Abstract
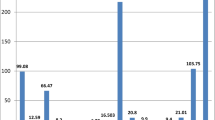
Serum zinc, copper and manganese levels were estimated in normal subjects (NS) and stone formers (SF). There was no significant difference in the serum levels of Zn, Cu, and Mn in NS and SF, the values being 101.5±35.1 μg% and 94.3±45.6 for Zn; 91.75±27.0 μg% and 88.5±34.1 for Cu; and 87.0±36.7 μg% and 79.6±35.5 for Mn, respectively. Zinc excretion was relatively high in NS (790.08±172.88 μg/dl) as compared to other populations and was significantly higher in SF (1154.92±290.17 μg%, p<0.001). Copper and manganese excretions in SF were significantly lower than in NS (p<0.001).
Zinc was present in substantial quantities in renal (2.52±3.98 g%), ureteric (0.75±0.51 g%) and vesical (1.71±3.20 g%) stones. Manganese was present in traces in all the stones and copper in two-thirds of the stones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liunghall, S.: Incidence of renal stones in Western countries. In: Urolithiasis and Related Clinical Research. Plenum Press, New York-London 1985.
Pyrah, L. N.: Renal calculus. Springer Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York 1979.
Kabra, S. G., Gaur, S. B., Sharma, S. S., Patni, M. K., Banerjee, P.: Urolithiasis: Incidence of urinary calculi in South Eastern Rajasthan—Report of 1144 cases.Indian J. Surg., 34, 261 (1972).
Pendse, A. K., Srivastava, A. K., Kumawat, J. L., Goyal, A., Ghosh, R., Sharma, H. S., Singh, P. P.: Urolithiasis in Udaipur (Rajasthan).J. Indian Med. Ass., 82, 151 (1984).
Singh, P. P., Pendse, A. K.: Multidimensional approach to urolithiasis. Urolithiasis Society of India, Chandigarh 1987.
Pendse, A. K., Singh, P. P.: The etiology of urolithiasis in Udaipur (Western part of India).Urol. Res., 14, 59 (1986).
Singh, P. P., Pendse, A. K., Goyal, A., Ghosh, R., Srivastava, A. K., Kumawat, J. L.: Blood and urine chemistry of stone formers in local population and evaluation of cystone treatment.Indian Drugs, 20, 264 (1983).
Singh, P. P., Kothari, L. K., Sharma, D. C., Saxena, S. N.: Nutritional value of foods in relation to their oxalic acid content.Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 25, 1147 (1972).
Singh, P. P., Pendse, A. K., Hada, P., Nagori, P. C., Rathore, V., Dashora, P. K.: Sodium is neither a risk nor a protective factor in urolithiasis?Urol. Res., 15, 105 (1987).
Abdulla, M., Chmielnick, J.: International Symposium on Trace Elements. Unesco Head Quarters, Paris, France 1987.
Aggett, P. J.: Physiology and metabolism of essential trace elements: An outline. In: Clinics in Endocrinology and Metabolism. W. B. Saunders Company, London-Philadelphia-Toronto 1985.
Meyer, J. L., Angino, E. E.: The role of trace metals in calcium urolithiasis.Invest Urol., 14, 347 (1977).
Meyer, J. L., Thomas, W. C. Jr.: Trace metal citric acid complexes as inhibitors of calcification and crystal growth. I. Effects of Fe(III), Cr(III) and Al(II) complexes on calcium phosphate crystal growth.J. Urol., 128, 1372 (1982).
Meyer, J. L., Thomas, W. C. Jr.: Trace metal citric acid complexes as inhibitors of calcification and crystal growth II. Effects of Fe(III), Cr(III) and Al(III) complexes on calcium oxalate crystal growth.J. Urol., 128, 1376 (1982).
Pleban, P. A., Numerof, B. S., Wirth, F. H.: Trace elements metabolism in the fetus and neonate. In: Clinics in Endocrinology and Metabolism. W. B. Saunders Company, London-Philadelphia-Toronto 1985.
Srivastava, B. N., Mehta, V. K., Iyer, S. R.: Plasma and urinary zinc in renal disorders.J. Assoc. Phys. India, 30, 287 (1982).
Underwood, E. J.: Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition. 4th ed. Academic Press, New York-San Francisco-London 1977.
Bird, E. D., Thomas, W. C.: Effect of various metals on mineralisation in vitro.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 112, 640 (1963).
Sutor, D. J.: Growth studies on calcium oxalate in the presence of various ions and compounds, I.Br. J. Urol., 41, 171 (1969).
Sutor, D. J., Wooley, S. E.: Growth studies on calcium oxalate in the presence of various ions and compounds, II.Br. J. Unol., 42, 296 (1970).
Dorothy, T. L., Old Royd, N. O.: Analysis of urinary calculi. Stones. In: Clinical Management of Urolithiasis. Williams and Wilkins, Ealtimore-London 1983.
King, E. J., Wootton, I. D. J.: Microanalysis in Medical Biochemistry. 3rd ed. J. & A. Churchill Ltd., London 1956.
Natelson, S.: In: Techniques of Clinical Chemistry. 3rd ed. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Illinois, USA 1971.
Hodgkinson, A., Williams, A.: An improved colorimetric procedure for urine oxalates.Clin. Chim. Acta, 36, 127 (1972).
Varley, H.: Practical Clinical Biochemistry 4th ed., The English Language Book Society and William Heinemann Medical Books Ltd., London 1969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komleh, K., Hada, P., Pendse, A.K. et al. Zine, copper and manganese in serum, urine and stones. International Urology and Nephrology 22, 113–118 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02549826
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02549826