Abstract
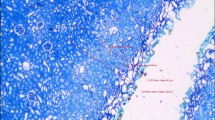
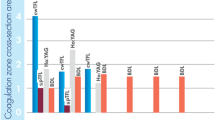
Interstitial laser photocoagulation (ILP) is a new percutaneous technique of thermal destruction (necrosis) of deep-seated tumours, using low power laser energy. Our purpose was to investigate: (i) the effects of different laser wavelengths on the extent of thermal damage produced; and (ii) the role of charring around the fibre tip during ILP. Forty-five normal Wistar rats (250–300 g) had ILP to their liver (exposed at laparotomy) by inserting a 400 μm optical fibre into the liver, and activating the laser at 1, 2 or 3W. This was performed at three laser wavelengths (1064 nm Nd-YAG, 1320 nm Nd-YAG, 805 nm diode) using a clean plane-cleaved fibre, and at two wavelengths (1064 nm and 1320 nm Nd-YAG) using a fibre with pre-charring at its tip. The 805 nm and 1320 nm laser wavelengths produced significantly greater necrosis than the 1064 nm, using a clean fibre tip (mean diameters at 2 W were 21.7 mm, 18.3 mm, 8 mm respectively). Pre-charring the fibre significantly increased the necrotic lesion size at 1064 nm (mean diameter at 2 W was 14.7 mm). Using more strongly absorbed wavelengths (805 nm and 1320 nm) and pre-charring the fibre tip give greater thermal damage during ILP, contrary to previously held views that the optimal wavelength for ILP was 1064 nm in the absence of charring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bown SG Phototherapy of tumours.World J Surg 1983,7:700–9
Steger AC, Lees WR, Walmsley K, Bown SG Interstitial laser hyperthermia: a new approach to local destruction of tumours.BMJ 1989,299:362–5
Amin Z, Donald JJ, Masters A et al. Hepatic metastases: Interstitial laser photocoagulation with real-time US monitoring and dynamic CT evaluation of treatment.Radiology 1993 (in press)
Amin Z, Lees WR, Bown SG. Interstitial laser photocoagulation for the treatment of prostatic cancer.Br J Radiol (in press)
Roux FX, Merrienne L, Leriche B et al. Laser interstitial thermotherapy in stereotactical neurosurgery.Laser Med Sci 1992,7:121–6
Castro DJ, Lufkin RB, Saxton RE et al. Metastatic head and neck malignancy treated using MRI guided interstitial laser phototherapy: an initial case report.Laryngoscope 1992,102:26–32
Matthewson K, Coleridge-Smith P, O'Sullivan JP et al. Biological effects of intrahepatic Neodymium: Yttrium-Aluminium-Garnet laser photocoagulation in rats.Gastroenterology 1987,93:550–7
Svaasand LO, Boerslid T, Oeveraasen M. Thermal and optical properties of living tissue. Application to laser-induced hyperthermia.Laser Surg Med 1985,5:589–602
Svaasand LO, Gomer CJ, Morinelli E On the physical rationale of laser induced hyperthermia.Lasers Med Sci 1990,5:121–8
Cheong WF, Prahl S, Welch AJ A review of the optical properties of biological tissues.IEEE J Quantum Elec 1990,26:2166–85
Welch AJ, Motamedi M, Rastegar S et al. Laser thermal ablation.Photochem Photobiol 1991,53:815–25
Panjehpour M, Overholt BF, Milligan AJ et al. Nd:YAG laser-induced interstitial hyperthermia using a long frosted contact probe.Lasers Surg Med 1990,10:16–24
Dowlatshahi K, Babish D, Bangert JD, Kluiber R. Histologic evaluation of rat mammary tumour necrosis by interstitial Nd:YAG laser hyperthermia.Lasers Surg Med 1992,12:159–64
Nolsøe C, Torp-Pedersen S, Olldag E, Holm HH. Bare fibre low power Nd-YAG laser interstitial hyperthermia. Comparison between diffuser tip and nonmodified tip. An in vitro study.Lasers Med Sci 1992,7:1–7
Hashimoto D, Takami M, Ideezuki Y In depth radiation therapy by Nd:YAG laser for malignant tumours of the liver under ultrasonic imaging.Gastroenterology 1985,88:A1663
Huang G, Wang T, Sheu J et al. Low-power laserthermia for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Cancer 1991,27:1622–7
Wyman DR, Whelan WM, Wilson BC. Interstitial laser photocoagulation: Nd:YAG 1064 nm optical fiber source compared to point heat source.Laser Surg Med 1992,12:659–64
Stokes LF, Auth DC, Tanaka D et al. Biomedical utility of 1.34μm Nd:YAG laser irradiation.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1981,28:297–9
Mordon S, Roux FX, Mondragon S et al. A comparative study of coagulation effects on the cortex of the rat using Nd-YAG (1.32 μm), Nd-YAG (1.06 μm) and CO2 lasers.Lasers Med Sci 1990,5:293–6
Jacques SL, Rastegar S, Motamedi M et al. Liver photocoagulation with diode laser (805 nm) vs Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm). InProceedings of SPIE, Laser-Tissue Interaction III, Los Angeles 1992,1646:107–17
Thomsen S. Pathologic analysis of photothermal and photomechanical effects of laser-tissue interactions.Photochem Photobiol 1991,53:825–35
Manni J Surgical diode lasers.J Clin Laser Med Surg 1992,10:377–80
Wyman A, Duffy S, Sweetland HM et al. Preliminary evaluation of a new high power diode laser.Lasers Surg Med 1992,12:506–9
McGahan JP, Browning JP, Brock JM et al. Hepatic ablation using radiofrequency electrocautery.Invest Radiol 1990,25:267–70
Steger AC, Lees WRL, Shorvon P et al. Multiple-fibre low-power interstitial laser hyperthermia: studies in the normal liver.Br J Surg 1992,79:139–45
Van Eeden PJ, Steger AC, Bown SG. Fibre tip considerations for low power laser interstitial hyperthermia.Lasers Med Sci 1988,3:A336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, Z., Buonaccorsi, G., Mills, T. et al. Interstitial laser photocoagulation: Evaluation of a 1320 nm Nd-YAG and an 805 nm diode laser: the significance of charring and the value of precharring the fibre tip. Laser Med Sci 8, 113–120 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02547807
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02547807