Abstract
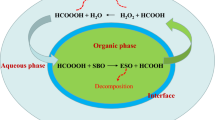
The process ofin situ epoxidation consists of a two-phase system that involves reactions in both phases, mass transfer between phases, and thermodynamic driving forces for the mass transfer. In this paper, we present a model that treats the process as a two-phase system and uses local phase concentrations to calculate reaction and mass transfer rates. The process ofin situ epoxidation has been broken down into a set of systematic steps, and rate constants for each step have been determined. A conventional stirred tank reactor, equipped with cooling coils, eliminated the heat and mass transfer limitations so that the true kinetics ofin situ epoxidation were observed. It is shown that significantly larger rates (larger by factors of 2–10) are obtained when heat and mass transfer limitations are removed. The two-phase model adequately predicts the epoxidation kinetics over a wide range of temperatures (50–90°C). In addition, the model also correctly predicts the effect of adding an inert solvent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lutz, J.T., inEncyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 3rd edn., edited by J.G. Wallace, John Wiley & Sons, Vol. 9, 1978, pp. 251–266.
Findley, T.W., D. Swern and J.T. Scanlan,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 67:412 (1945).
Terry, D.E., and D.H. Wheeler, U.S. Patent 2,458,484 (1949).
Greenspan, F.P., U.S. Patent 2,490,800 (1949).
Swern, D., inOrganic Peroxides Volume II, edited by D. Swern, Wiley-Interscience (John Wiley), New York, 1971, pp. 337–533.
French, W.H., U.S. Patent 3,360,531 (1971).
Solvay Interox,Epoxidation, A1.1.4.UK-2C-989 (1989).
Solvay Interox,Considerations for the Safe Design of Processes Using H 2 O 2 and Organics, Houston, 1989.
Chou, T.C., and J.Y. Chang,Chem. Eng. Commun. 41:253 (1986).
Gan, L.H., S.H. Goh and K.S. Ooi,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 69:347 (1992).
Wohlers, H.C., M. Sack and H.P. LeVan,Ind. Eng. Chem. 50:1685 (1958).
Zaher, F.A., M.H. El-Mallah and M.M. El-Hefnawy,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 66:698 (1989).
Paquot, C., inStandard Methods for the Analysis of Oils, Fats and Derivatives, Part I, 6th edn., IUPAC, Pergamon Press, New York, 1979.
Abraham, M.E., and R.F. Benenati,AIChE J. 18:807 (1972).
Swern, D., inOrganic Peroxides, Volume I, edited by D. Swern, Wiley-Interscience (John Wiley), New York, 1970.
Sack, M., and H.C. Wohlers,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 36:623 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Rangarajan, B., Havey, A., Grulke, E.A. et al. Kinetic parameters of a two-phase model forin situ epoxidation of soybean oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 72, 1161–1169 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02540983
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02540983