, P. D., Wolman, S. R.: Extensive gene alterations in prostate cancer revealed by dual PCR and FISH analysis.Genes Chrom. Cancer 8, 88 (1993).
Montie, J. E., 1992 staging system for prostate cancer.Semin. Urol., 11, 10 (1993).
Salo, J. O., Kivisaari, L., Ranniko, S.: Computerized tomography and transrectal ultrasound in the assessment of local extension of prostatic cancer before radical retropubic prostatectomy.J. Urol., 137, 435 (1987).
Pontes, J. E., Eisenkraft, S., Watanabe, H.: Preoperative evaluation of localized prostatic carcinoma by transrectal ultrasonography.J. Urol., 134, 289 (1985).
Rifkin, M. D., Zerhhouni, E. A., Gatsonis, C. A., Quint, L. E., Panshter, D. M., Epstein, J. I., Hamper, U., Walsh, P. C., McNeil, B. J.: Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography in staging early prostate cancer. Results of a multi-institutional cooperative trial.N. Engl. J. Med., 323, 62 (1990).
Biondetti, P. R., Lee, J. K. T., Ling, D.: Clinical Stage B prostate carcinoma: Staging with MRI imaging.Radiology, 162, 625 (1987).
Mukamel, E., Hannah, J., Barbaric, Z., DeKernion, J. B.: The value of computerized tomography scan and magnetic resonance imaging in staging prostatic carcinoma: Comparison with the clinical and histological staging.J. Urol., 136, 1231 (1986).
McSherry, S. A., Levy, F., Schiebler, M. L.: Preoperative detection of pathologic tumor volume and stage in clinically localized prostate cancer: Comparison of digital rectal examination, transrectal ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging.J. Urol., 146, 85 (1991).
Phillips, M. E., Kressel, H. Y., Spritzer, C. E.: Prostatic disorders: MR imaging at 1.5 T.Radiology, 164, 386 (1987).
Hoisaeter, P. A., Norlén, B. J., Norming, U., Ebert, T. Mattrey, R., Nilsson, S., Norberg, M., Pollack, H., Salo, J., Torp-Pedersen, S.: Imaging in the diagnosis and assessment of prognosis in localized prostate cancer. In: Andersson, L. (ed.): Proceedings of a Symposium in Stockholm, Sweden.Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. (Suppl.),162, 89 (1994).
Schnall, M., Kressel, H. Y., Pollack, K. P., Lenkinski, R. L.: The development of an intracavitary surface coil for high resolution proton imaging and spectroscopy. In: Book of Abstracts: Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 1986.
Martin, J. F., Hajek, P., Baker, L., Gylys-Morin, V., Fitzmorris-Glass, R., Mattery, R. R.: Inflatable surface coil for MR imaging of the prostate.Radiology, 167, 268 (1988).
Schnall, M. D., Imai, Y., Tomaszeeoski, J., Pollack, H. M., Lenkinski, R. E., Kressel, H. Y.: Prostate cancer: Local staging with endorectal surface coil MR imaging.Radiology, 178, 797 (1991).
Chelsky, M. J., Schnall, M. D., Seidmon, E. J., Pollack, H. M.: Use of endorectal surface coil imaging for local staging of prostate cancer.J. Urol., 150, 391 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarcan, T., Türkeri, L., Biren, T. et al. The effectiveness of imaging modalities in clinical staging of localized prostatic carcinoma. International Urology and Nephrology 28, 773–779 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550726
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550726